RDStealer, a data-stealing malware, utilizes the Go programming language. This malware chain incorporates the Logutil backdoor, which establishes a system “backdoor” to advance the infection. Logutil, also developed using Go, is a cross-platform malware capable of infecting systems running Windows, Linux, and VMware ESXi.
RDStealer focus on various sensitive data types, but what sets this campaign apart is its ability to monitor and infect RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) clients. Campaigns that spread RDStealer have been active since early 2022, indicating a highly sophisticated operation. The overall style of execution allow us to presume it is a state-sponsored threat actor. While it is challenging to pinpoint the exact origin, the campaign’s targets align with Chinese interests.
The malware’s author is not new and first appeared in 2020. Earlier attacks utilized AsyncRAT and Cobalt Strike, but later shifted to customized malware like RDStealer and Logutil.
RDStealer Overview
RDStealer campaigns exhibit a high level of sophistication, employing several techniques to avoid detection on compromised machines. This includes concealing the malware in folders that often bypass security solutions. For instance, an analysis of a Dell device infected with RDStealer revealed the malware in the following folders:
- %WinDir%\System32\
- %WinDir%\System32\wbem\
- %WinDir%\security\database\
- %PROGRAM_FILES%\f-secure\psb\diagnostics
- %PROGRAM_FILES_x86%\dell\commandupdate\
- %PROGRAM_FILES%\dell\md storage software\md configuration utility\
The selection of folders may vary, with the aim of evading detection by security tools. As mentioned earlier, RDStealer is a data-stealing malware that extracts and exfiltrates information from infected machines. This malicious program scans systems for various types of data and exfiltrates it from specific folders and applications.
The targeted data includes, but is not limited to, browsing history and saved login credentials from the Google Chrome browser, mRemoteNG (remote connections manager), MobaXterm (remote desktop client), and KeePass (password manager). In addition, RDStealer possesses keylogging capabilities to record keystrokes and can extract clipboard content (data copied to the copy/paste buffer).
Moreover, the malware’s reach extends beyond the initial infection, as it can spread to other devices connected through RDP. By monitoring incoming RDP connections, the infection can be transmitted to remote machines, especially if client drive mapping is enabled. Drive mapping is often enabled in large networks for tasks like file sharing between servers.
If conditions are favorable, the Logutil backdoor infects the remotely connected device and subsequently installs RDStealer. It’s worth noting that malware developers frequently enhance their creations, streamlining processes and adding additional functionalities. Therefore, future versions of RDStealer may possess different capabilities.
| Name | RDStealer |
| Damage | Severe privacy issues, financial losses, and the risk of identity theft. It can lead to the unauthorized extraction and exfiltration of sensitive data from infected machines, posing a significant threat to individuals and organizations. The malware’s capabilities, such as capturing login credentials and browsing history, can compromise personal and confidential information, potentially resulting in financial harm and the misuse of sensitive data. |
| Fix Tool | See If Your System Has Been Affected by RDStealer Virus |
Stealing from Remote Desktop
The Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a proprietary Microsoft protocol that enables users to connect to Windows desktops remotely and interact with them as if they were physically present. This functionality is particularly beneficial for tasks such as remote work, technical support, system administration, and server management.
However, it is important to be aware that internet-exposed RDP servers are a sweet target for threat actors. The reason behind this is that gaining access to an RDP server provides attackers with a potential entry point into a corporate network. Once inside, they can move laterally, spreading their influence and potentially conducting data theft and ransomware attacks.
One of the features included in the Remote Desktop Protocol is ‘device redirection.’ This feature allows users to connect their local drives, printers, clipboard, ports, and other devices to the remote host, making them accessible within the remote desktop session. When using device redirection in a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) session, you can access the shared resources on your local machine through a special network share called ‘\\tsclient’ (terminal server client).
This ‘\\tsclient’ network share allows you to map the shared resources to drive letters within your RDP connection. For instance, if you have shared your local C:\ drive via device redirection, you will be able to access it as the ‘\\tsclient\c’ share within the RDP session. This enables you to access files stored on your local machine directly from the remote Windows desktop. By leveraging this feature, users can seamlessly work with files and data that resides on local drives while connected to a remote desktop session. This, obviously, enhances productivity and convenience.
