Google has fixed a dangerous GhostToken vulnerability in the Google Cloud Platform (GCP). The problem affected all users and allowed attackers to create backdoors for other people’s accounts using malicious applications with OAuth installed from the Google store or third-party vendors.
The vulnerability was discovered by the Israeli startup Astrix Security. Moreover, the bug was found back in the summer of 2022, but it was only possible to fix it with the help of a global fix released in early April 2023.Let me remind you that we also wrote that Google Fixes the Second 0-Day Vulnerability in Chrome in a Week, and also that For years, Google ignored dangerous vulnerability in Google Authenticator.
And also information security specialists noted that Researcher Earned $10,000 by Finding XSS Vulnerability in Google Maps.
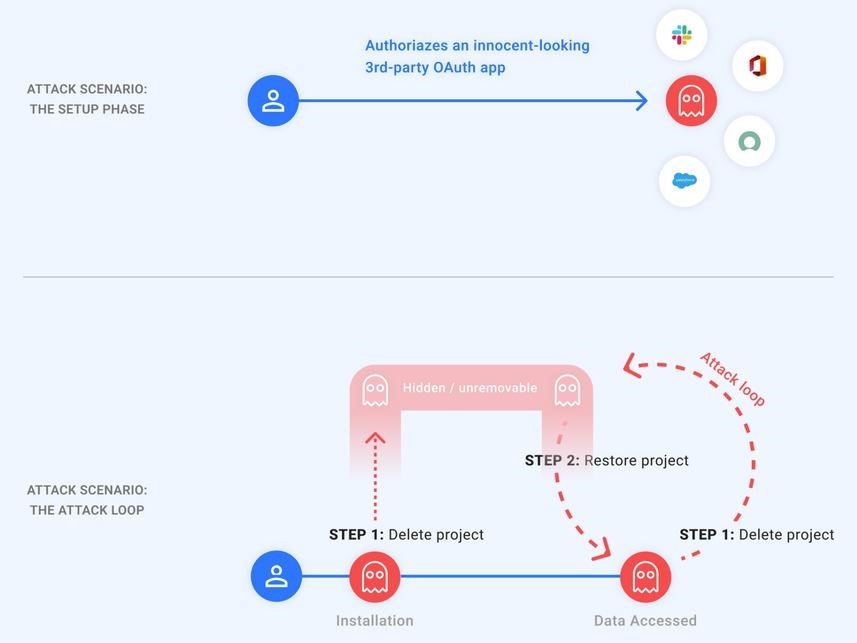
The essence of GhostToken is that after authorization and binding to an OAuth token that gives access to a Google account, a malicious application can become “invisible” by exploiting this vulnerability. As a result, the application will be hidden from the application management page, the only place where Google users can manage their applications connected to their accounts.
To make the malicious applications authorized by the victims “invisible”, the attacker could simply put them in the “pending removal” state by removing the associated GCP project. Moreover, after the restoration of the project, the hacker will be provided with a refresh token, which allows him to get a new access token that can be used to access the data of the victims.
Worse, all this could be done in a loop, deleting and rebuilding the GCP project to hide the malicious application from the victim.
The consequences of such an attack depended on the specific permissions granted by the victim to the malicious application. This could include data stored in the victim’s Google apps, including Gmail, Drive, Docs, Photos, Calendar, as well as Google Cloud Platform services (BigQuery, Google Compute, and so on).
The patch released by Google engineers makes all GCP OAuth applications with a “pending deletion” status visible on the “Apps with access to your account” page, allowing users to see and delete them.
Astrix Security researchers advise all Google users to visit the application management page and check that they have been granted only those permissions that are really necessary for their work.
