The malicious program known as RedLine Stealer aims to grab various personal information from the infected system. It can spread as stand-alone malware or in conjunction with other malicious apps. This malware represents an example of a banking stealer, but it can also delve into different browsers to extract various other categories of information.
What is RedLine Stealer Malware?
RedLine Stealer, available for purchase on underground forums, exists in two forms: a standalone version priced at $100 or $150 (depending on the version) and a subscription-based service costing $100 per month.
Its primary purpose is to gather sensitive information from web browsers, encompassing saved credentials, autocomplete data, and credit card details.
Moreover, when operating on a targeted machine, RedLine Stealer acquires system inventory information such as the username, location data, hardware configuration, and details concerning installed security software.
Recent iterations of RedLine Stealer have incorporated the capability to pilfer cryptocurrency. This malware category also sets its sights on FTP and IM clients, enabling it to upload and download files, execute commands, and periodically transmit information regarding the infected computer.
Stealers strive to remain as stealthy as possible since their efficiency heavily relies on staying undetected within the system for as long as possible. While some samples perform their basic operations and then self-destruct, others continue running until they are detected or receive a self-destruction command from the command and control (C&C) server.
Functionality of RedLine Stealer
RedLine Stealer functions primarily as a banking stealer, targeting banking credentials stored in web browsers. To achieve this objective, RedLine has the capability to thoroughly extract information from any browser, including Chromium, Gecko-based, and others. In addition to banking data, it also captures cookies and passwords stored in the browser. However, not many popular browsers store passwords in plain text format, so the focus is more on attacking users of alternative applications.
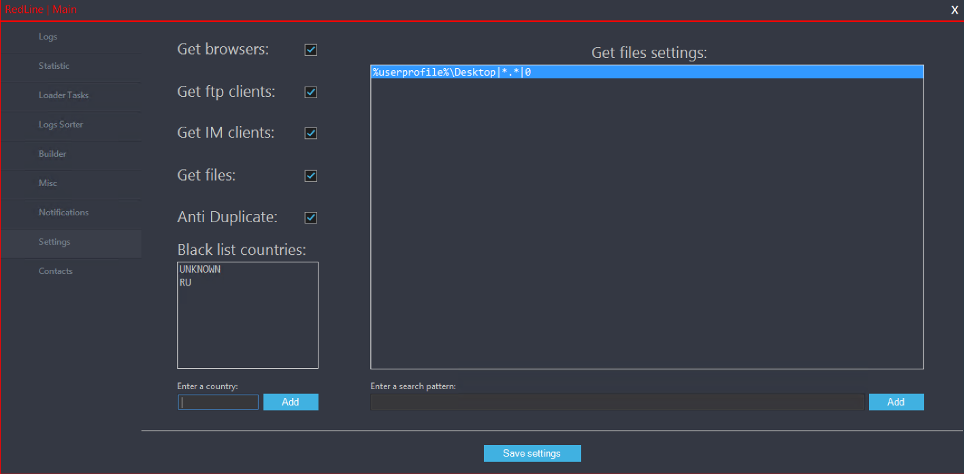
Administrative panel of RedLine Stealer
However, web browsers are not the only source of information for that stealer. Along with them, RedLine malware scans the device for various apps, such as Telegram, Discord, and Steam. It also aims at grabbing the credentials for FTP/SCP and VPN connections. Its code, recovered by reverse engineering, also shows its ability to scan for crypto wallets and then steal their information.
At the end of a procedure, RedLine collects detailed information about the system – OS version, installed hardware, the list of software, IP address, and so forth. Then, the entire pack of collected information is stored in the ScanResult folder. The latter is created in the same directory with the stealer executive file.
RedLine Stealer Tech Analysis
After reaching the target machine, RedLine malware launches a single process – Trick.exe, and a single instance of a console window. Soon after, it establishes a connection with the command and control server at the address of newlife957[.]duckdns[.]org[:]7225. It is worth noting that the initial code contains pretty legit functions – likely taken from a real program. Malicious content is getting downloaded dynamically through the functionality in the initial code. Such a trick is used to win some time for disabling the anti-malware solutions inside the system after the initial access.
