Host Process for Windows Tasks is a very important system element that handles an important function which is required for the system to perform properly. In this post, you will see the explanation of the functions of this process, as well as the troubleshooting guide in case it consumes too much system resources.
The purpose of Host Process for Windows Tasks
That process serves as a “frame” for a massive construction of internal system services. Host Process for Windows Tasks is used to provide the access to needed DLLs to Windows services at the moment of system launch, and every time when a service launches in the process of computer usage. For every service group, the separate Host Process will be generated.
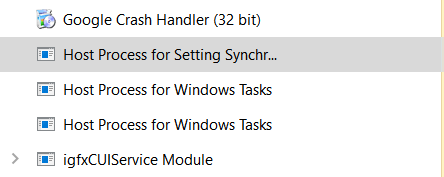
Every Host Process from this list is responsible for its own group of tasks
Host Process for Windows Tasks is launched together with the operating system, since its functions are needed to make the system stable and usable. Its tasks are related to Service Host process – another Windows process, that manages the correct distribution of access to DLLs for all apps that are present in the system.1
Can I stop this process?
No way. It is deeply integrated with the operating system, and you will see the “access denied” error even if you have an administrator account. In my opinion, there is no need to stop this process, because it consumes very little amount of CPU/RAM resources.
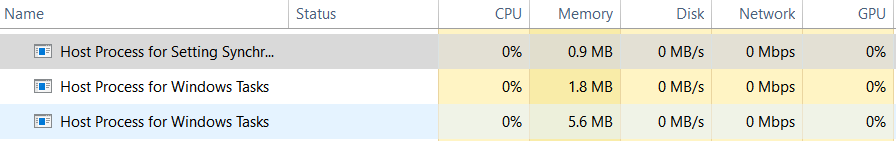
Normal consumption of Host Process for Windows Tasks
