Cur malware, a sophisticated threat, spreads primarily through targeted malspam campaigns. It often arrives disguised as innocuous archives, exploiting the DLL side-loading technique.
Once inside a system, Cur malware can lead to data theft, privacy breaches, financial losses, and system compromises. It’s noteworthy for its precision-targeted attacks, posing significant dangers to organizations and individuals alike.
Cur Malware Overview
The Cur malware group, a cluster of malicious programs, comprises software that exhibits minimal commonalities among its members. Notably, there are no discernible code similarities. These programs, however, are linked through a common infrastructure, and indications point to their association with a Chinese-affiliated cyber-espionage group known as ToddyCat.
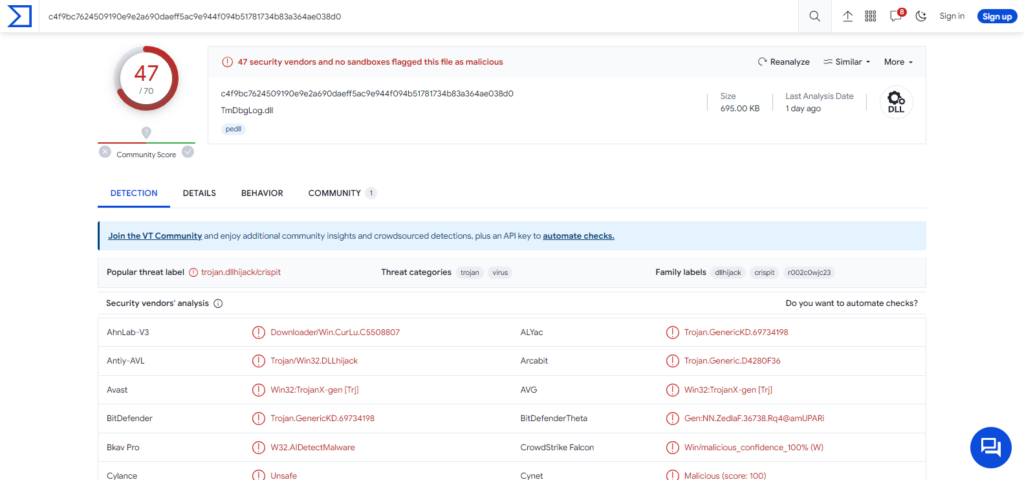
CurKeep malware on Virus Tortal site
At the time of this report, the Cur malware family is actively employed in an ongoing campaign referred to as “Stayin’ Alive,” which has been operational since at least 2021. This operation primarily targets Asia, with a focus on countries like Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Pakistan, and Vietnam. The attacks are directed at the telecommunications sector and entities with connections to government bodies.
| Name | Cur |
| Threat Type | Trojan, backdoor, loader. |
| Distribution methods | Infected email attachments, malicious online advertisements, social engineering, software ‘cracks’. |
| Detection | Microsoft (Trojan:Win32/Injector!MSR) |
| Damage | Stolen passwords and banking information, identity theft, the victim’s computer added to a botnet. |
| Fix Tool | See If Your System Has Been Affected by Cur Virus |
Technical Analysis of Cur Malware
The Cur malware group encompasses backdoors and loaders, which are program types designed to prepare systems for subsequent infiltration and introduce additional malicious software. These family members are specifically tailored for precision-targeted attacks. They exhibit a simplistic and lightweight nature, characterized by their small size.
Indications suggest that these programs are designed to be easily disposable due to their high specialization and limited versatility.
