QuiteRAT, a Remote Access Trojan, exploits methods adapted for each victim’s context. Its origins are tied to the Lazarus Group. Utilizing Qt Framework, it collects device data and interacts with a Command and Control server.
It manipulates files and can trigger chain infections. Although distribution methods remain undisclosed, it commonly employs phishing and diverse tactics like malicious attachments, deceptive downloads, and scams. Vigilance against these methods is crucial to thwart its infiltration and the potential for compromised systems.
QuiteRAT Overview
QuiteRAT is identified as a Remote Access Trojan (RAT), constituting malicious software. Its primary purpose is to facilitate remote access and control over compromised systems. Emerging in early 2023, QuiteRAT has been attributed to the Lazarus Group, a threat entity reportedly supported by North Korea. This RAT was notably utilized in an assault against a pivotal Internet infrastructure provider in Europe.
| Name | QuiteRAT |
| Threat Type | Trojan, RAT, spyware |
| Detection | Trojan:Win32/Malgent!MSR (Microsoft) |
| Similar Behavior | FateGrab, Enigma Stealer |
| Damage | Stolen passwords and banking information, identity theft, the victim’s computer added to a botnet. |
| Fix Tool | See If Your System Has Been Affected by QuiteRAT Virus |
Technical Analysis
QuiteRAT shares numerous traits and functionalities with MagicRAT, a fellow malware linked to the Lazarus Group. While both utilize the Qt Framework, QuiteRAT notably maintains a much smaller file size, ranging from 4 to 5 MB. This blend of characteristics, combined with additional intricate mechanisms adopted by QuiteRAT, contributes to the complexity of its analysis.
Upon infiltrating a system, the RAT promptly commences the collection of pertinent device data, encompassing details like device name, MAC address, active user’s username, and IP address. This compiled information is then dispatched to the attackers’ Command and Control (C&C) server, awaiting subsequent directives. The response can encompass command codes or Windows commands designated for execution via a child cmd.exe process.
While QuiteRAT incorporates persistence strategies, these mechanisms are external to the malware’s core architecture. The RAT showcases the ability to manipulate victim files, encompassing actions like renaming, relocating, and deletion. Noteworthy is its potential for initiating chain infections. While theoretically capable of introducing various malware types (trojans, ransomware, cryptocurrency miners), such programs generally adhere to defined operational boundaries.
Crucially, malware developers frequently refine their creations and methodologies. This implies potential forthcoming iterations of QuiteRAT might introduce supplementary or altered features. In essence, the presence of software akin to QuiteRAT on systems entails risks ranging from multiple infections and data loss to severe privacy breaches, financial repercussions, and identity theft. Notably, attacks targeting exceptionally sensitive targets accentuate the gravity of the threat.
Spreading Methods
The specific dissemination tactics employed by QuiteRAT remain undisclosed. Recognizing that targeted attacks frequently tailor their methods to individual victims is essential. Generally, cybercriminals propagate malware using phishing and social engineering strategies. The malevolent files may take the form of executables, archives, documents, JavaScript, and more.
Prominent mechanisms for malware dispersion encompass inconspicuous “drive-by” downloads, malevolent attachments and links within spam communications (emails, DMs/PMs, SMSes), untrustworthy download sources (freeware websites, third-party platforms, P2P networks), online scams, malvertising, counterfeit software activation tools (“cracks”), and counterfeit updates. Specific malicious programs can propagate autonomously through local networks and removable storage devices (external hard drives, USB flash drives, etc.).
Remove QuiteRAT with Gridinsoft Anti-Malware
We have also been using this software on our systems ever since, and it has always been successful in detecting viruses. It has blocked the most common Stealers as shown from our tests with the software, and we assure you that it can remove QuiteRAT as well as other malware hiding on your computer.
To use Gridinsoft for remove malicious threats, follow the steps below:
1. Begin by downloading Gridinsoft Anti-Malware, accessible via the blue button below or directly from the official website gridinsoft.com.
2.Once the Gridinsoft setup file (setup-gridinsoft-fix.exe) is downloaded, execute it by clicking on the file.
3.Follow the installation setup wizard's instructions diligently.
4. Access the "Scan Tab" on the application's start screen and launch a comprehensive "Full Scan" to examine your entire computer. This inclusive scan encompasses the memory, startup items, the registry, services, drivers, and all files, ensuring that it detects malware hidden in all possible locations.
