People got so used to all the technologies out there in the world that they often forget: the device in your pocket is a computer million of times more powerful than the systems used for the moon landings in 1969. Incredible, isn’t it?
You’ve probably heard about those fake banking mobile apps. They’re ones which pretend to be from some legit bank but actually perform quite deceptive actions. They actually belong to the banking trojan malicious apps family. But it’s not enough to talk only about these. There are not only fake banking apps but a whole range of ones that try to fake different stuff. We will walk you through them so you would know what they are, and how they work. You will learn the most common signs of malicious or fake apps presence. Additionally, you will see what are the most common kinds of such apps, and do they only affect Android or iOS as well. Finally, we’ll answer the most important question – how to stay away from them?
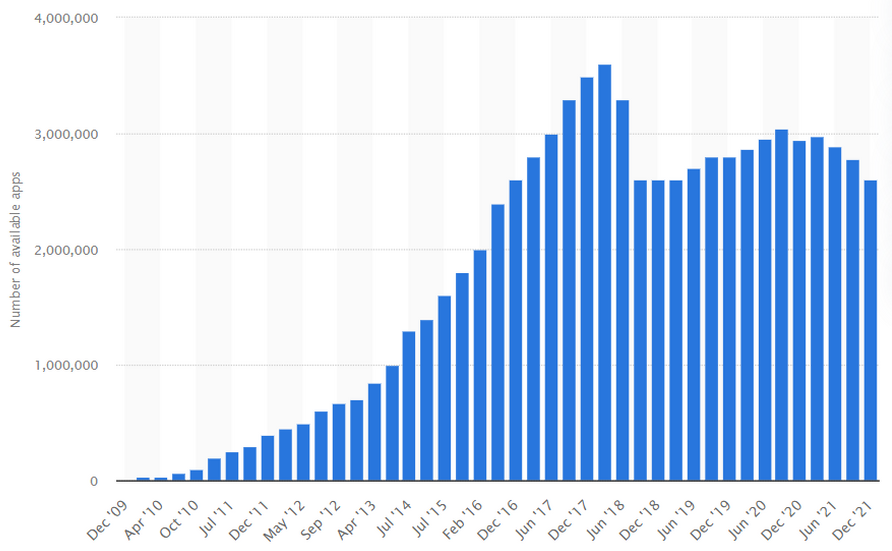
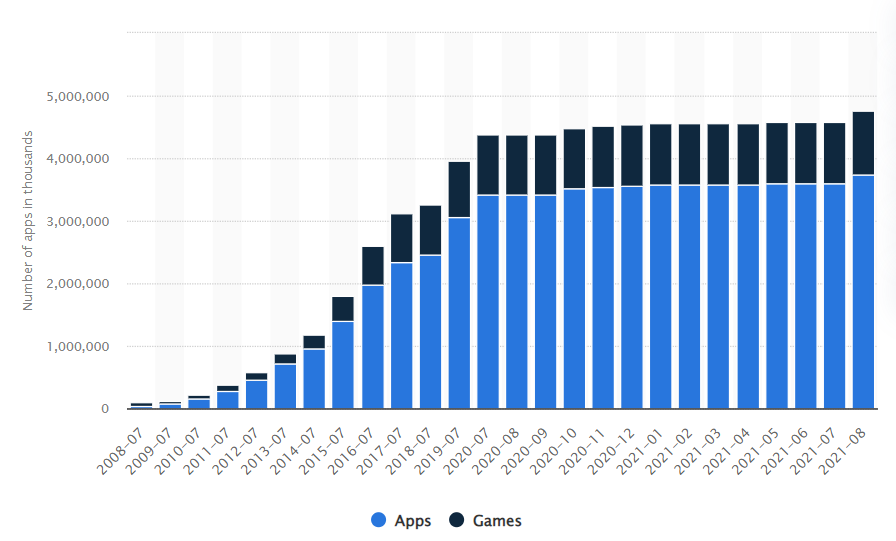
Short statistic on mobile apps usage
Before we start with the main questions I want you to know the following interesting statistics on this topic. Currently, in the world there are almost 6.3 bln smartphone users1 and that’s nearly half of the total population on Earth. With such growth, the downloads of mobile apps are steadily growing too. For the period from 2016 to 2020 the number of downloads of mobile applications for the quarter increased by more than 1.5 times – from 20 billion to 36 billion. In total, over 204 billion downloads were made in 2020. The number of mobile applications in stores is growing as well. According to statistics, about 100,000 new apps for Google Play and 30,000 apps for the App Store appear every month.