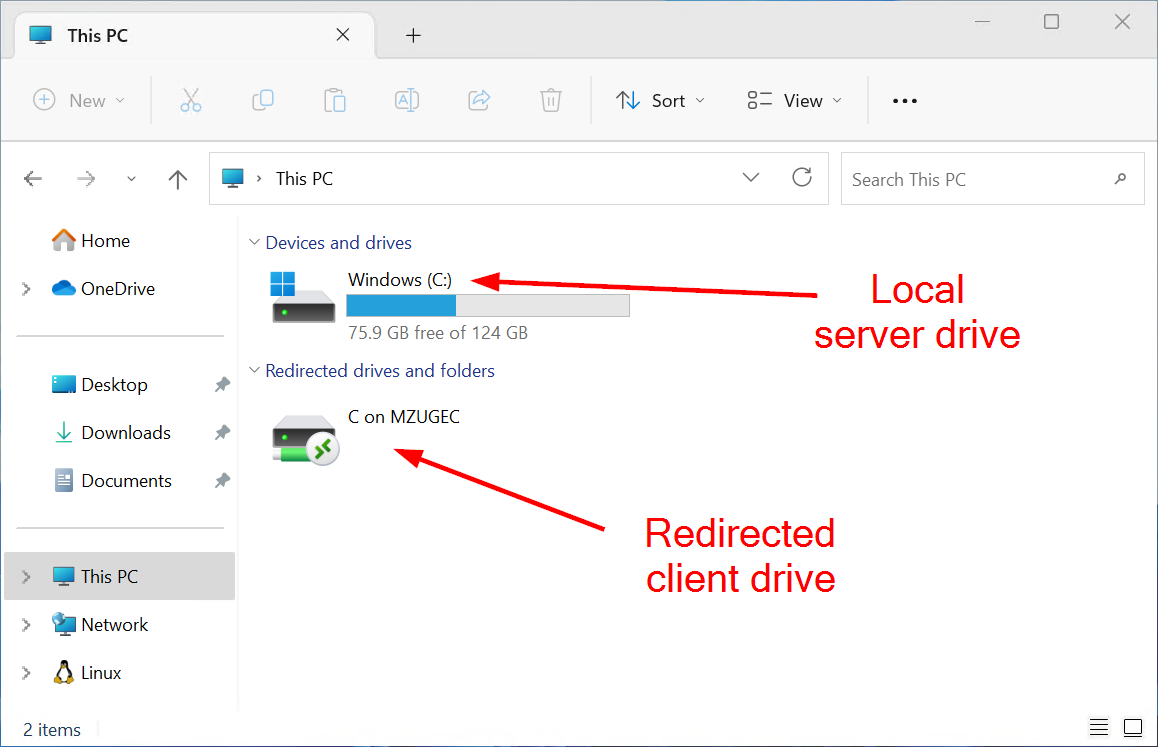
Client Drive Mapping is a feature in RDP that allows to display the drives of the local machine (the computer initiating the RDP session) within the remote desktop session.
RDStealer is a sophisticated malware consisting of five modules designed for malicious purposes. These modules include a keylogger, a persistence establisher, a data theft and exfiltration staging module, a clipboard content capturing tool, and a module controlling encryption/decryption functions, logging, and file manipulation utilities.
Upon execution, RDStealer enters an infinite loop where it continuously calls the “diskMounted” function. This function checks for the presence of C, D, E, F, G, or H drives on the \\tsclient network shares. If it finds any of these drives, the malware notifies its command and control (C2) server and proceeds to exfiltrate data from the connected Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) client.
It is worth noting that RDStealer targets specific locations and file extensions on the C:\ drives, including the KeePass password database, SSH private keys, Bitvise SSH client, MobaXterm, mRemoteNG connections, and more. This indicates that the attackers behind RDStealer are primarily interested in obtaining credentials that can be used for lateral movement within a network.
In summary, high-risk malware infections like Logutil and RDStealer can lead to severe privacy issues, financial losses, and identity theft. When targeted at highly sensitive entities such as institutions, organizations, and governmental bodies, the consequences can be even more significant.
Examples of Stealer-type malware
Our recent research has covered numerous stealers, including FadeStealer, RustyStealer, Mystic Stealer, and Skuld.
