Seeing the Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] detection name usually means that your PC is in big danger. This malware can correctly be identified as ransomware – type of malware which encrypts your files and asks you to pay for their decryption. Stopping it requires some specific steps that must be taken as soon as possible.
Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] detection is a virus detection you can spectate in your system. It usually appears after the preliminary actions on your computer – opening the suspicious email, clicking the banner in the Internet or mounting the program from suspicious resources. From the instance it appears, you have a short time to do something about it until it starts its malicious action. And be sure – it is better not to wait for these malicious actions.
What is Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] virus?
Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] is ransomware-type malware. It searches for the files on your disk drive, ciphers it, and then asks you to pay the ransom for receiving the decryption key. Besides making your documents inaccessible, this malware additionally does a lot of damage to your system. It alters the networking settings in order to avoid you from checking out the removal tutorials or downloading the anti-malware program. In rare cases, Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] can even block the setup of anti-malware programs.
Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] Summary
In summary, Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] virus activities in the infected system are next:
- Behavioural detection: Executable code extraction – unpacking;
- Sample contains Overlay data;
- Yara rule detections observed from a process memory dump/dropped files/CAPE;
- Creates RWX memory;
- Dynamic (imported) function loading detected;
- Reads data out of its own binary image;
- CAPE extracted potentially suspicious content;
- Unconventionial binary language: Russian;
- Unconventionial language used in binary resources: Russian;
- The binary contains an unknown PE section name indicative of packing;
- The binary likely contains encrypted or compressed data.;
- Authenticode signature is invalid;
- Anomalous binary characteristics;
- Encrypting the files located on the target’s disks — so the victim cannot open these documents;
- Blocking the launching of .exe files of anti-malware apps
- Blocking the launching of installation files of security tools
Ransomware has actually been a headache for the last 4 years. It is difficult to imagine a more dangerous virus for both individuals and businesses. The algorithms used in Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] (usually, RHA-1028 or AES-256) are not hackable – with minor exclusions. To hack it with a brute force, you need more time than our galaxy currently exists, and possibly will exist. But that malware does not do all these bad things without delay – it can take up to a few hours to cipher all of your files. Thus, seeing the Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] detection is a clear signal that you should begin the removal process.
Where did I get the Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj]?
Standard tactics of Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] distribution are standard for all other ransomware variants. Those are one-day landing websites where users are offered to download the free software, so-called bait emails and hacktools. Bait emails are a pretty modern method in malware distribution – you get the e-mail that imitates some standard notifications about deliveries or bank service conditions changes. Within the email, there is an infected MS Office file, or a web link which opens the exploit landing page.
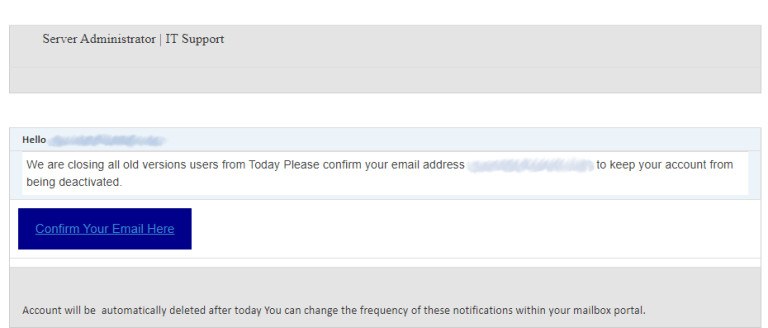
Malicious email message. This one tricks you to open the phishing website.
Preventing it looks fairly easy, however, still demands a lot of focus. Malware can hide in different spots, and it is better to prevent it even before it gets into your system than to depend on an anti-malware program. Standard cybersecurity knowledge is just an essential thing in the modern world, even if your interaction with a PC stays on YouTube videos. That can save you a great deal of money and time which you would spend while looking for a fixing guide.
Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] malware technical details
File Info:
name: 46D6DD3A797DCF4877FA.mlwpath: /opt/CAPEv2/storage/binaries/ac739dc5acef932a4adec6215e7c2e2710b9ef1991119d745a9cfccbe075cce6crc32: 9EE82D16md5: 46d6dd3a797dcf4877fa8e9ba4ba19acsha1: 08243aeff48dc2c4f5b2fcb37d01ff1bba038f28sha256: ac739dc5acef932a4adec6215e7c2e2710b9ef1991119d745a9cfccbe075cce6sha512: ebf0ffc43e4405a80efdc2e8702044adaa4757b804328e1d6a484c55ad45e5be08ed8e648c79365c97285a3e667c3ecdf775b0866354f16c44a38f551841702essdeep: 24576:NMnKtay3fADe0OvKDqjnwFufmKQ0cUPHn1o1zzzxK/cRgOnmq9g6C3hMfz1:CKYyvAq50qzwFRKNcq1o8cOU7m6C3hkxtype: PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for MS Windowstlsh: T1BD3523F1A5DFD84CC488D27DA818FF22C21B9573B6564577A7C8336FF2A1340AE82256sha3_384: 4247c969c409844104e1e0f7bda97dddbb06b73dd5607a87a3c58d96c8629d9a6de7de12b9debba3387897b6c2c6a9faep_bytes: 6801f07000e801000000c3c3f1b0b024timestamp: 2010-11-20 02:56:30Version Info:
CompanyName: WinZip+FileDescription: WinZip+ Self-ExtractorFileVersion: 1.8.0.620InternalName: LegalCopyright: WinZip+LegalTrademarks: WinZip+OriginalFilename: ProductName: ProductVersion: 1.8.0Comments: Translation: 0x0419 0x04e3
Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] also known as:
| DrWeb | Trojan.SMSSend.220 |
| MicroWorld-eScan | Gen:Heur.Zilix.5 |
| FireEye | Gen:Heur.Zilix.5 |
| ALYac | Gen:Heur.Zilix.5 |
| Cylance | Unsafe |
| Sangfor | ASP45 |
| K7AntiVirus | Trojan ( 7000000f1 ) |
| K7GW | Trojan ( 7000000f1 ) |
| Cybereason | malicious.a797dc |
| BitDefenderTheta | Gen:NN.ZelphiF.34786.eX2aaGWKaSpo |
| Cyren | W32/FakeInstall.B.gen!Eldorado |
| Symantec | PUA.SMSFastLoads |
| ESET-NOD32 | a variant of Win32/Hoax.ArchSMS.AS |
| Kaspersky | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.FakeInstaller.alva |
| BitDefender | Gen:Heur.Zilix.5 |
| NANO-Antivirus | Trojan.Win32.bwwqfj.eaawfr |
| SUPERAntiSpyware | Trojan.Agent/Gen-FakeInst |
| Tencent | Win32.Trojan.Fakeinstaller.Pezu |
| Ad-Aware | Gen:Heur.Zilix.5 |
| Comodo | Application.Win32.SMSsend.A@2nalbs |
| VIPRE | Gen:Heur.Zilix.5 |
| McAfee-GW-Edition | BehavesLike.Win32.Dropper.tc |
| Sophos | ML/PE-A + Mal/FakeInst-B |
| Ikarus | Trojan-Ransom.FakeInstaller |
| Jiangmin | Trojan/FakeInstaller.qj |
| Avira | TR/Crypt.XPACK.Gen3 |
| Antiy-AVL | Trojan/Generic.ASMalwS.94 |
| Microsoft | Trojan:Win32/Ninunarch.N |
| GData | Gen:Heur.Zilix.5 |
| SentinelOne | Static AI – Suspicious PE |
| AhnLab-V3 | Win-Trojan/Fakeinst.Gen |
| McAfee | SMSFraud.s |
| VBA32 | TScope.Trojan.Delf |
| Panda | Trj/Genetic.gen |
| APEX | Malicious |
| Rising | Ransom.FakeInstaller!8.1D69 (CLOUD) |
| Yandex | Trojan.GenAsa!vKOZfIKLW+o |
| MAX | malware (ai score=81) |
| MaxSecure | Trojan.Ransom.FakeInstaller.alva |
| Fortinet | Adware/FakeInstaller |
| AVG | Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] |
| Avast | Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] |
| CrowdStrike | win/malicious_confidence_70% (W) |
How to remove Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj]?
Win32:FakeInst-AE [Trj] malware is extremely hard to eliminate manually. It stores its documents in multiple locations throughout the disk, and can get back itself from one of the elements. Furthermore, a range of modifications in the windows registry, networking configurations and Group Policies are quite hard to discover and revert to the original. It is better to utilize a specific program – exactly, an anti-malware tool. GridinSoft Anti-Malware will fit the most ideal for malware removal reasons.
Why GridinSoft Anti-Malware? It is pretty lightweight and has its detection databases updated almost every hour. Furthermore, it does not have such bugs and vulnerabilities as Microsoft Defender does. The combination of these aspects makes GridinSoft Anti-Malware perfect for taking out malware of any type.