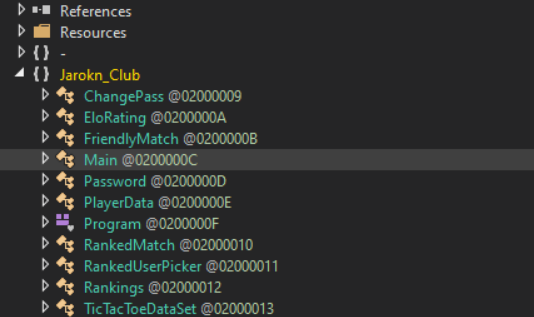
TicTacToe references in the RedLine code
When the malicious payload is installed, the first thing malware does is check the IP address of the PC. It uses the api[.]ip[.]sb site for that purpose. If there are no conflicts with its internal blacklists – countries and IP addresses that are not allowed to launch in – malware proceeds to further operations. RedLine starts scanning the environment step by step, following the list it receives after configuring.
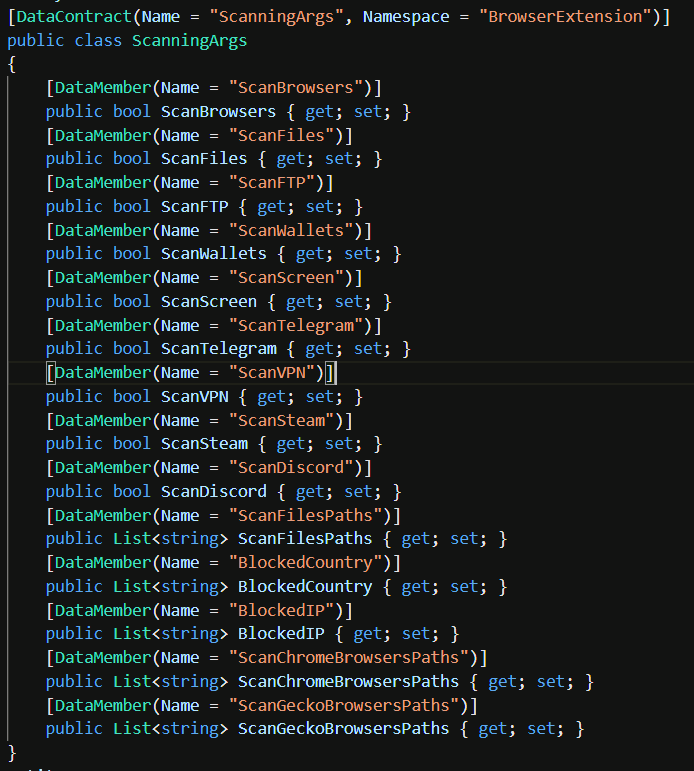
Sequence of scanning for elements to steal on the infected PC
Then, it forms a log file that contains the information extracted from the attacked system. It is not possible to see all the details, as malware features data encryption at the stage of data extraction. However, the data types are clearly visible, hence you can expect what this malware shares with the rascals.
Data types collected by RedLine Stealer
| Function name | Description |
|---|---|
| ScannedBrowser | Browser name, user profile, login credentials and cookies |
| FtpConnections | Details about FTP connections present on the target machine |
| GameChatFiles | Files of in-game chats related to any games found |
| GameLauncherFiles | The list of installed game launchers |
| InstalledBrowsers | List of installed browsers |
| MessageClientFiles | Files of messaging clients located on the target machine |
| City | Detected city |
| Country | Detected country |
| File Location | The path where malware .exe file is executed |
| Hardware | Information about the installed hardware |
| IPv4 | Public IPv4 IP address of the victim PC |
| Language | OS language |
| ScannedFiles | Possibly valuable files found in the system |
| ScreenSize | Screen resolution of the target system |
| Function name | Description |
|---|---|
| ScannedWallets | Information about the wallets found in the system |
| SecurityUtils | List and status of all detected antivirus programs |
| AvailableLanguages | Languages, supported by the OS version on target PC |
| MachineName | Name of the target machine |
| Monitor | The screenshot of the screen at the moment of execution |
| OSVersion | Information about operating system version |
| Nord | Credentials for NordVPN |
| Open | Credentials for OpenVPN |
| Processes | List of processes running in the system |
| SeenBefore | Checkup if the report is about a new victim or the one that was attacked earlier |
| TimeZone | Time zone of the attacked computer |
| ZipCode | Victim’s Zip-code |
| Softwares | List of the programs installed on the attacked PC |
| SystemHardwares | Details about PC configuration |
Different researches show that RedLine is not completely consistent with the browsers it attacks. The biggest effectiveness is observed in Chrome, Opera, Chromium and Chromodo browsers. Among the apps based on other engines than Chromium there is a Chinese WebKit-based 360Browser. Web browsers on Gecko engine – Firefox, Waterfox and so forth – are also vulnerable, but the stealer sometimes has problems while extracting data from them.
