If you have noticed that your computer has become strangely slow lately, there are several things you’d better check before taking it to the junkyard. The running speed issues may relate to software or hardware, but if no physical damage has been done to your PC before the problem occurred, it’s likely software. In this article, we retrace the matters you need to check before you rule out software issues as the cause of your computer’s deceleration. Most probably, you will solve the problem with software-related measures. If you don’t – you may proceed to hardware replacement or upgrade.
Restart
If you are sure that your computer is slow beyond normal, you have probably rebooted it more than once. But just in case, close all programs and restart it again, just to begin with.
Background processes
Some programs launch automatically upon Windows startup (antiviruses or Skype, for instance). If you went on a spree installing programs from the web, you might once find your system bedecked with startup programs you have long forgotten about. Yet every program working in the background slows down your system.
READ ALSO: How to Disable Fast Startup Windows 10 (Guide).
In Windows 10, do the following to check which programs start upon system boot:
- Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc to open the Task Manager.
- Select the Startup tab, and you will see the list of programs that attempt to launch as the system boots. In the Status column, you can see “enabled” or “disabled” values. The latter means that, although the software tries to launch on startup, the user or Windows has blocked this function.
- Right-click on any enabled program, and you’ll see a dropdown menu. Click Properties, and in the text field near the program icon, you will find the original filename of the program in question. You can copy this filename and Google it (adding its extension after the period) to learn what the program’s purpose is. You can google the program’s title as well, though.
- To exclude the application from the startup list, right-click its entry and click Disable.
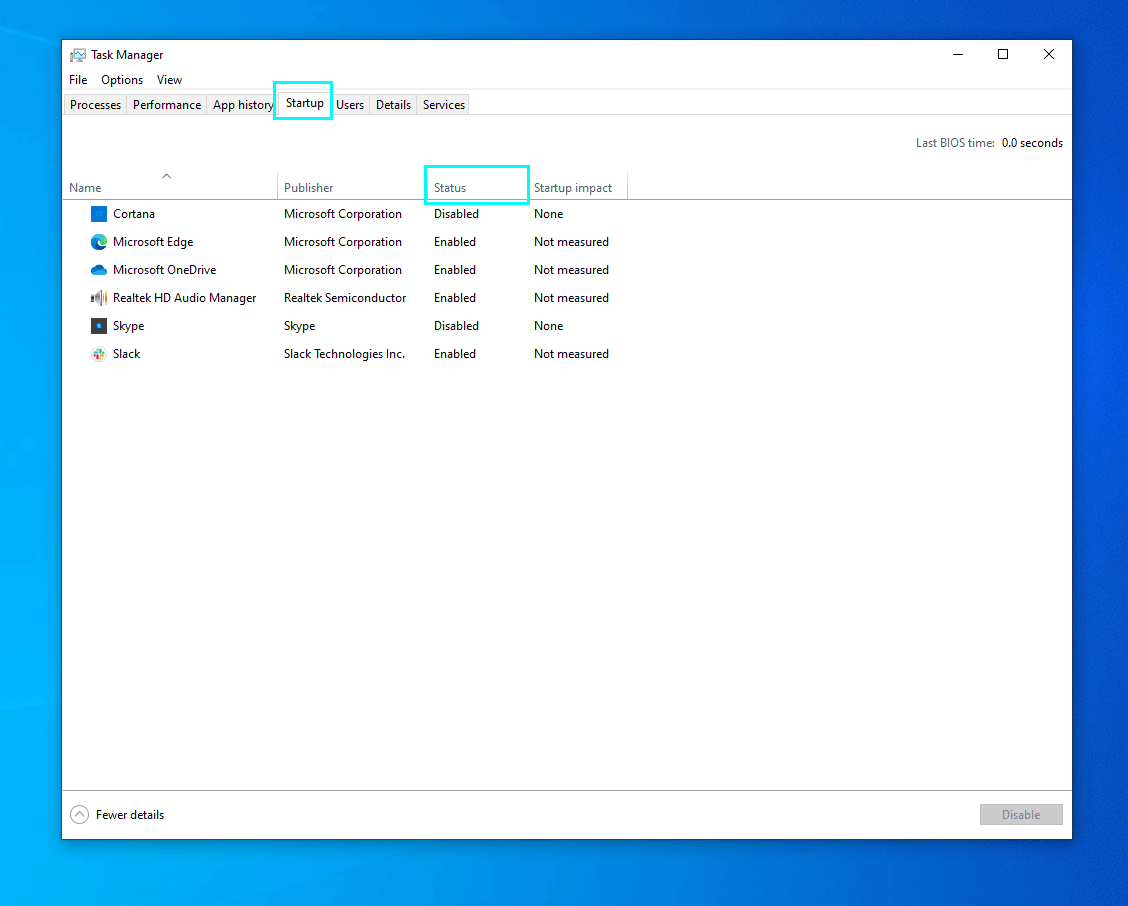
In the Task Manager Startup tab, you can see what programs are launched automatically upon system boot.