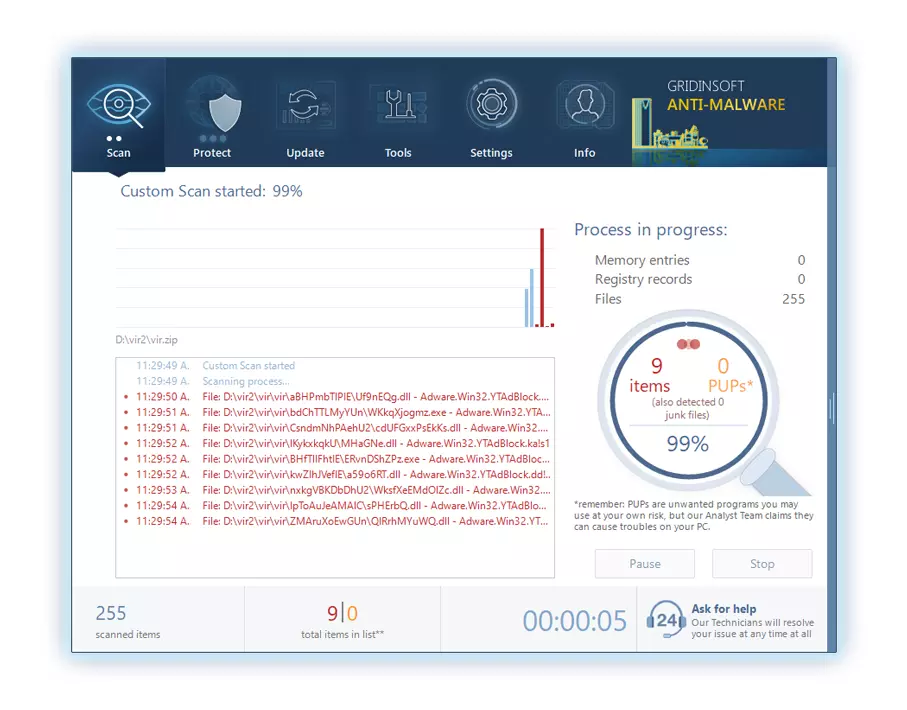
Be patient, as the scan duration depends on the number of files and your computer's hardware capabilities. Use this time to relax or attend to other tasks.
5. Upon completion, Anti-Malware will present a detailed report containing all the detected malicious items and threats on your PC.
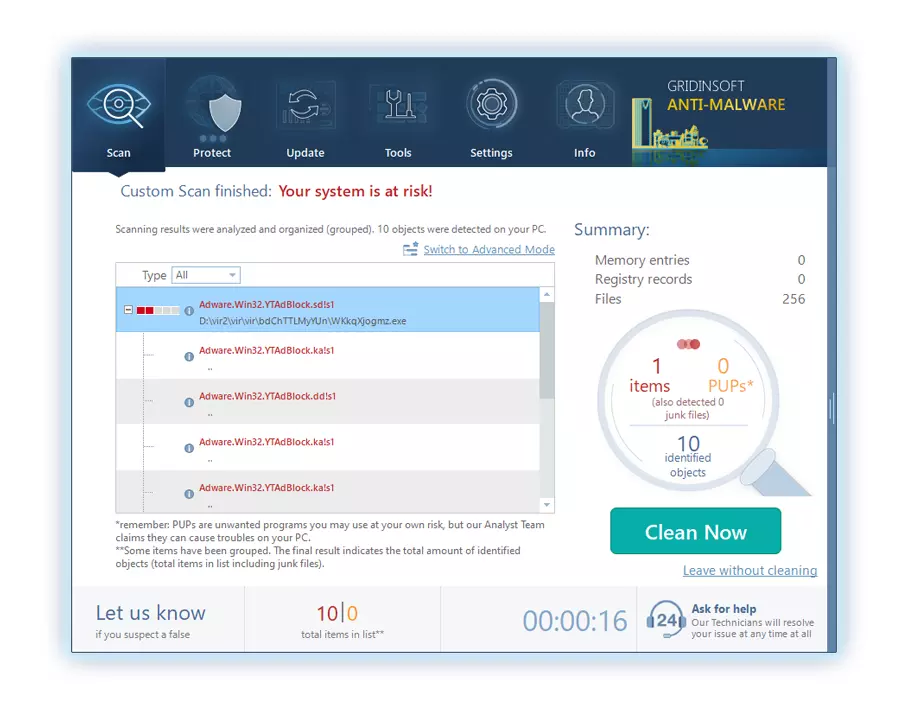
6. Select all the identified items from the report and confidently click the "Clean Now" button. This action will safely remove the malicious files from your computer, transferring them to the secure quarantine zone of the anti-malware program to prevent any further harmful actions.