RedLine malware orients at long-term staying in the system. A lot of stealers have a self-removal functionality once there is no data left to thief. Meanwhile, this stealer offers a spyware-style mechanism: an operator can order it to destroy itself, but there are no timers inside.
RedLine Stealer IoC
- SHA256: f4d1b970bc9e5d319c5432be9e3863b5a20bf26e557c8cea6f3949df0012cf01
- SHA256: 80f306d656669534f8996c5b83c6b0c1aa87e0097bac53b79d8ec30550ea5e44
- SHA256: d62fc9601bbf082cd097af67c9a6b74179a636c8dbf8ac04f614df2a6c0c9fe6
- SHA256: 77436bfe8498d733a09f07608054731d5f7ddb28e56ea7166c89fbae134fe334
- SHA256: acbb409f6fbe45fe6be7346c2d5ef43b86e095b2f63fe83d3edb4d3ca9eb4d7b
- SHA256: 156a6f7f50aab5d04e30ddbaee8557857f48b5386d09150b178693731eac7b35
- SHA256: 78df5dd27086d25674a6b62028226b22b87a9a35c719324f6ed25618babb8409
- SHA256: bb69aa08bdbcaa8860d26feaa036760b683f0e164fb18b5a772f0c4321e63b1d
- SHA256: 7bdcd02e33aee2a01a66cd98b8fb045b7cc7386b3a08c3841698a668fe353c5a
- SHA256: c7343df34a196ab643130de666b93ced7114b958d38381619aa63c3b427d920d
| Indicator | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| newlife957[.]duckdns[.]org[:]7225 | URL | C2 URL |
| 1741984cc5f9a62d34d180943658637523ac102db4a544bb6812be1e0507a348 | Hash | SHA-256 hash – disguise (undetected) |
| ee4608483ebb8615dfe71924c5a6bc4b0f1a5d0eb8b453923b3f2ce5cd00784b | Hash | SHA-256 hash of malware part |
| 9dc934f7f22e493a1c1d97107edc85ccce4e1be155b2cc038be8d9a57b2e430f | Hash | SHA-256 hash of malware part |
| 76ca4a8afe19ab46e2f7f364fb76a166ce62efc7cf191f0f1be5ffff7f443f1b | Hash | SHA-256 hash of malware part |
| 258445b5c086f67d1157c2998968bad83a64ca3bab88bfd9d73654819bb46463 | Hash | SHA-256 hash of system info grabber |
Widespread RedLine variants detected in the wild
- Trojan:Win32/RedLine.BS!MTB
- Trojan:Win32/Redline.WON!MTB
- Trojan:Win32/Redline.UR!MTB
- Trojan:Win32/Redline.KB!MTB
- Trojan:Win32/Redline.SHL!MTB
- Trojan:MSIL/Redline.RA!MTB
- Trojan:Win32/Redline.DD!MTB
RedLine Stealer Distribution
As I’ve mentioned before, RedLine Stealer may come as a solitary malware, as well as in a bundle with other viruses. Its activity rapidly grew over the last time, as it is convenient for crooks and can easily be purchased even in the surface web. For example, its developers have a group in Telegram messenger, where this malware is offered under different subscription types. As the stealer has outstanding functionality, these offers are never getting stale.

RedLine marketing bot in Telegram Messenger
In a stand-alone form, RedLine Stealer is usually spread through email phishing. Alternatively, it may be disguised as installation files of some popular programs, like Discord, Telegram, Steam, and cracked apps. In one specific case, RedLine appeared as a browser extension, and its download link was embedded into a YouTube video description. However, phishing email messages remain the most potent and popular forms of malware distribution – and RedLine Stealer is not an exclusion.