Basically, none of the programs included in the startup list are essential. You can disable any of them.
NOTE: If your antivirus program is scanning your drives for viruses at the moment, your computer will decelerate. It’s ok. Let the program finish the scan, and your PC’s running speed will come back to normal.
Check for malware
There’s plenty of malware that can be slowing down your computer. One of the brightest examples is a Coin Miner Trojan. Just imagine, you’re loading your computer with whatever tasks you have for it, but besides those, your machine is busy mining Bitcoins for some offshore tamperers. Of course, it will slow down if that’s the case.
Run an antivirus scan. For the best results, use your primary antivirus and then take a scan with an additional anti-malware utility. We recommend GridinSoft Anti-Malware. It has proven itself great as a backup software that detects malicious agents other security programs often miss.
OS and hardware drivers update
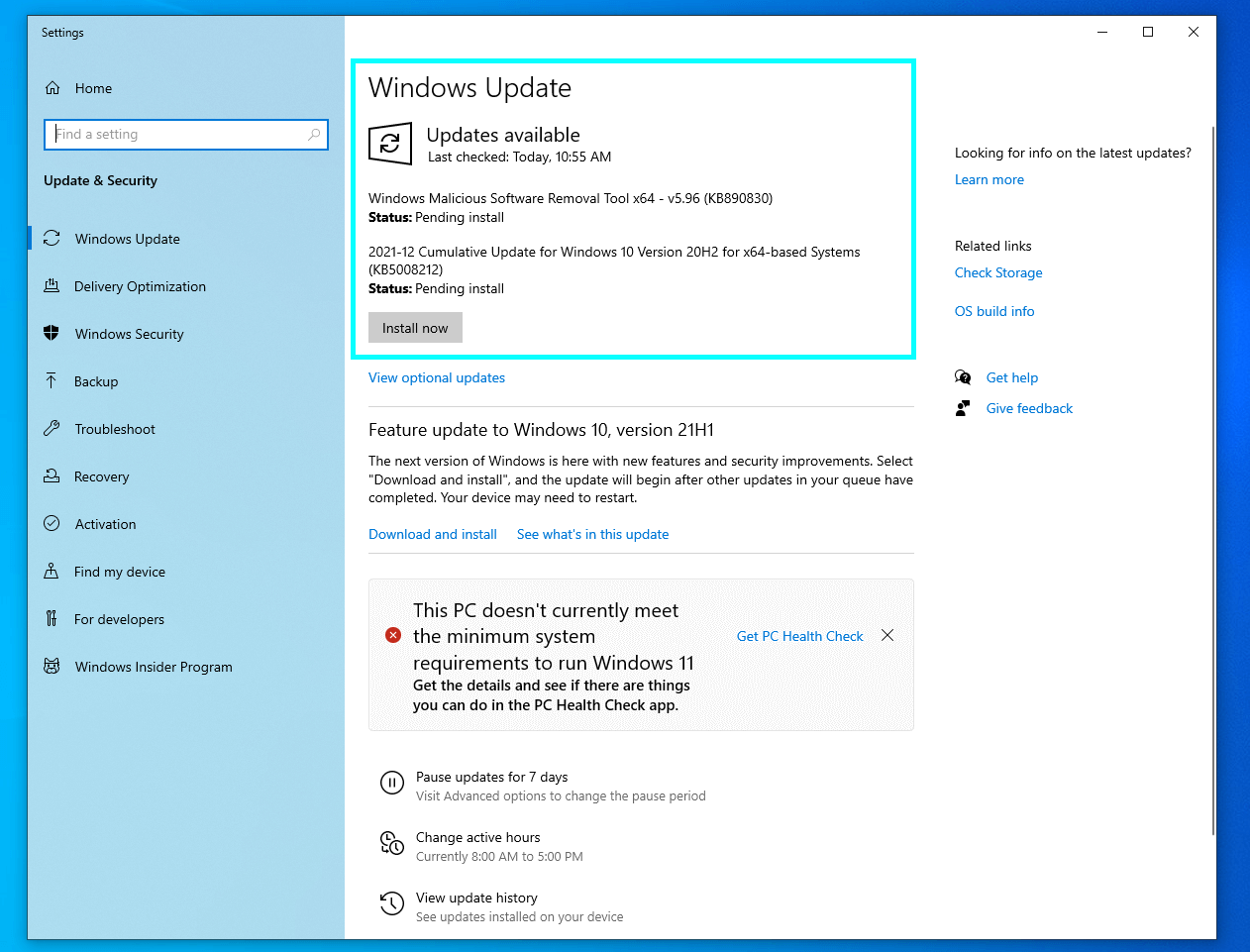
Make sure your operating system and hardware drivers are up-to-date. Windows executes system updates automatically by default, but you may have either paused the updates or set the date in the future when Windows carries them out. So maybe it is time to update your OS despite the postponing. Use the Start Menu search bar and find Windows Update. Open the found item and check whether any updates are pending.
As for the hardware drivers, it’s a little complicated. Windows updates drivers of the devices automatically only as a part of major system updates. In-between the updates, it is advisable to check for new drivers and install them manually, especially drivers for minor and not widely used devices.