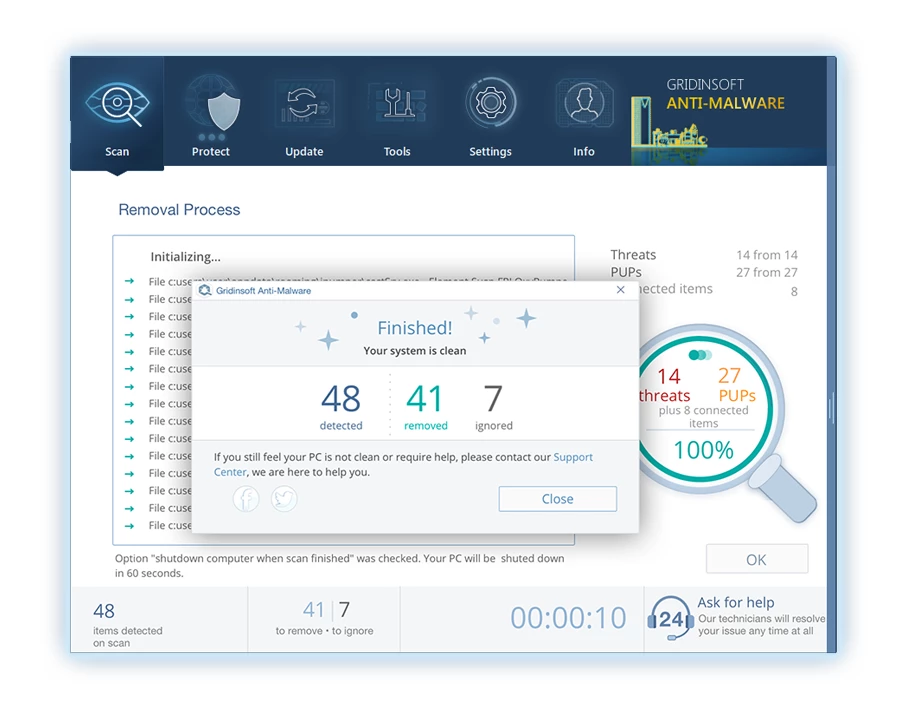
8. If prompted, restart your computer to finalize the full system scan procedure. This step is crucial to ensure thorough removal of any remaining threats. After the restart, Gridinsoft Anti-Malware will open and display a message confirming the completion of the scan.
Remember Gridinsoft offers a 6-day free trial. This means you can take advantage of the trial period at no cost to experience the full benefits of the software and prevent any future malware infections on your system. Embrace this opportunity to fortify your computer's security without any financial commitment.
Trojan Killer for “QuiteRAT ” removal on locked PC
In situations where it becomes impossible to download antivirus applications directly onto the infected computer due to malware blocking access to websites, an alternative solution is to utilize the Trojan Killer application.
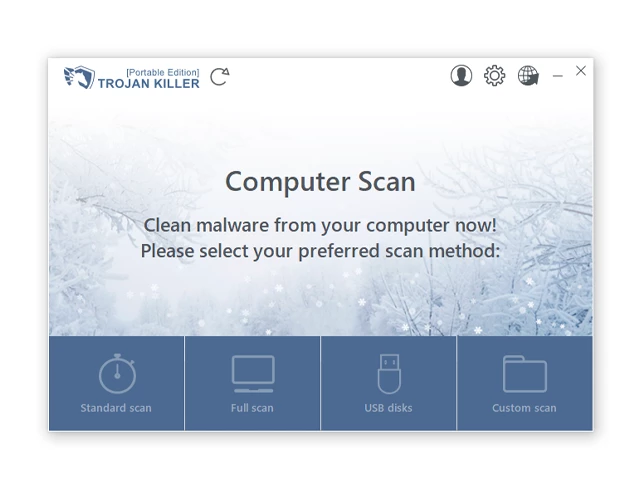
There is a really little number of security tools that are able to be set up on the USB drives, and antiviruses that can do so in most cases require to obtain quite an expensive license. For this instance, I can recommend you to use another solution of GridinSoft - Trojan Killer Portable. It has a 14-days cost-free trial mode that offers the entire features of the paid version. This term will definitely be 100% enough to wipe malware out.