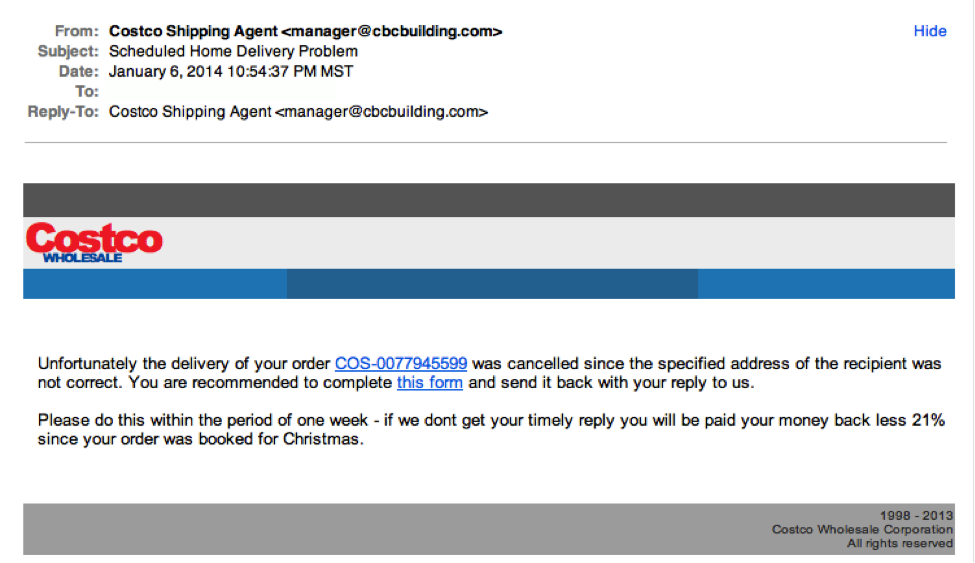
The example of a typical phishing email
When it comes to spreading together with other malware, RedLine is often mated with different ransomware samples. However, the biggest share of in-bundle spreading is after the RedLine compound with Djvu ransomware. Actually, this ransomware features not only this stealer but also 2 other malware – SmokeLoader backdoor and Vidar stealer. Such a package can take away every piece of valuable data and flood the computer with other malware. And don’t forget about ransomware – this thing will already create a mess of your files.
What is Djvu ransomware?
STOP/Djvu ransomware is a notable example of a long-living cybercriminal group, that terrorizes mostly individuals. They quickly gained a dominant position on the ransomware market, reaching over 75% share in total ransomware submissions at a certain point of time. These days, it lost such a big tempo but remains as dangerous as ever. The additional malware it brings to the user device is likely needed to compensate for the shed in the number of new victims. Earlier, they were deploying Azorult stealer but then switched to the malware we mentioned earlier.
How to stay protected?
Knowing the ways of spreading gives you great instruction on preventing it. Methods of email spam counteraction are well-known and have a large variety of possible approaches. Same does malware spreading with a disguise of a legitimate application. Methods that feature unique and occasional ways are the hardest to avoid, but it is still possible.
Spam emails can easily be distinguished from genuine messages. Almost every fishy message tries to mimic the real company or a sender familiar to you. However, it cannot counterfeit the sender’s address, as well as predict if you are waiting for that letter. Actually, they can acknowledge what emails you may receive through preliminary phishing, but that situation is pretty rare. Hence, seeing a strange letter you shouldn’t receive with an unusual address of its sender means someone tries to fool you. If the information looks convincing to you, it is better to go check things manually.
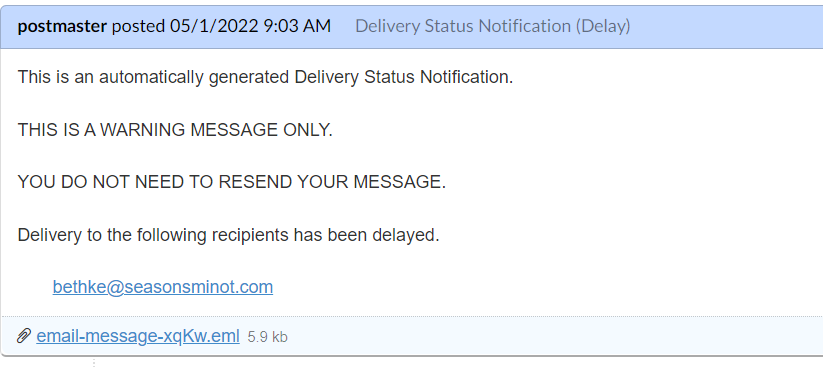
The typical example of a bait email. The attached file contains malware
Fake app installers do not require that much of your attention but need you to follow the rules. For instance, those counterfeits are often spread in online communities, such as Discord or Reddit. Using them is risky, especially once you can get the same installer from the official site for free. When it comes to cracked programs, that’s one thing you should remember – nothing is free under the sun. Even if the crack looks legit, and you are sure about the sender, it is better to check that file with anti-malware software. There’s a big temptation to monetise the app cracking through adding malware – hackers break the law anyway. Another solution is to use genuine copies of software – paid and downloaded from the vendor’s website.