Information-stealing software can focus on specific details or a wide range of data. Additionally, malicious functionalities are not mutually exclusive, allowing malware to possess different combinations of capabilities.
Regardless of the operating mechanisms of malicious software, its presence on a system jeopardizes device integrity and user safety. Therefore, immediate elimination of all threats upon detection is crucial.
How did RDStealer infiltrate my computer?
The precise method of RDStealer infiltration remains unknown. Generally, malware is propagated through phishing and social engineering techniques. In sophisticated campaigns targeting specific entities, such as RDStealer, these tactics are often tailored for the intended targets.
Malicious software is typically disguised as or bundled with ordinary program/media files. These files can be executables (.exe, .run, etc.), archives (ZIP, RAR, etc.), documents (Microsoft Office, Microsoft OneNote, PDF, etc.), JavaScript, and more. Once a malicious file is executed, run, or opened, the infection chain is triggered.
The most commonly used methods for distributing malware include malicious attachments/links in spam emails, drive-by (stealthy/deceptive) downloads, suspicious download channels (freeware and free file-hosting websites, P2P sharing networks, etc.), illegal software activation tools, fake updates, online scams, and malvertising. Furthermore, certain malicious programs can self-propagate through local networks and removable storage devices (external hard drives, USB flash drives, etc.). RDStealer is capable of spreading to RDP-connected devices.
How to remove the RDStealer from my PC?
RDStealer malware is incredibly difficult to delete by hand. It puts its files in a variety of places throughout the disk, and can recover itself from one of the elements. Moreover, numerous alterations in the registry, networking configurations and also Group Policies are pretty hard to locate and revert to the initial. It is far better to make use of a specific program – exactly, an anti-malware program. GridinSoft Anti-Malware will fit the most ideal for malware elimination objectives.
Why GridinSoft Anti-Malware? It is pretty light-weight and has its detection databases updated nearly every hour. Additionally, it does not have such bugs and exploits as Microsoft Defender does. The combination of these aspects makes GridinSoft Anti-Malware ideal for getting rid of malware of any type.
Remove RDStealer with Gridinsoft Anti-Malware
We have also been using this software on our systems ever since, and it has always been successful in detecting viruses. It has blocked the most common stealers as shown from our tests with the software, and we assure you that it can remove RDStealer as well as other malware hiding on your computer.
To use Gridinsoft for remove malicious threats, follow the steps below:
1. Begin by downloading Gridinsoft Anti-Malware, accessible via the blue button below or directly from the official website gridinsoft.com.
2.Once the Gridinsoft setup file (setup-gridinsoft-fix.exe) is downloaded, execute it by clicking on the file.
3.Follow the installation setup wizard's instructions diligently.
4. Access the "Scan Tab" on the application's start screen and launch a comprehensive "Full Scan" to examine your entire computer. This inclusive scan encompasses the memory, startup items, the registry, services, drivers, and all files, ensuring that it detects malware hidden in all possible locations.
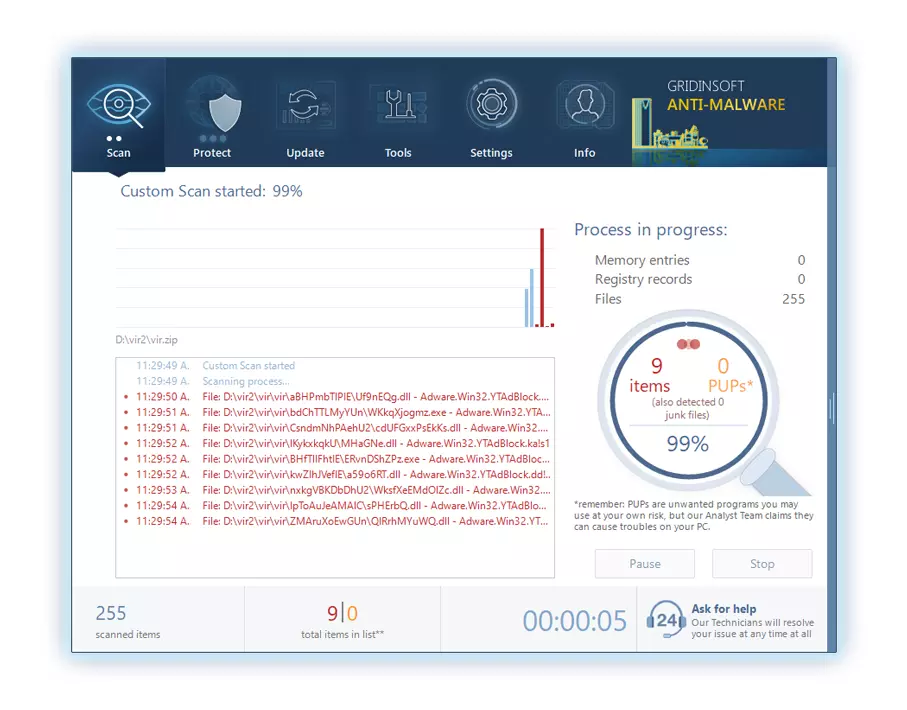
Be patient, as the scan duration depends on the number of files and your computer's hardware capabilities. Use this time to relax or attend to other tasks.
