CISA experts warned that a PoC exploit for the BrakTooth problem, which threatens millions of devices, has become public.
Let me remind you that the BrakTooth name hides a whole set of 16 vulnerabilities that affect the Bluetooth stack in many popular SoCs that are used in laptops, smartphones, industrial devices and IoT devices. These bugs allow disabling or “hanging” the device, and in the worst case, they help to execute arbitrary code and take over the entire system.For example, the most serious issue in BrakTooth, CVE-2021-28139, allows remote attackers to run their own malicious code on vulnerable devices via Bluetooth LMP.
BrakTooth became known in September this year, when specialists from the Singapore University of Technology and Design studied Bluetooth libraries for 13 different SoCs from 11 manufacturers. As it turns out, the same Bluetooth firmware was used in over 1,400 SoCs, which were the basis for a wide variety of devices.
Worse, all BrakTooth attacks can be performed using standard Bluetooth hardware, which costs no more than $ 15. Then the authors of the report emphasized that the number of problem devices, according to their calculations, is in the billions, although the degree of vulnerability depends on the SoC of the device and the Bluetooth software stack.
A PoC exploit for BrakTooth was posted on GitHub last week by one of the authors of the original research.
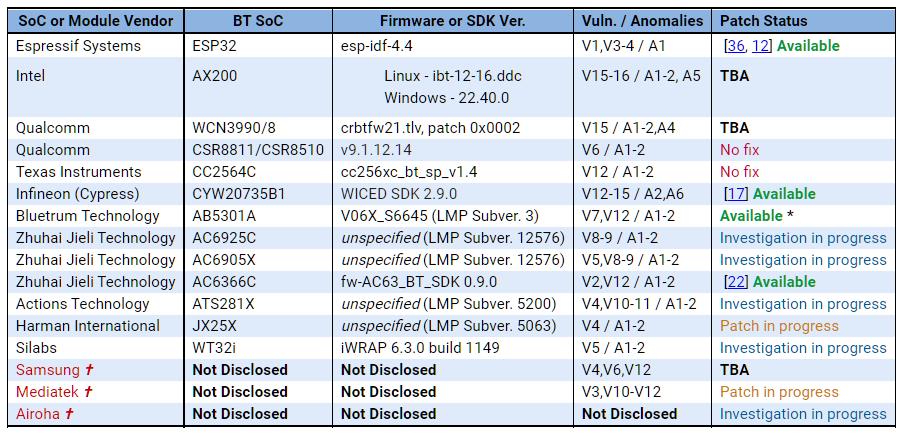
Because of this, experts at the Department of Homeland Security’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Protection Agency (DHS CISA) urged manufacturers, vendors, and developers to review their code as soon as possible and apply patches or workarounds to vulnerable Bluetooth System-on-a- applications. Chip (SoC). Unfortunately, the situation with patches still leaves much to be desired, as can be clearly seen in the table below, recently updated by the researchers.
Let me also remind you that CISA warned that GPS devices may behave unpredictably due to a bug in the GPS Daemon.