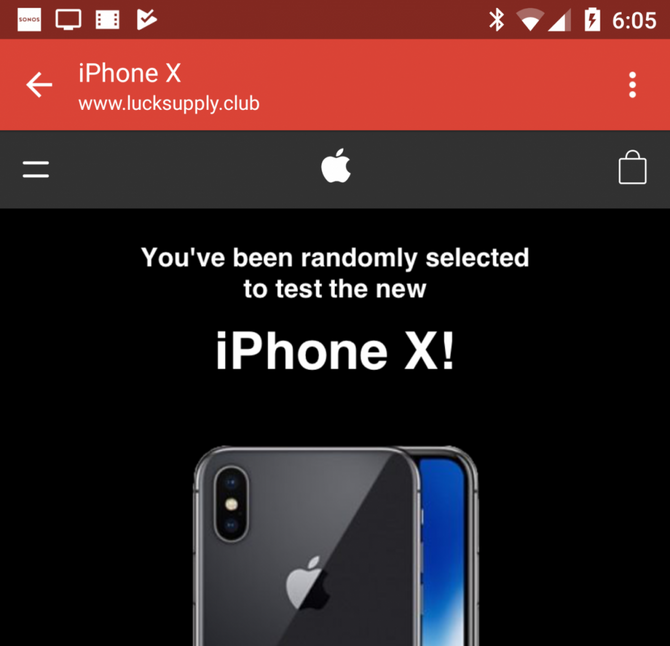
Naturally, in places where information technologies are used so massively you can meet numerous cyber fraudsters. Obviously, there will be more of them than elsewhere. Their main purpose is information stored on phones, which can be both personal (photos, copies of documents, bank card data) or work-related. Sometimes leakage of certain types of such information can be extremely unpleasant for their owner. For a long time attackers used social engineering and other similar techniques to steal information. They devised to some degree sophisticated kinds of schemes. But nowadays everything is much more simple: all you need is for the user to download a fake application on their device that will pretend to be real. It can even be with real functions but it will also silently perform certain malicious functions.
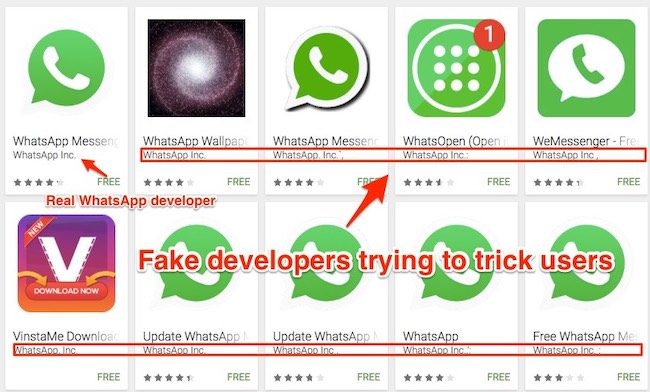
Legit and fake WhatsApps in Play Market
However, such programs are also engaged not only in data theft, but also in cryptocurrency mining, advertising fraud, etc.
Of course, Google Play and the Apple Store do not look indifferently at cybercriminals creating apps with illicit purposes. They are actively fighting such programs: apps are reviewed before publication, and also periodically later. But the reality shows even this is not enough to completely screen out fraudulent applications.
What are common signs of malicious or fake mobile apps presence?