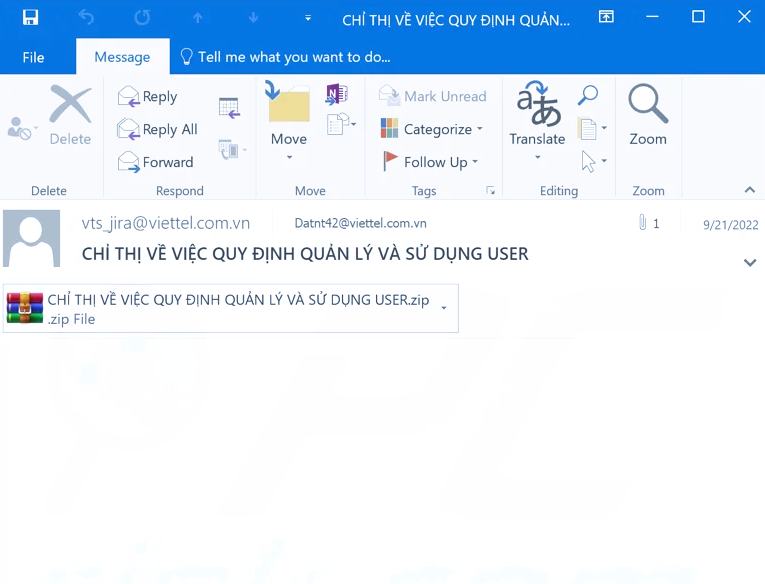
Screenshot of a spam email used to distribute CurKeep
Most documented Cur infections are initiated through targeted spam emails, utilizing the DLL side-loading technique to compromise systems. This approach involves exploiting the Windows DLL search order mechanism to utilize legitimate software for executing a malicious payload.
CurKeep is a lightweight backdoor program, with a mere 10KB in size, typical of this malware group. Once installed, it promptly transmits fundamental device data to its Command and Control (C&C) server. Following this, the malware remains in a state of readiness to receive commands.
CurKeep has been disseminated through various archives, including:
- “QForm V8.zip”: This archive masquerades as “QForm,” professional engineering software employed for simulating metal forming processes.
- “Саммит 2022 г (парол – 0809).rar”: Translating to “Summit 2022 (password – 0809).rar,” this file, albeit in Russian, originated from Uzbekistan.
- “Приказ №83 от 29.05.2023г.rar”: This Russian archive signifies “Order No. 83 from 29/05/2023,” with “order” indicating a command or instruction. The date format is in DD/MM/YYYY, and it traces back to Kazakhstan.
CurLu, a loader in the Cur malware family, primarily functions to fetch payloads from its C&C server. It’s frequently associated with the “Stayin’ Alive” campaign. While many infections involve the DLL side-loading technique, it’s not exclusive to this method.
CurLog, another loader within the Cur family, serves the purpose of downloading and installing payloads. Multiple variants of CurLog exist. Like most Cur programs, it’s propagated through DLL side-loading. An instance includes an archive named “Compatible Products – Vector ver7.1.1.zip,” which contains an executable with the same filename. This ZIP archive was submitted from Kazakhstan.
CurCore, on the other hand, is a lightweight backdoor that likely plays a role in initial reconnaissance and payload delivery. CurCore possesses the capability to read and create files, copy their contents, encode the information, and transmit it to the C&C server. Furthermore, it can receive and execute commands as directed.
High-risk infections typically lead to reduced system performance or complete system failure, data loss, grave privacy breaches, financial setbacks, and the risk of identity theft. The perils escalate significantly when such malware is deployed against highly sensitive entities, a characteristic that aptly describes the Cur group.
Spreading methods
Cur malware is considered dangerous. While the level of danger can vary depending on the specific variant and how it’s used, Cur malware and related programs can pose significant threats to computer systems and data.
Cur malware infiltrates computers primarily through the following methods:
- Malspam
Cur malware is actively disseminated via targeted spam emails. These emails often carry archive file attachments. These archives frequently contain seemingly legitimate software executables that leverage the DLL side-loading technique to introduce the Cur malware. In some cases, researchers have even discovered Cur malware archives hosted on portals used by them. - Diverse File Types and Methods
Cur malware can also be distributed using various other file types and techniques. Malicious files can be in formats such as ZIP, RAR, executables (e.g., .exe, .run), documents (PDF, Microsoft Office, Microsoft OneNote), JavaScript, and more.
In a broader context of malware distribution, common methods include:
- Phishing attacks and social engineering techniques are widespread and often involve convincing individuals to click on malicious links or open malicious attachments.
- These can be delivered via emails, private messages, direct messages, SMS messages, and so on.
- Stealthy and deceptive downloads occur when users unknowingly download malicious content while visiting a website.