5. Upon completion, Anti-Malware will present a detailed report containing all the detected malicious items and threats on your PC.
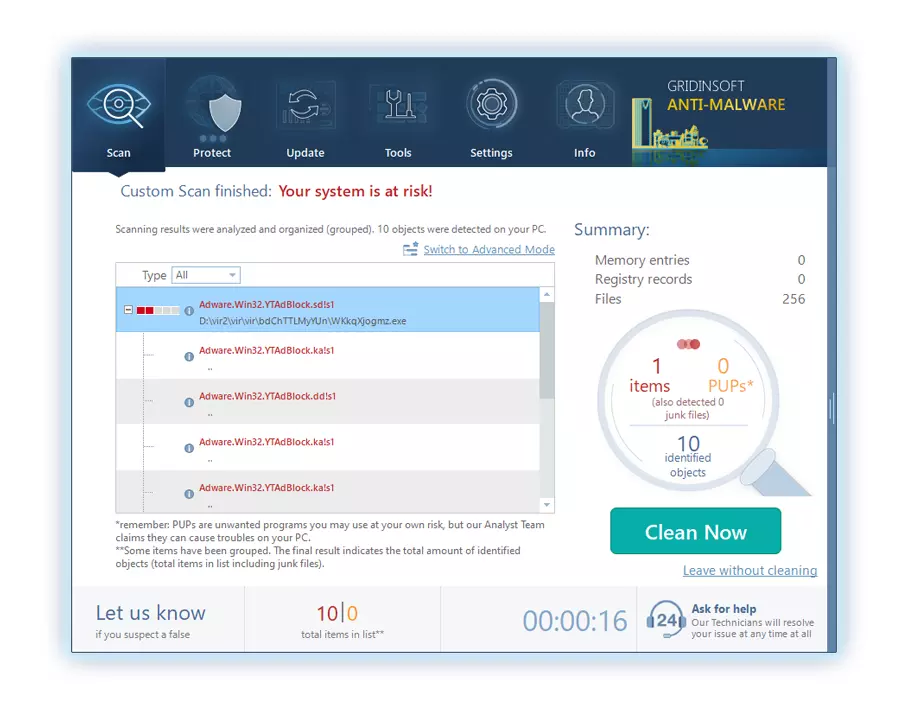
6. Select all the identified items from the report and confidently click the "Clean Now" button. This action will safely remove the malicious files from your computer, transferring them to the secure quarantine zone of the anti-malware program to prevent any further harmful actions.