If possible, you can use special programs by device manufacturers that take the work of tracking new drivers upon themselves. Big graphic cards manufacturers such as Nvidia or AMD provide such software (for example Catalyst Control Center), however not all companies do that. If that’s your case, check for new drivers on manufacturers’ websites.
Don’t forget to restart your computer after you install the updates.
Browser extensions removal
If you notice the loss of running speed as you browse the Web particularly, the problem can root in the browser extensions. Users often accrete multiple useless extensions as they surf the Web. You can either disable extensions or remove them.
In Google Chrome, press Options (three dots at the top-right of the Chrome window) and choose More Tools in the drop-down menu; in the following menu, select Extensions.
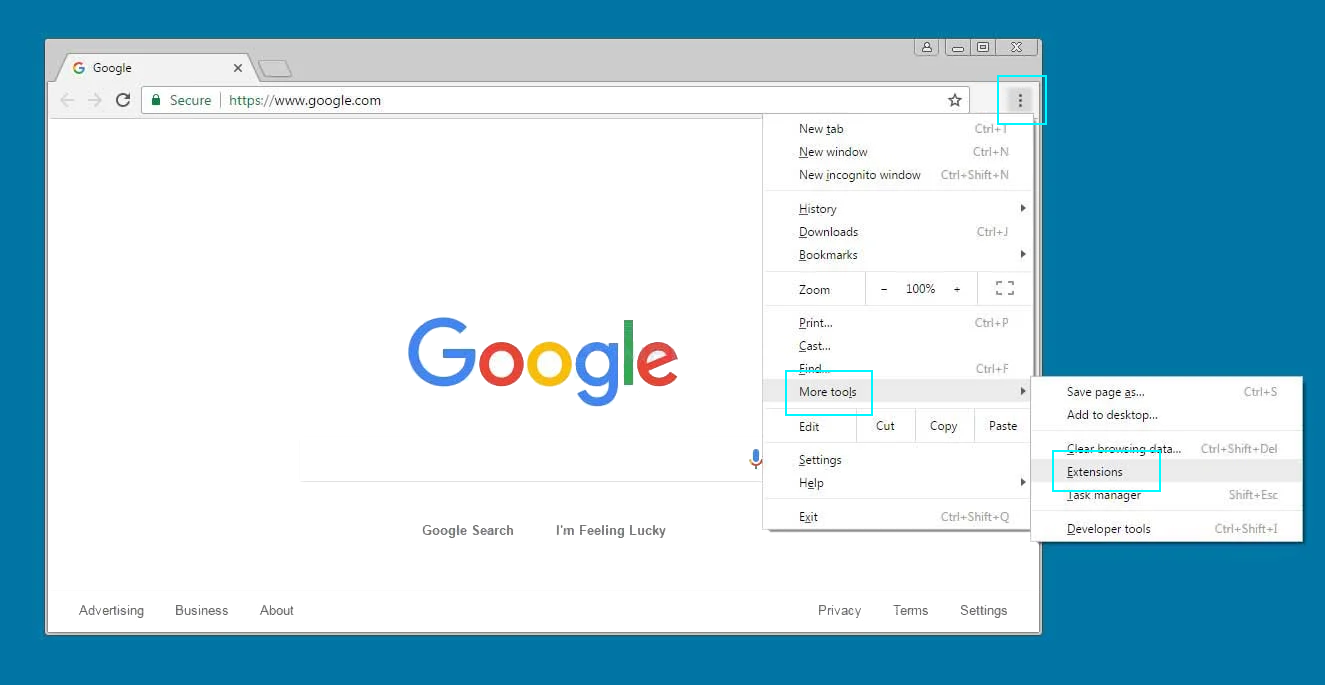
This is how you remove extensions from Google Chrome. This process slightly differs throughout browsers.
Find an extension you want to delete and press Remove.
Check out this article for how to remove unwanted extensions from other browsers.
By the way, see how many active tabs are there in your browser right now. Some people open new browser tabs without bothering to close them, brutally loading their PC memory.
Free space on the hard drive
If the programs being executed exceed the size of installed RAM, Windows employs some previously dedicated memory on the hard disk as virtual RAM. This process is called swapping, and it uses a so-called swap file (or page file). The size of this file can be up to four times bigger than the size of the physical RAM your PC uses. The minimum size of the swap file is one and a half sizes of the physical memory.
Therefore, mind that your operating system requires a certain amount of free space on the HDD.
Temporary files