- Malware can be distributed through sources like freeware websites, free file-hosting platforms, Peer-to-Peer sharing networks, and similar channels.
- Cybercriminals employ various online scams to trick users into downloading and executing malicious software.
Understanding these distribution methods is critical for preventing Cur malware and other threats from infiltrating computer systems.
Remove Cur with Gridinsoft Anti-Malware
We have also been using this software on our systems ever since, and it has always been successful in detecting viruses. It has blocked the most common Stealers as shown from our tests with the software, and we assure you that it can remove Cur as well as other malware hiding on your computer.
To use Gridinsoft for remove malicious threats, follow the steps below:
1. Begin by downloading Gridinsoft Anti-Malware, accessible via the blue button below or directly from the official website gridinsoft.com.
2.Once the Gridinsoft setup file (setup-gridinsoft-fix.exe) is downloaded, execute it by clicking on the file.
3.Follow the installation setup wizard's instructions diligently.
4. Access the "Scan Tab" on the application's start screen and launch a comprehensive "Full Scan" to examine your entire computer. This inclusive scan encompasses the memory, startup items, the registry, services, drivers, and all files, ensuring that it detects malware hidden in all possible locations.
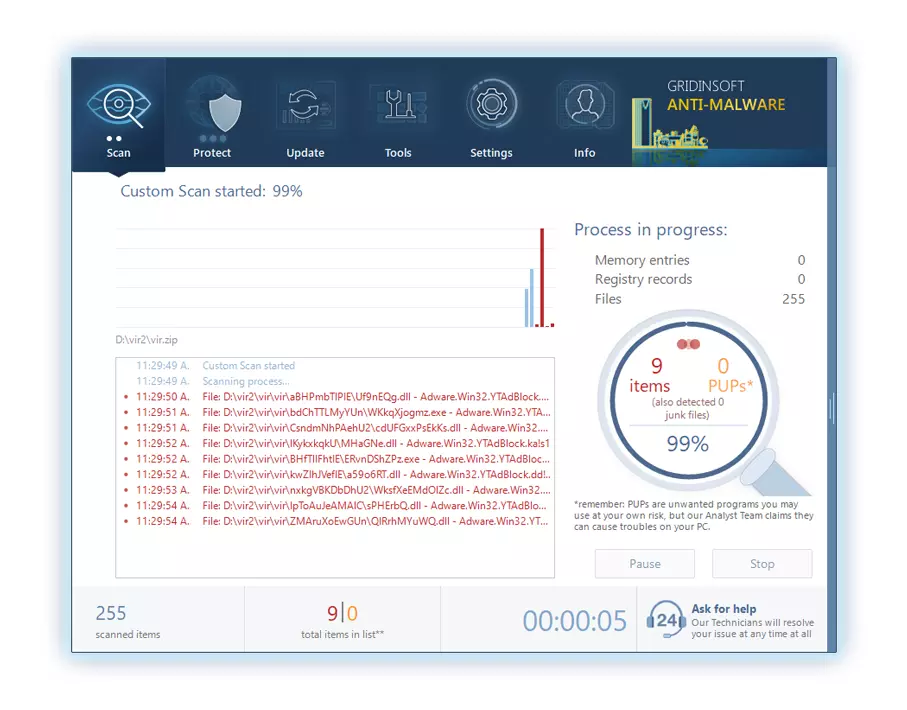
Be patient, as the scan duration depends on the number of files and your computer's hardware capabilities. Use this time to relax or attend to other tasks.
5. Upon completion, Anti-Malware will present a detailed report containing all the detected malicious items and threats on your PC.