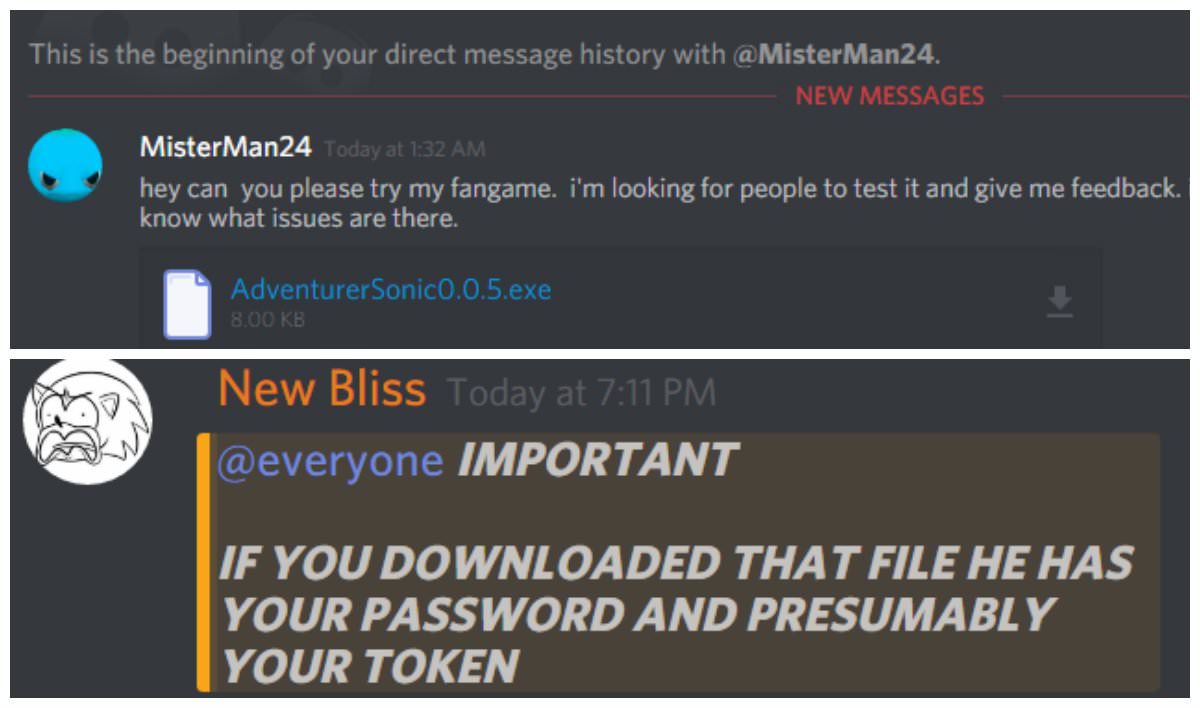
The example of malware spreading through Discord
Tricky ways are almost impossible to predict and detect proactively. However, the files and extensions will not launch themselves automatically. Once you see a situation you are not sure about, the best decision is to launch a full scan with a powerful security solution. If equipped with a modern scanning system, it will definitely spot unusual activities that are not visible to the human eye.
User Review
( votes) ![]() German
German ![]() Japanese
Japanese ![]() Spanish
Spanish ![]() Portuguese (Brazil)
Portuguese (Brazil) ![]() French
French ![]() Turkish
Turkish ![]() Chinese (Traditional)
Chinese (Traditional) ![]() Korean
Korean ![]() Indonesian
Indonesian ![]() Hindi
Hindi ![]() Italian
Italian