Trojan Killer is a valuable tool in your cybersecurity arsenal, helping you to effectively remove malware from infected computers. Now, we will walk you through the process of using Trojan Killer from a USB flash drive to scan and remove malware on an infected PC. Remember, always obtain permission to scan and remove malware from a computer that you do not own.
Step 1: Download & Install Trojan Killer on a Clean Computer:
1. Go to the official GridinSoft website (gridinsoft.com) and download Trojan Killer to a computer that is not infected.
2. Insert a USB flash drive into this computer.
3. Install Trojan Killer to the "removable drive" following the on-screen instructions.
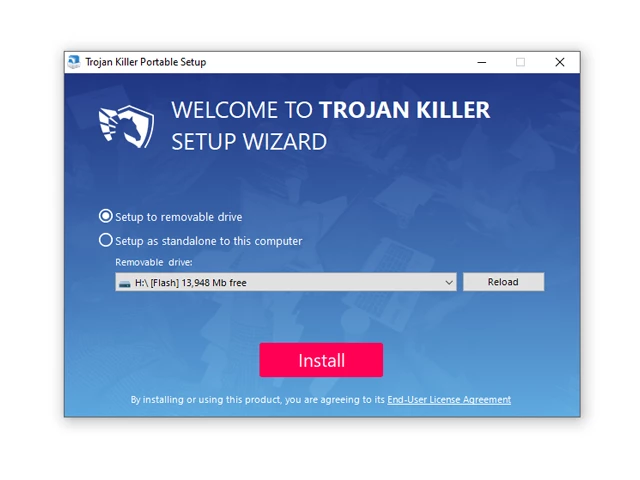
4. Once the installation is complete, launch Trojan Killer.
Step 2: Update Signature Databases:
5. After launching Trojan Killer, ensure that your computer is connected to the Internet.
6. Click "Update" icon to download the latest signature databases, which will ensure the tool can detect the most recent threats.
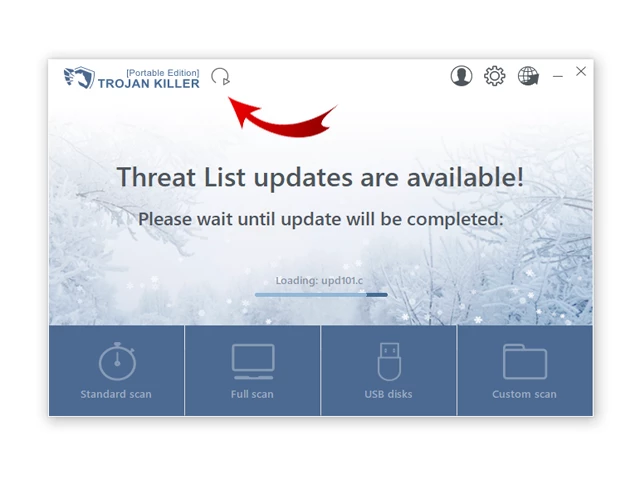
Step 3: Scan the Infected PC:
7. Safely eject the USB flash drive from the clean computer.
8. Boot the infected computer to the Safe Mode.
9. Insert the USB flash drive.
10. Run tk.exe
11. Once the program is open, click on "Full Scan" to begin the malware scanning process.
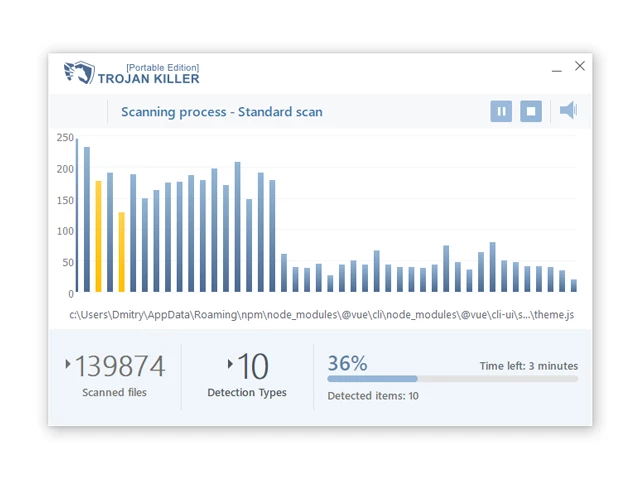
Step 4: Remove Found Threats:
12. After the scan is complete, Trojan Killer will display a list of detected threats.
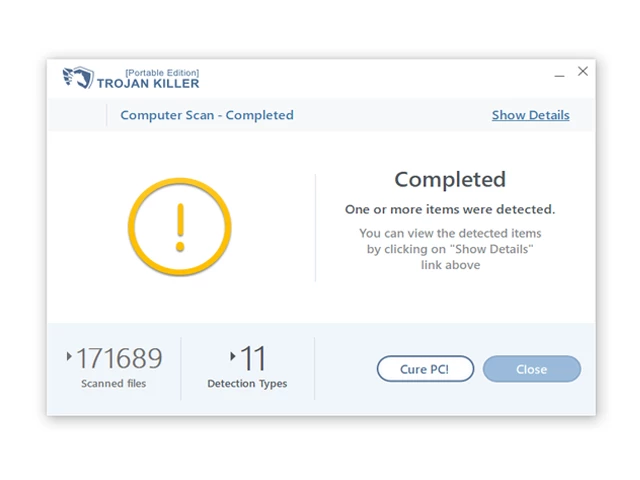
13. Click on "Cure PC!" to remove the identified malware from the infected PC.
14. Follow any additional on-screen prompts to complete the removal process.
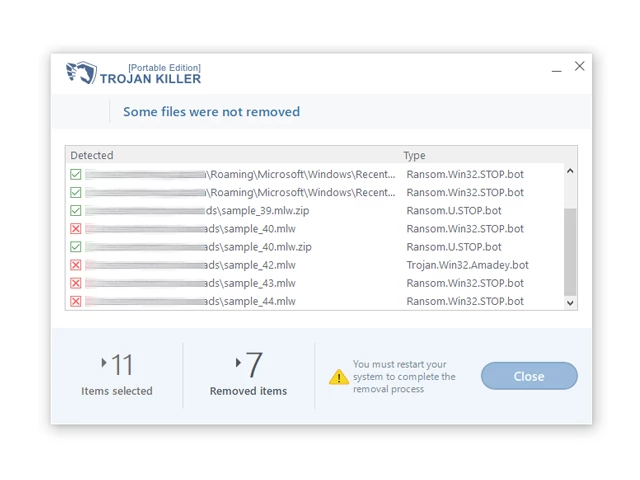
Step 5: Restart Your Computer:
15. Once the threats are removed, click on "Restart PC" to reboot your computer.
16. Remove the USB flash drive from the infected computer.
Congratulations on effectively removing QuiteRAT and the concealed threats from your computer! You can now have peace of mind, knowing that they won't resurface again. Thanks to Gridinsoft's capabilities and commitment to cybersecurity, your system is now protected.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Reformatting your storage device should only be considered as a last resort for removing QuiteRAT malware. Prior to taking such drastic action, it is advisable to perform a comprehensive scan using trustworthy antivirus or anti-malware software.
Malware poses a significant risk to the security and privacy of sensitive information, potentially leading to identity theft, financial loss, and unauthorized access to personal accounts. Furthermore, it can disrupt the normal operation of a system, causing performance issues, system crashes, and data corruption.
The purpose of QuiteRAT is to enable remote access and control of compromised devices. It allows threat actors to perform various malicious activities, such as unauthorized access, data theft, system manipulation, and disabling security measures, potentially causing significant harm to individuals and organizations.
Gridinsoft Anti-Malware has the ability to identify and eliminate most malware infections. Nevertheless, it is crucial to recognize that sophisticated malware can remain hidden deep within the system. Consequently, conducting a complete system scan is imperative to detect and eradicate malware.
How to Remove QuiteRAT Malware
Name: QuiteRAT
Description: QuiteRAT, a Remote Access Trojan, exploits methods adapted for each victim's context. Its origins are tied to the Lazarus Group. Utilizing Qt Framework, it collects device data and interacts with a Command and Control server. It manipulates files and can trigger chain infections. Although distribution methods remain undisclosed, it commonly employs phishing and diverse tactics like malicious attachments, deceptive downloads, and scams. Vigilance against these methods is crucial to thwart its infiltration and the potential for compromised systems.
Operating System: Windows
Application Category: Malware