Your computer produces temporary files as a matter of procedure for many programs. Windows stores these files on the hard drive. The operating system erases most of the temp files as soon as the task that involves them is complete. Some files stay longer, though. And some of them – much longer.
Temp files seldom affect the computer running speed. However, sometimes they pile up in such amounts that, together with the hard disk general overload, this creates evident work deceleration.
To remove the temporary files, do the following:
- In the Start Menu search bar, type %temp% and press Enter.
- The temporary files window will open.
- You’re welcome to delete all of them. If some program needs any of the temp files, Windows will notify you, and you’ll be able to skip that very object.
If the performance of your computer worsened due to the temp files pile-up, this would improve it at once.
Processor overheat
Modern PCs usually slow down their CPUs automatically upon overheat detection to avoid damage. Devices responsible for cooling in system units are most often fans. Some computers use a hydraulic cooling system and, maybe, there are other ways to maintain needed temperature, but since the most frequent variant is fans, we’ll reason from this.
Remove your system unit cover and see what’s inside. Hair and dust could be blocking airflow in the case. Accurately clean the interior of the system block. Pay attention to the cooling grids – they must be free of dust. Consider reading this good article on how to clean the inside of your computer.
Check whether the fans work properly. You might need to change your CPU fan if it malfunctions.
Hard disk check
If none of the recipes listed above is of any help, check your hard drive. You can check if your hard drive has failures and if it is fragmented.
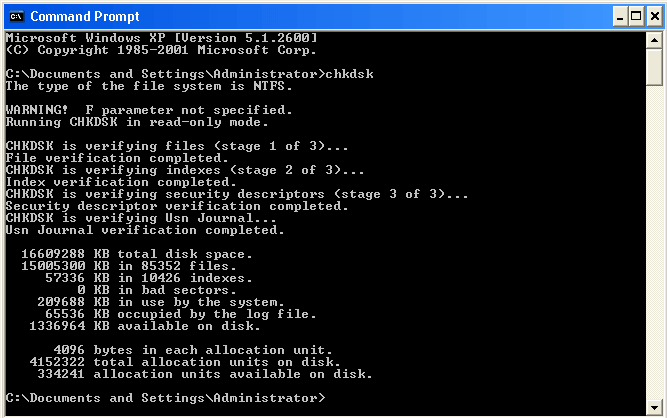
To check HDD for errors, launch CHKDSK.