Remove the viruses with GridinSoft Anti-Malware
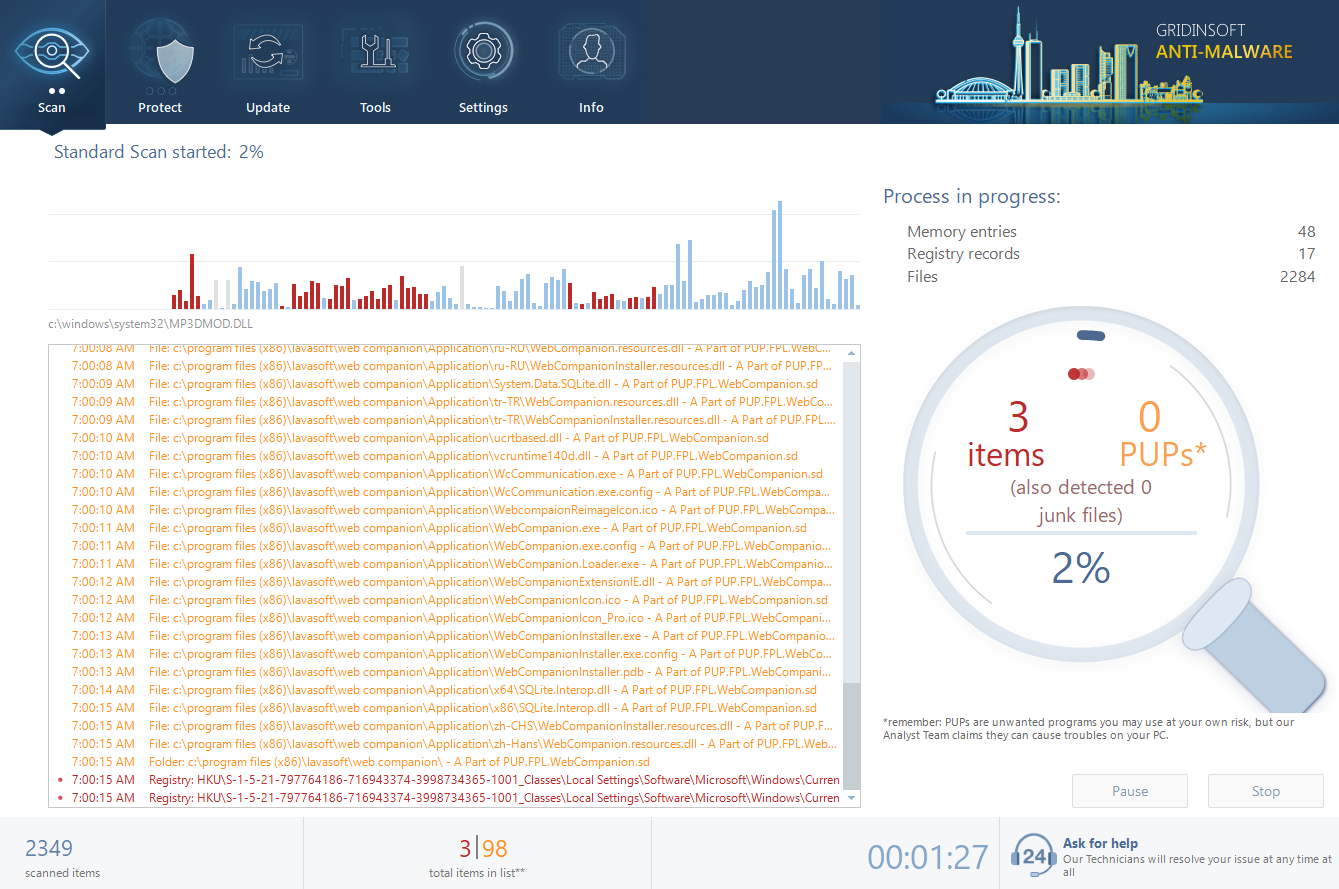
- Download and install GridinSoft Anti-Malware. After the installation, you will be offered to perform the Standard Scan. Approve this action.
- Standard scan checks the logical disk where the system files are stored, together with the files of programs you have already installed. The scan lasts up to 6 minutes.