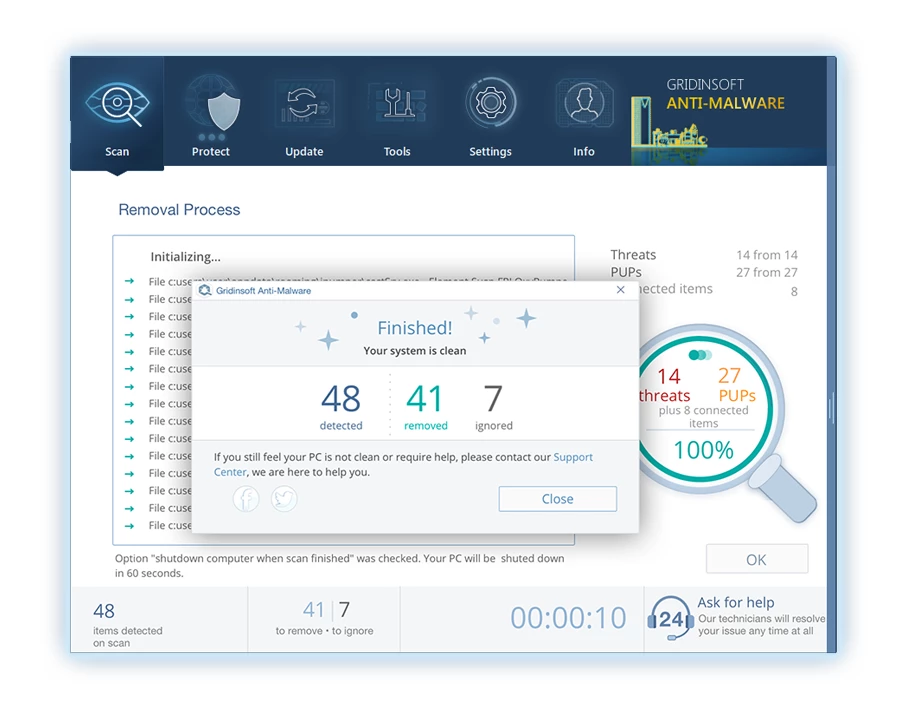
8. If prompted, restart your computer to finalize the full system scan procedure. This step is crucial to ensure thorough removal of any remaining threats. After the restart, Gridinsoft Anti-Malware will open and display a message confirming the completion of the scan.
Remember Gridinsoft offers a 6-day free trial. This means you can take advantage of the trial period at no cost to experience the full benefits of the software and prevent any future malware infections on your system. Embrace this opportunity to fortify your computer's security without any financial commitment.
Trojan Killer for “RDStealer” removal on locked PC
In situations where it becomes impossible to download antivirus applications directly onto the infected computer due to malware blocking access to websites, an alternative solution is to utilize the Trojan Killer application.
There is a really little number of security tools that are able to be set up on the USB drives, and antiviruses that can do so in most cases require to obtain quite an expensive license. For this instance, I can recommend you to use another solution of GridinSoft - Trojan Killer Portable. It has a 14-days cost-free trial mode that offers the entire features of the paid version. This term will definitely be 100% enough to wipe malware out.
Trojan Killer is a valuable tool in your cybersecurity arsenal, helping you to effectively remove malware from infected computers. Now, we will walk you through the process of using Trojan Killer from a USB flash drive to scan and remove malware on an infected PC. Remember, always obtain permission to scan and remove malware from a computer that you do not own.
Step 1: Download & Install Trojan Killer on a Clean Computer:
1. Go to the official GridinSoft website (gridinsoft.com) and download Trojan Killer to a computer that is not infected.
2. Insert a USB flash drive into this computer.
3. Install Trojan Killer to the "removable drive" following the on-screen instructions.
4. Once the installation is complete, launch Trojan Killer.
Step 2: Update Signature Databases:
5. After launching Trojan Killer, ensure that your computer is connected to the Internet.
6. Click "Update" icon to download the latest signature databases, which will ensure the tool can detect the most recent threats.
Step 3: Scan the Infected PC:
7. Safely eject the USB flash drive from the clean computer.
8. Boot the infected computer to the Safe Mode.
9. Insert the USB flash drive.
10. Run tk.exe
11. Once the program is open, click on "Full Scan" to begin the malware scanning process.
Step 4: Remove Found Threats:
