New peer-to-peer (P2P) botnet, dubbed Mozi, attacks the Netgear, D-Link, and Huawei routers during a recent malware campaign and checked them for unsafe Telnet passwords.
According to security researchers at Qihoo 360 Netlab, cybercriminals use a botnet to launch DDoS attacks.
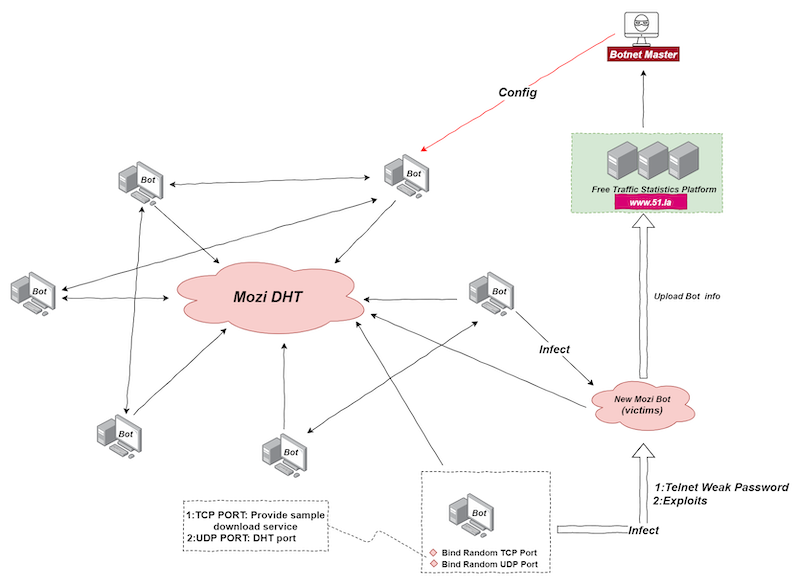
The botnet uses part of the Gafgyt code but is not derived from it. Mozi implements a DHT protocol based on a standard protocol commonly used by torrent clients and other P2P platforms to store host contact information”, – say experts from Qihoo 360 Netlab.
Thus, attackers can infect new devices faster without the need for servers, as well as “hide the payload in a huge amount of normal DHT traffic”. Mozi also uses the ECDSA384 and XOR algorithms to ensure the integrity and security of the botnet and P2P network components.
The malware uses the Telnet protocol and hardware vulnerabilities to infect new devices. Operators log in to the target CCTV router or DVR with an unreliable password and then download and execute the payload after successfully exploiting vulnerabilities in unpatched hosts.
Mozi infects new devices through weak telnet passwords and exploits. The current Bot node randomly uses a local port to start the http service to provide sample downloads or receives the sample download address in the Config file issued by the Botnet Master. Provides a sample download address for future infected targets. Bot node logs in to the target device with a weak password, writes the downloader file in echo mode and runs it, and downloads the sample file from the sample download address provided by the current Bot node”, — write researchers from Qihoo 360 Netlab.
However, not only weak Telnet passwords can bring malware to your system – take a look at remote desktop applications. As we already said, the Zeppelin Ransomware operators use for distribution remote desktop tools.
After launching malware on a compromised device, the bot automatically joins the Mozi network as a new node, which is later used to search for and infect other vulnerable devices.
To provide protection against interception by other criminal groups, Mozi operators also set up an automatic check of all commands sent to the botnet nodes and synchronized configurations. In this way, the nodes accept and execute only the validated configurations.
Mozi’s functionality includes the ability to conduct DDoS attacks, collect and exfiltrate information about infected hosts, download and execute payloads from certain resources, download updates, and execute commands.
Currently, the botnet attack list includes the following: Eir D1000, Vacron NVR, devices with Realtek SDK, Netgear R7000 and R6400, DGN1000 Netgear, MVPower DVR, Huawei HG532, D-Link, CCTV DVR and GPON routers.
Suggestestions
Qihoo 360 Netlab recommends that users update the patch in a timely manner, and determine whether they are infected by looking up the process and file name, and HTTP, DHT network connection characteristics created by Mozi Botnet.