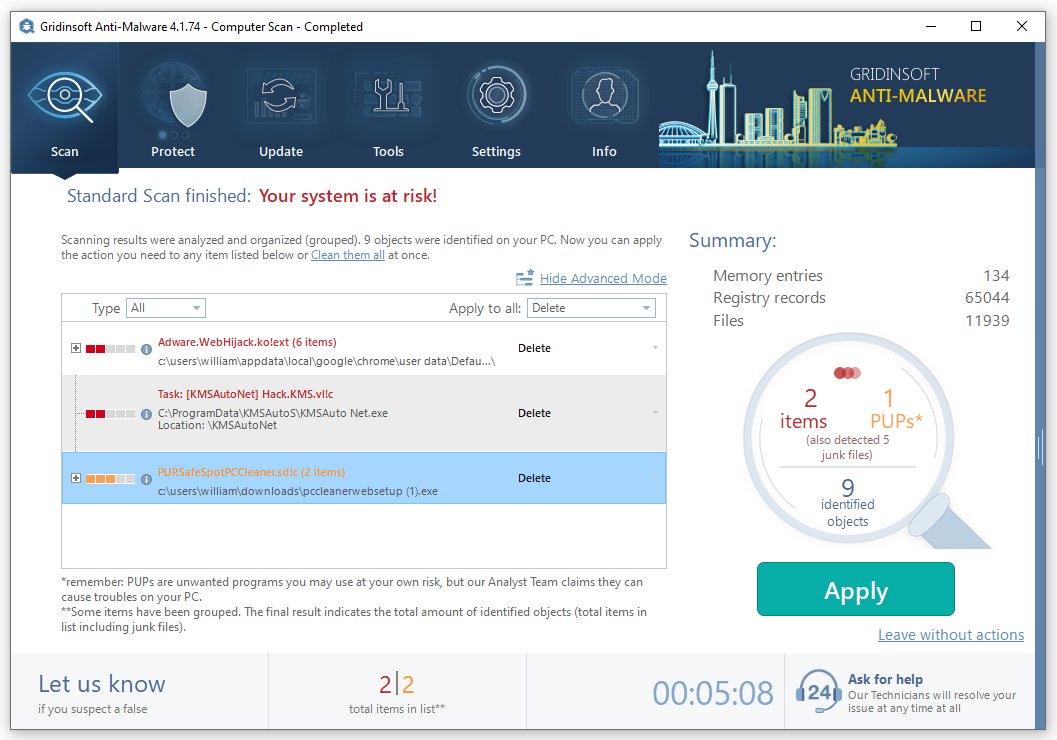
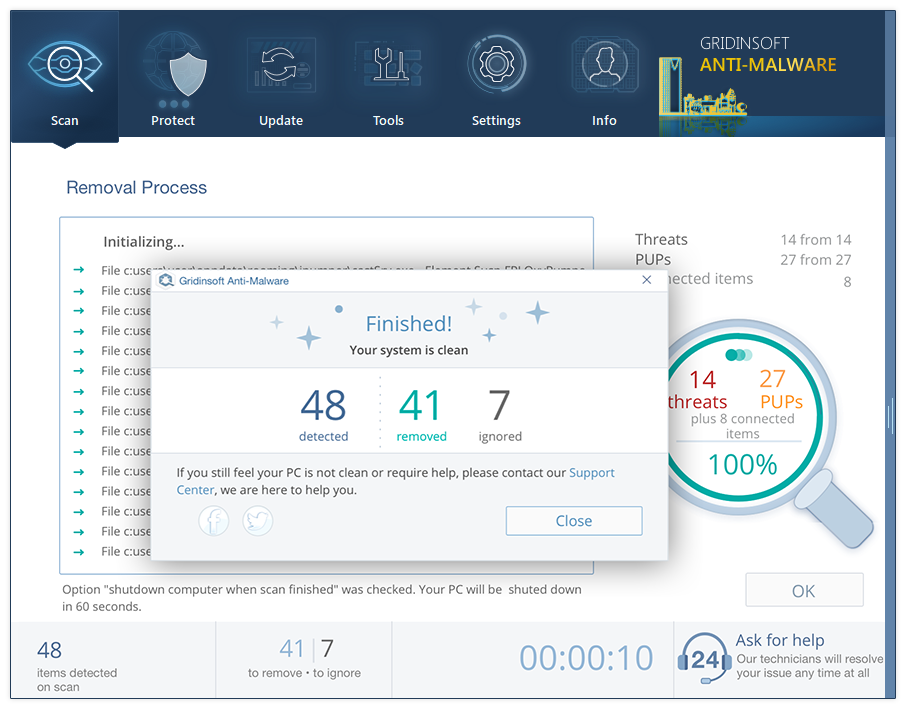
- When the scan is over, you may choose the action for each detected virus. For all files of [SHORT_NAME] the default option is “Delete”. Press “Apply” to finish the malware removal.