12. After the scan is complete, Trojan Killer will display a list of detected threats.
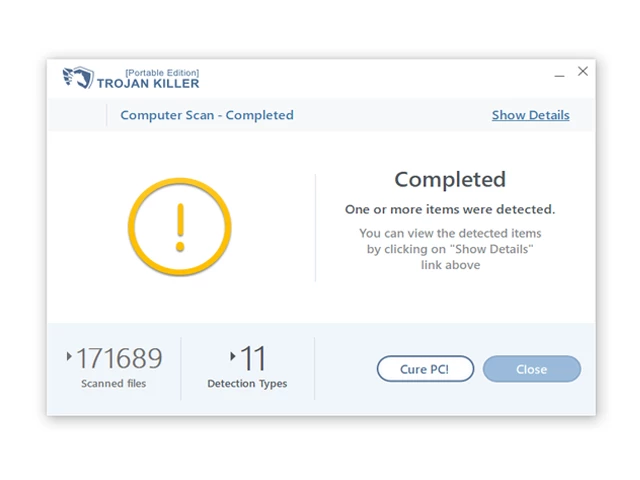
13. Click on "Cure PC!" to remove the identified malware from the infected PC.
14. Follow any additional on-screen prompts to complete the removal process.
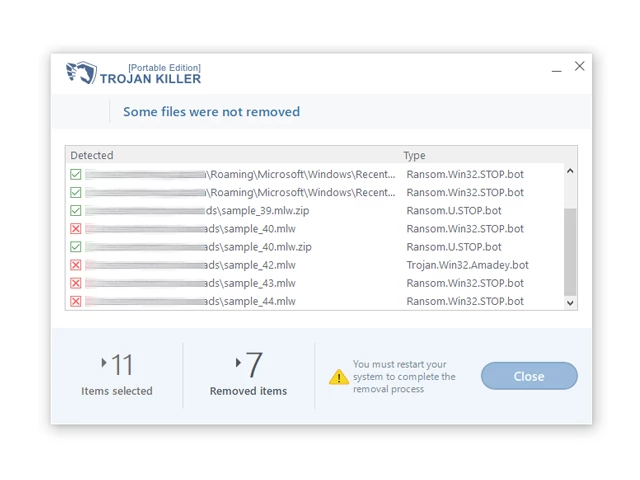
Step 5: Restart Your Computer:
15. Once the threats are removed, click on "Restart PC" to reboot your computer.
16. Remove the USB flash drive from the infected computer.
Congratulations on effectively removing RDStealer and the concealed threats from your computer! You can now have peace of mind, knowing that they won't resurface again. Thanks to Gridinsoft's capabilities and commitment to cybersecurity, your system is now protected.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
RDStealer is a data-stealing malware designed to extract sensitive information from infected machines. It operates as a stealer and can infiltrate various systems.
The exact method of RDStealer’s infiltration is unknown. However, malware typically spreads through phishing, social engineering techniques, and disguising itself within ordinary files or programs.
RDStealer can infect systems running Windows, Linux, and VMware ESXi due to its cross-platform capabilities.
RDStealer targets a range of sensitive data, including browsing history, saved login credentials, and information from applications such as Google Chrome, mRemoteNG, MobaXterm, and KeePass. It also has keylogging capabilities and can extract clipboard content.
To protect against RDStealer and similar malware, it is important to employ robust security measures. This includes keeping your operating system and applications up to date, using reputable antivirus software, avoiding suspicious downloads and email attachments, and practicing safe browsing habits.
Yes, RDStealer has the ability to spread to other devices connected through Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) if client drive mapping is enabled. This can pose a risk to large networks with drive mapping enabled for file sharing between servers.
RDStealer can lead to severe privacy issues, financial losses, and identity theft. If targeted at highly sensitive entities like institutions or governmental bodies, the consequences can be even more significant.
Malware developers often enhance their creations over time. Future versions of RDStealer could potentially have different capabilities, streamlined processes, or additional functionalities.
Detecting and removing RDStealer requires robust antivirus software capable of identifying and eliminating the malware. Conducting full system scans, employing intrusion detection systems, and promptly addressing any suspicious activity can help in the detection and removal process..
If you suspect an RDStealer infection, it is crucial to isolate the affected system from the network, immediately run a comprehensive antivirus scan, and seek assistance from IT professionals to ensure proper mitigation and remediation of the threat.
What is RDStealer Malware?
Name: RDStealer
Description: RDStealer is a type of malware that steals data from computers. It's called a "stealer" because it primarily aims to gather and send data from your computer to someone else. This malware can target various information types, like browsing history, login details, and data from specific software programs. RDStealer can also record keystrokes and copy/paste information. It can infect other devices connected to your computer if they're connected through Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). This malware can infect computers running Windows, Linux, and VMware ESXi. RDStealer often uses phishing and social engineering techniques, and it can look like a legitimate file or program.
Operating System: Windows
Application Category: Malware

