The Apache Software Foundation has patched a dangerous 0-day vulnerability in its HTTP web server. It is reported that the problem is already being actively exploited by hackers.
Apache HTTP Server is an open source, cross-platform web server that is extremely popular for its versatility, reliability, and free software. Thus, any vulnerability in a product has widespread consequences.The vulnerability has the identifier CVE-2021-41773 and affects only Apache web servers running version 2.4.49. Also, the vulnerable server must have the “require all denied” option disabled, but unfortunately this is the default configuration.
The bug occurs because of the way Apache performs the conversion of various URL path schemes (a process called URI normalization). The experts explain that the vulnerability allows attackers to carry out a path traversal attack by matching URLs to files outside the expected document root. As a result, such an attack can lead to leakage of CGI scripts and more.
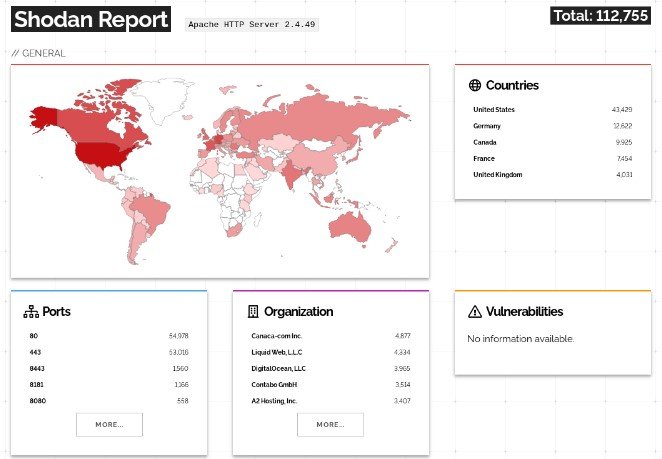
Also, the publication Bleeping Computer notes that a search with Shodan reveals over 100,000 installations of Apache HTTP Server 2.4.49 on the network, many of which may be vulnerable to a fresh bug.
Information security specialist Ash discovered attacks that are already abusing this error, together with the cPanel team, who reported the problem to the Apache developers.
A few hours after the release of version 2.4.50, a number of researchers were able to reproduce the vulnerability and have already published several experimental exploits on Twitter and GitHub.
Let me remind you that we also reported that 0-day vulnerability in Microsoft MHTML is exploited to attack Office 365 users.