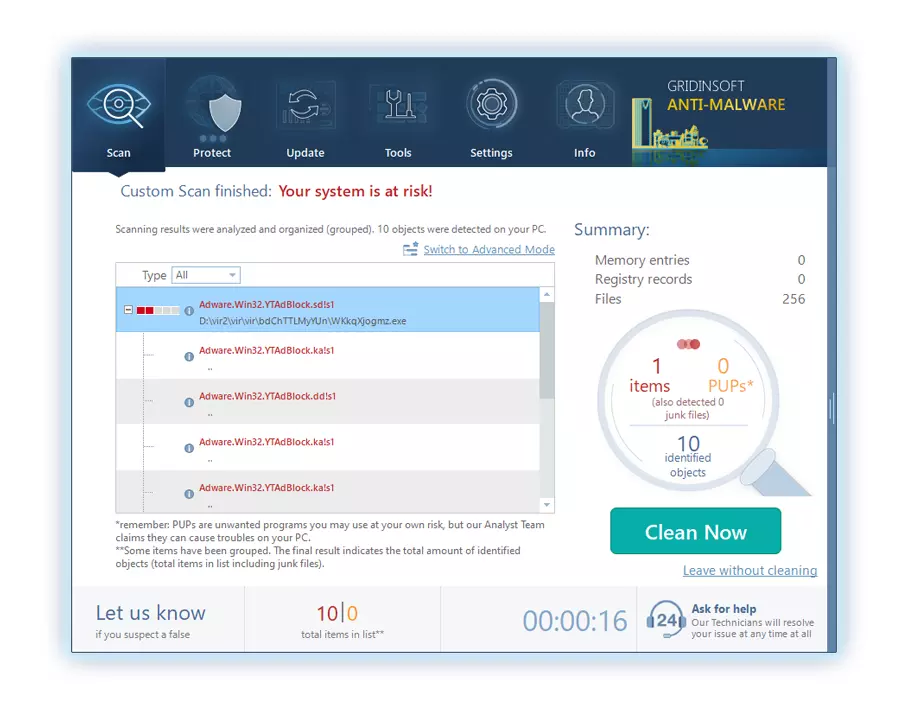
6. Select all the identified items from the report and confidently click the "Clean Now" button. This action will safely remove the malicious files from your computer, transferring them to the secure quarantine zone of the anti-malware program to prevent any further harmful actions.
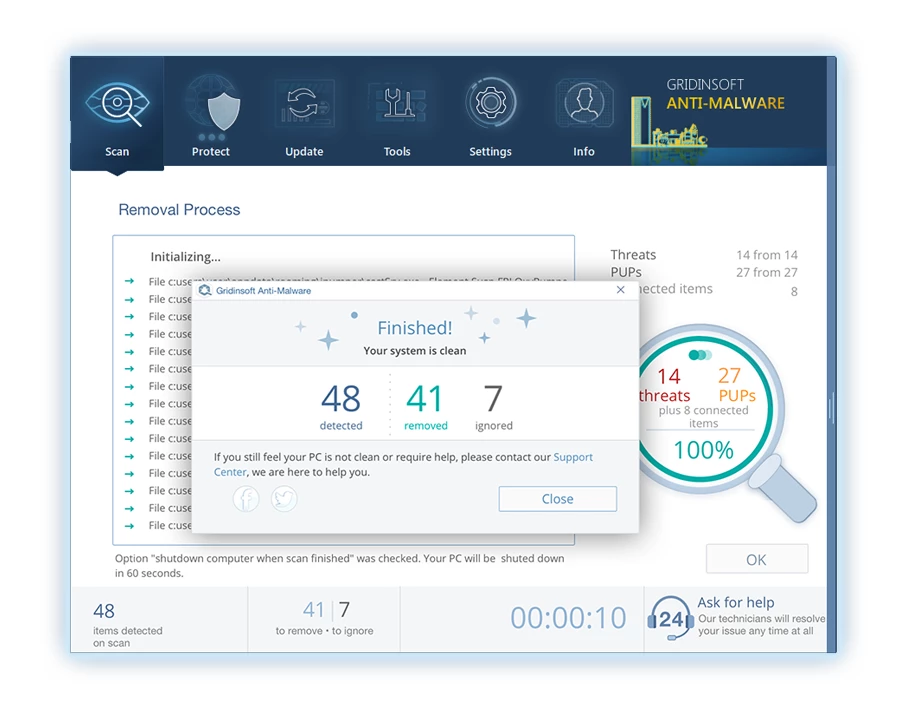
8. If prompted, restart your computer to finalize the full system scan procedure. This step is crucial to ensure thorough removal of any remaining threats. After the restart, Gridinsoft Anti-Malware will open and display a message confirming the completion of the scan.