- Use the Start Menu search bar and type there: ‘cmd‘.
- You will see a found item: Command Prompt.
- Right-click on it and launch it as an administrator.
- Type in the command prompt:
chkdsk C: /f /r /x
The current command will check your disk C for errors trying to repair everything fixable. If you want to check another drive, type its letter instead of C.
On Apple computers, use the Disk Utility program. To find it follow this path:
Launchpad (Dock icon) – Other – Disk Utility
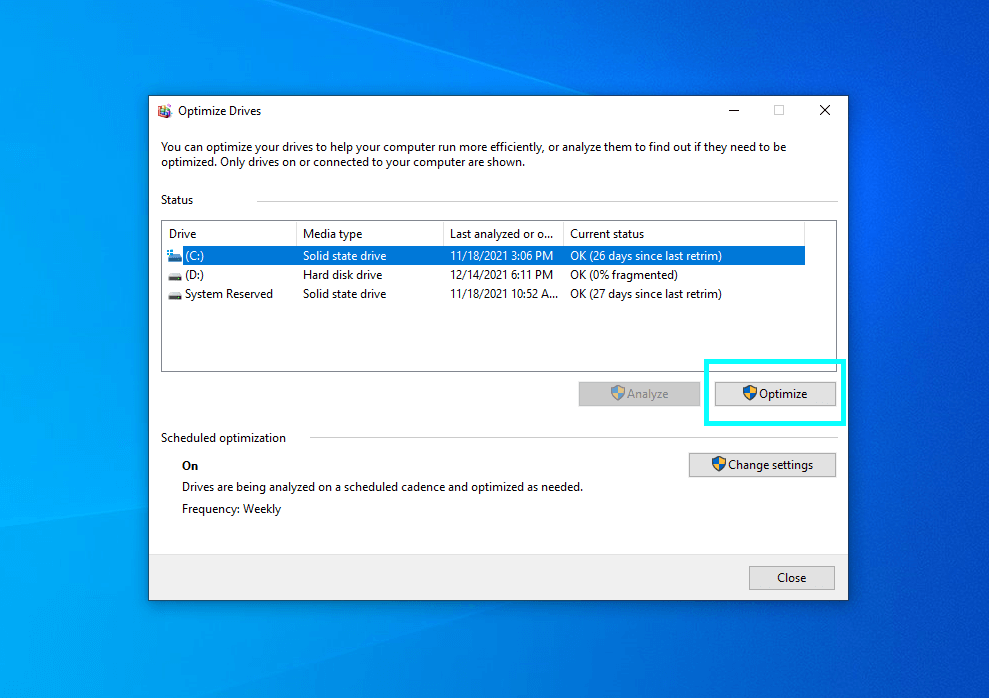
Your computer might also be slow if its drives are fragmented, meaning data is not optimally arranged on them. To run defragmentation use the Start Menu search bar and look for Defragment and Optimize Drives. As you open the utility, choose one of the drives and press the Optimize button near the entry.
Both CHKDSK and defragmentation take time.
System Reset
Any operating system itself is an exceptionally complex program. When you customize it, install other programs, customize them, save and erase files, use online services, do whatever a user usually does – it gets even more complicated.
As a matter of fact, one of the previously mentioned recipes should have already solved the problem of the low running speed or at least indicated that the issue was related to hardware. However, different software nuances might tangle up so much that figuring out the real root of the problem is as easy as cleansing the Augean stables. Therefore, you might want to reinstall Windows, and that’s it.
Here is the Windows 10 Reset Manual.
Hardware damage
If none of the presumed cases is your case, maybe there is a hardware problem in your computer, not connected with the hard drive. Let’s see what devices could be troublemakers resulting exactly in slow PC performance. These are CPU, motherboard, and RAM.
In order to check what’s wrong, you can use Ultimate Boot CD, software designed to detect hardware problems via measuring the time it takes your computer to complete some specially crafted test tasks.
You can find UBCD on a flash disk nowadays, don’t you worry. It is not necessarily on a compact disk, of course.
Consider changing a device the UBCD deems defective.
READ ALSO: How to Fix High CPU Usage.
User Review
( votes)