It’s never too late to check everything once again. Even if you are sure you don’t have any mobile malware on your device. Maybe that quick battery drainage comes directly from some kind of malware hiding in your phone. Of course, there may be plenty of reasons for that fast discharge, but malware activity may be one of the reasons. So here are some warning signs you should pay attention to in case they appear. It should be mentioned that the signs are common both for iOS and Android.
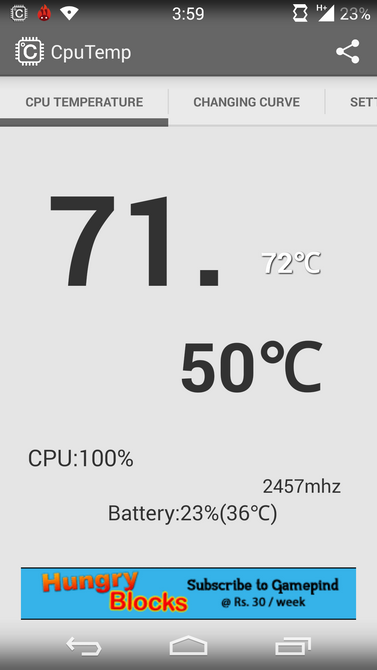
High CPU usage and temperature caused by malware
Long-term effects of malware presence
If that thing happens for a long time, you will likely detect an irreversible effect – wear. In particular, your battery is in danger. Since the charge in the electrolyte, as well as its conductivity, depends on the temperature, the long-time overheating may lead to a sharp decrease in the peak battery capacity. In very rare cases it may even lead to battery explosions.
Visual symptoms

Multiplicated Play Market is not normal
What are the most common kinds of malicious and fake mobile apps?
Cybercriminals exploit different types of mobile malware, since the purpose of their activities is different. Mobile devices nowadays are used more actively than desktops or laptops, hence their chance to get more personal or valuable information is bigger. That’s why there is a strict division on malware for money and malware for the valuable info.
Malware for private information

Android Screenlockers – the peculiar variant of ransomware
Just making money on you
The example of fake ad demostrated by adware
Users should know that the list could never be enough written because often the kinds of malicious apps overlap with one another combining several features, for example, a fake app can also be a trojan virus or RAT.
How to avoid malicious and fake apps?
Even though cybercriminals won’t give up creating malicious and fake apps, you can protect yourself from them and their apps by simply knowing the most common ways they get to you.
The first and the most obvious rule is to download any app only from the official stores, no side downloads. Usually, cybercriminals put their “traps” on various sites with freeware. These murky sites offer the highest chances possible that someone will eventually download the app. If it’s not the official app store then look for the legitimate site of the app you wish to download.
But even if you download something from an official app store it would not be odd to check the reviews, the official website of a developer, rates. On the official website for the app, you can also find a link that will redirect you to this specific app in the app store so you won`t need to find the app by yourself.
Avoid the apps that are blocked in your country. Most likely the ones you will find on the app store are just the counterfeits.
Things to pay attention
Before downloading look carefully at what types of access the app is asking. A simple calculator won’t need access to your contact list. Go through each app that you have on your phone and see what access they have been granted. Delete the apps that you no longer use.
Don’t forget to update the software regularly. I mean both operating system and third-party applications. It will make you protected against the latest uncovered vulnerabilities.
Don’t root your device as it puts your security in more danger than before. Rooting or jailbreaking your phone means that the internal protection of the device has been surpassed and the user now has unrestricted access to the operating system. People do this in order to install third-party apps that their operating system won’t support or they make certain customization that was not possible with the default protection.
You see the cyberworld as the real one is full of danger but the right knowledge will guide you truthfully. The practice shows that mobile devices can fall in danger the same way as your PC and is in most cases your main device can put you in danger as well.
User Review
( votes)References
- See the stats about the number of smartphone users on Statista.
- Thread on Quora about the advertisements in the new MIUI firmware.