Remember Gridinsoft offers a 6-day free trial. This means you can take advantage of the trial period at no cost to experience the full benefits of the software and prevent any future malware infections on your system. Embrace this opportunity to fortify your computer's security without any financial commitment.
Trojan Killer for “Cur” removal on locked PC
In situations where it becomes impossible to download antivirus applications directly onto the infected computer due to malware blocking access to websites, an alternative solution is to utilize the Trojan Killer application.
There is a really little number of security tools that are able to be set up on the USB drives, and antiviruses that can do so in most cases require to obtain quite an expensive license. For this instance, I can recommend you to use another solution of GridinSoft - Trojan Killer Portable. It has a 14-days cost-free trial mode that offers the entire features of the paid version. This term will definitely be 100% enough to wipe malware out.
Trojan Killer is a valuable tool in your cybersecurity arsenal, helping you to effectively remove malware from infected computers. Now, we will walk you through the process of using Trojan Killer from a USB flash drive to scan and remove malware on an infected PC. Remember, always obtain permission to scan and remove malware from a computer that you do not own.
Step 1: Download & Install Trojan Killer on a Clean Computer:
1. Go to the official GridinSoft website (gridinsoft.com) and download Trojan Killer to a computer that is not infected.
2. Insert a USB flash drive into this computer.
3. Install Trojan Killer to the "removable drive" following the on-screen instructions.
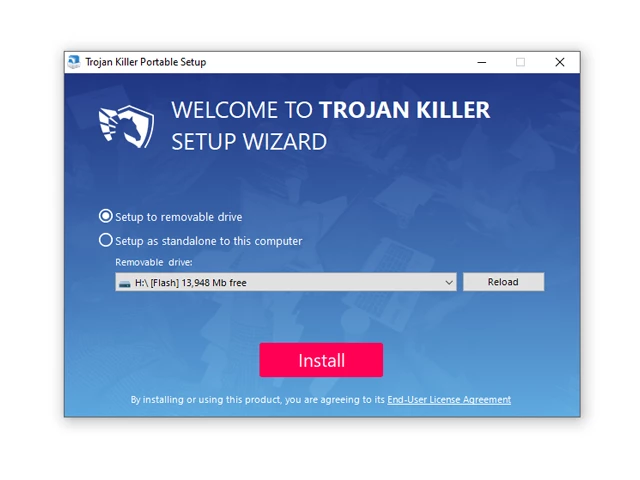
4. Once the installation is complete, launch Trojan Killer.
Step 2: Update Signature Databases:
5. After launching Trojan Killer, ensure that your computer is connected to the Internet.
6. Click "Update" icon to download the latest signature databases, which will ensure the tool can detect the most recent threats.
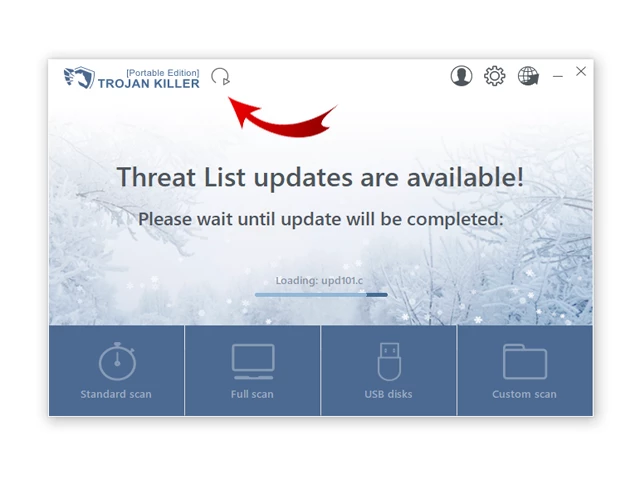
Step 3: Scan the Infected PC:
7. Safely eject the USB flash drive from the clean computer.
8. Boot the infected computer to the Safe Mode.
9. Insert the USB flash drive.
10. Run tk.exe
11. Once the program is open, click on "Full Scan" to begin the malware scanning process.
Step 4: Remove Found Threats:
12. After the scan is complete, Trojan Killer will display a list of detected threats.
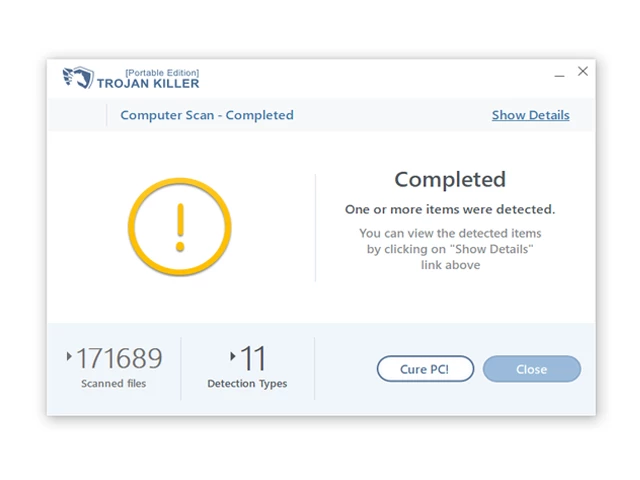
13. Click on "Cure PC!" to remove the identified malware from the infected PC.
14. Follow any additional on-screen prompts to complete the removal process.
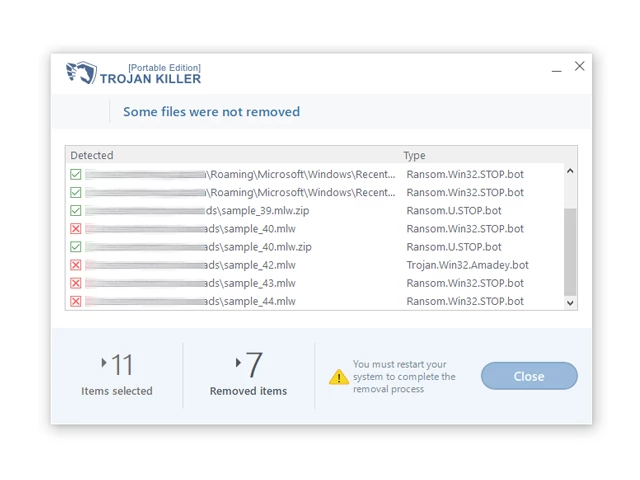
Step 5: Restart Your Computer:
15. Once the threats are removed, click on "Restart PC" to reboot your computer.
16. Remove the USB flash drive from the infected computer.
Congratulations on effectively removing Cur and the concealed threats from your computer! You can now have peace of mind, knowing that they won't resurface again. Thanks to Gridinsoft's capabilities and commitment to cybersecurity, your system is now protected.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Reformatting your storage device should only be considered as a last resort for removing Cur malware. Prior to taking such drastic action, it is advisable to perform a comprehensive scan using trustworthy antivirus or anti-malware software.
Malware poses a significant risk to the security and privacy of sensitive information, potentially leading to identity theft, financial loss, and unauthorized access to personal accounts. Furthermore, it can disrupt the normal operation of a system, causing performance issues, system crashes, and data corruption.
The purpose of Cur is to enable remote access and control of compromised devices. It allows threat actors to perform various malicious activities, such as unauthorized access, data theft, system manipulation, and disabling security measures, potentially causing significant harm to individuals and organizations.
Gridinsoft Anti-Malware has the ability to identify and eliminate most malware infections. Nevertheless, it is crucial to recognize that sophisticated malware can remain hidden deep within the system. Consequently, conducting a complete system scan is imperative to detect and eradicate malware.
How to Remove Cur Malware?
Name: Cur malware
Description: Cur malware is a formidable threat, primarily disseminated through targeted malspam campaigns. These deceptive emails often contain seemingly harmless archive file attachments, which house the malware. A notable feature is its use of the DLL side-loading technique to infiltrate systems. Once embedded, Cur malware exhibits a range of malicious actions, including data theft, privacy breaches, financial losses, and system compromises. Its custom-built, lightweight nature enables precision-targeted attacks, making it particularly dangerous for organizations and individuals. To combat Cur malware effectively, it's vital to implement stringent cybersecurity measures and educate users on recognizing its deceptive distribution methods.
Operating System: Windows
Application Category: Malware

