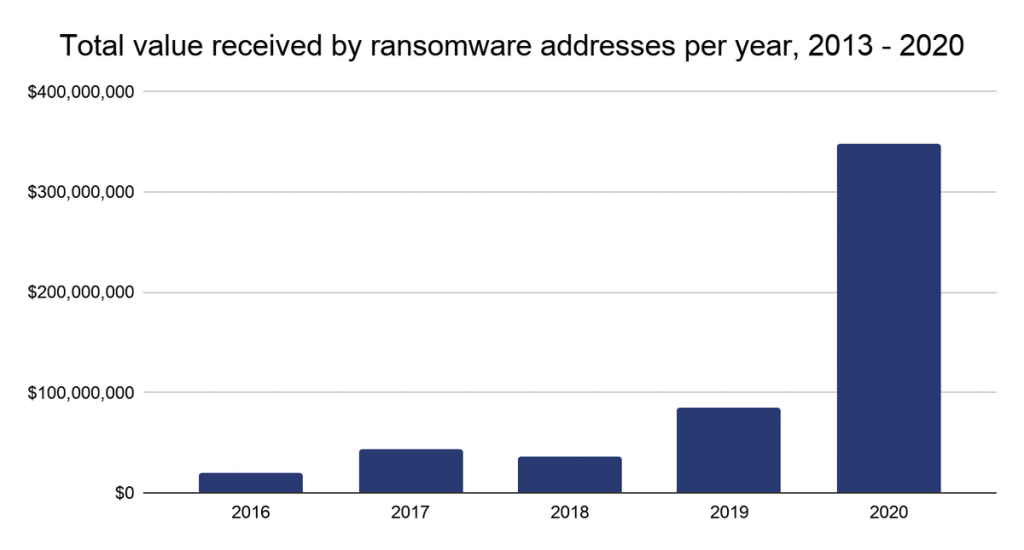
According to a study by the analytical company Chainalysis, the earnings of ransomware operators consisted more than $350,000,000 in 2020. These disappointing statistics were compiled by observing bitcoin address transactions associated with attacks by various ransomware.
While Chainalysis has one of the most comprehensive datasets of cryptocurrency-related crime, the company points out that this estimate is likely only a lower bound on the sums that is earned by hackers.In 2020, ransomware attacks accounted for only 7% of the total number of crimes related to cryptocurrencies, but the total amount of ransom payments that were paid increased by 311% compared to 2019.
Analysts explain this in a very simple way: the number of ransomware is still growing, and not only new threats have appeared on the market, whose operators demand huge sums from the affected companies, but several previously known malwares have sharply increased their activity and profits.
According to Chainalysis, hack groups such as Ryuk, Maze (no longer active), Doppelpaymer, Netwalker (recently the authorities attempted to liquidate it), Conti and REvil (aka Sodinokibi) boasted to have conducted the most profitable operations of last year. Snatch, Defray777 (RansomExx) and Dharma ransomware also brought millions of dollars to their operators.
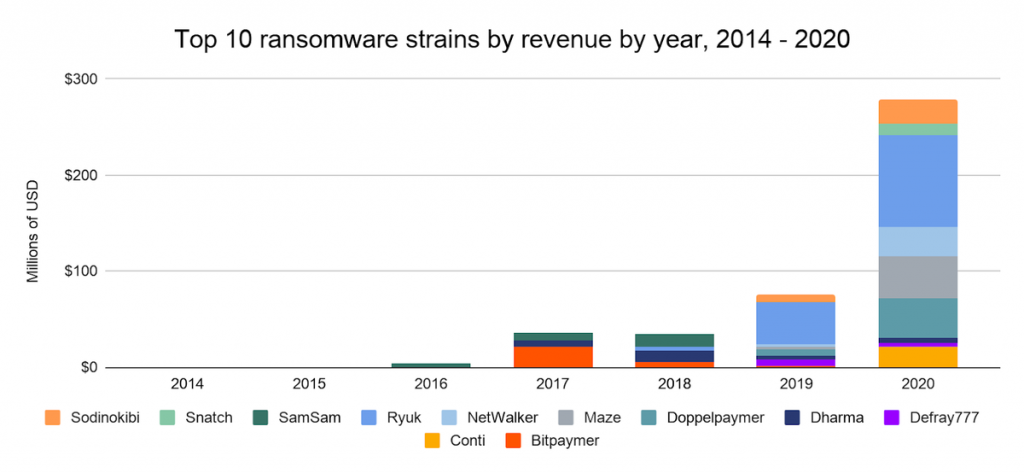
Based on information about how victims paid ransoms, as well as how profits in the RaaS (Ransomware-as-a-Service, Ransomware-as-a-Service) sphere grew and fell, experts conclude that, in general, the ransomware scene has far fewer attackers than originally intended. The fact is that criminals are constantly switching from one RaaS to another.
With regard to laundering the money received, hackers still use special mixing services for this, and then forward the cryptocurrency to both legitimate and well-known exchangers and to high-risk services for converting to fiat.
For example, the Chainalysis report says that 82% of all ransomware “proceeds” in 2020 went through just five exchange portals. In theory, in the future, law enforcement agencies can put pressure on these exchanges and thereby affect the work of many ransomware.
Let me remind you that the ransom amount in the ransomware attacks decreased by one third due to companies’ refuse to pay.