However, the instances when its consumption rises to 20-30% are usually an indicator of possible hardware failure or driver issues. Because of the high amount of read/write operation, that service is sensible to disk drive problems. Try to find and install a new driver from the official website of the manufacturer – it may be especially useful when you have a 2TB+ disk drive on your computer.
The times when Windows processes may be disabled to increase the system performance have passed long ago. When Windows XP was the last actual OS version, computers were quite weak, and their upgrade was quite expensive, disabling several services could really make your PC faster without any significant problems. Nowadays, such tricks can make things even worse.
Is Host Process for Windows Tasks a virus?
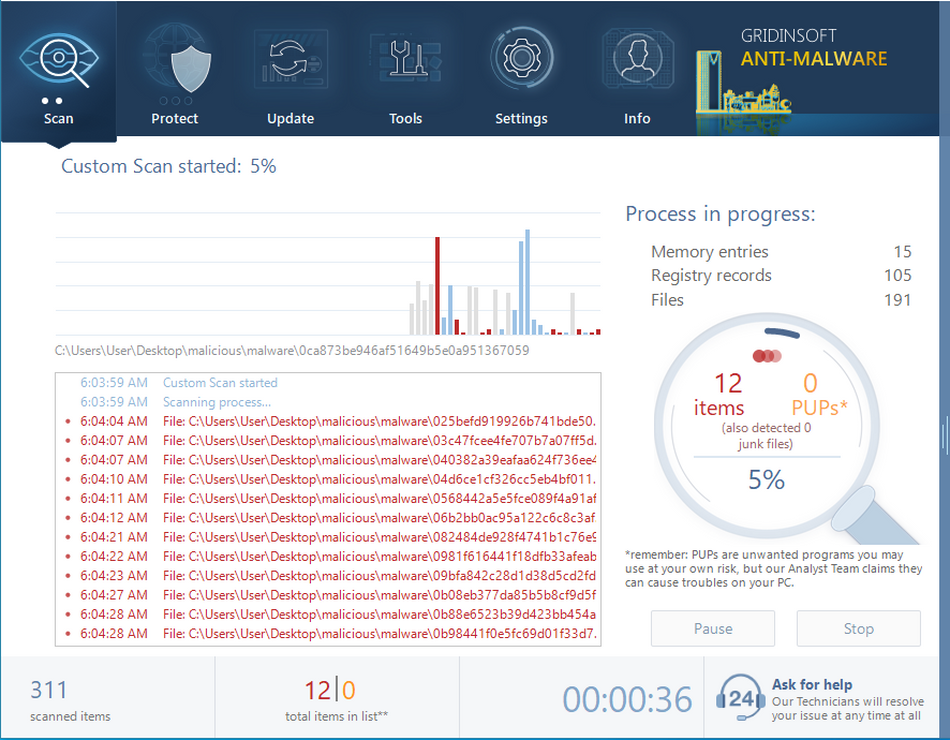
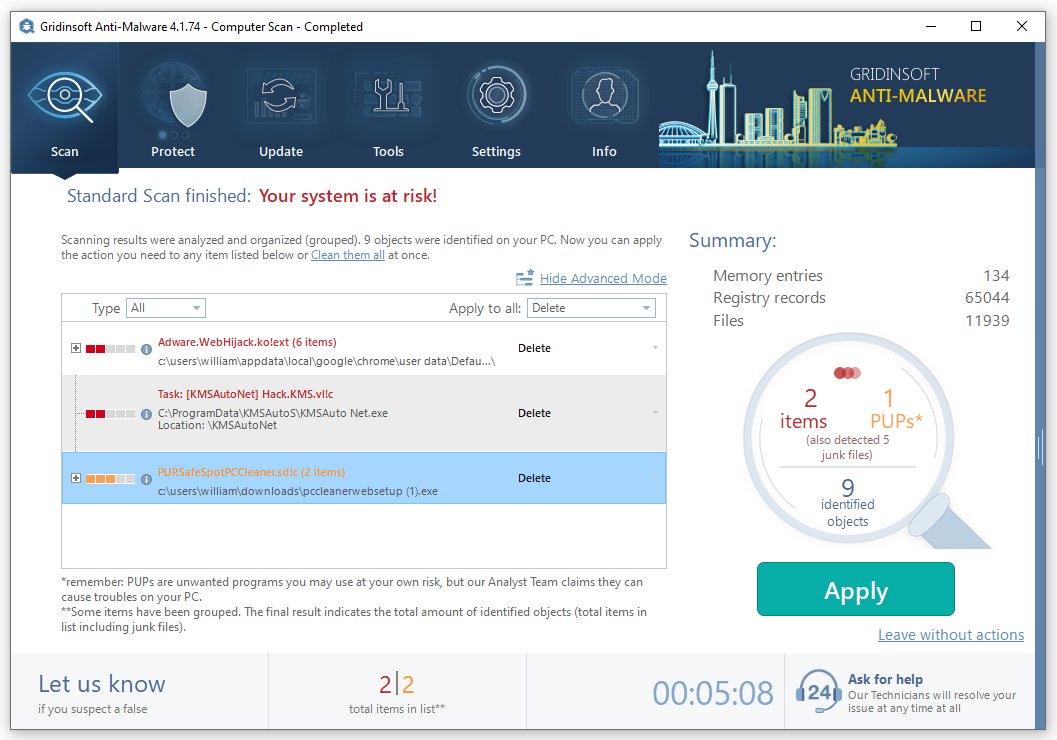
The perfect way to check if the process is launched by a malicious program is to open its file location. Find the Host Process for Windows Tasks process in Task Manager, and click it with a right mouse button. Choose the “Open file location” option, and you will see the folder where the .exe file is located. If the Host Process for Windows Tasks is located in C:/Windows/System32, everything is ok, but any other location of the source file means that you have malware on your computer. To check your PC for viruses, I can offer you to use GridinSoft Anti-Malware2.
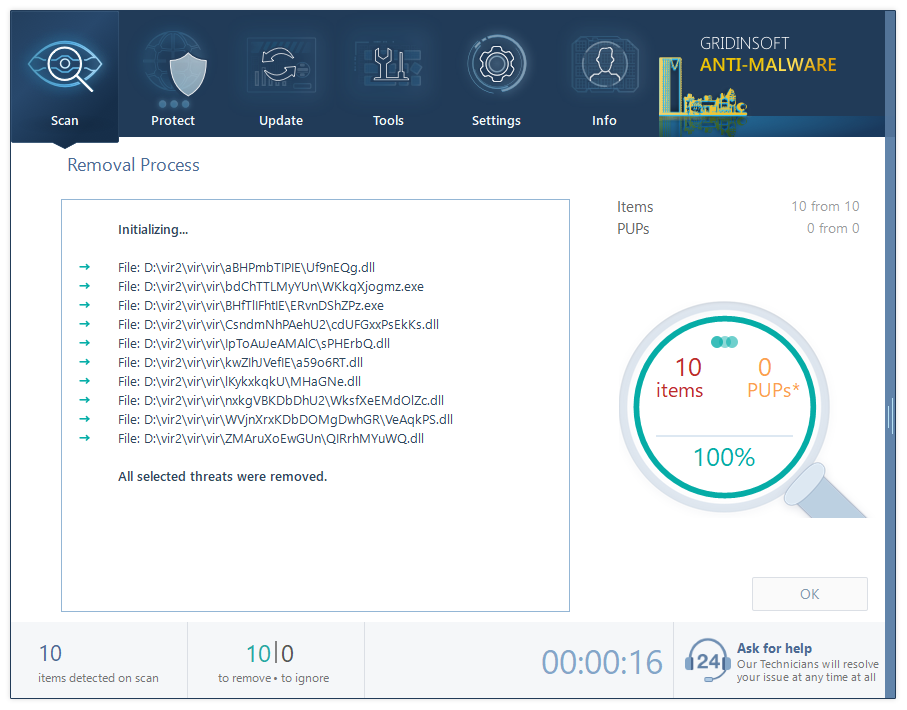
Removing the viruses with GridinSoft Anti-Malware
Frequently Asked Questions
No. In case if the process belongs to the legitimate system element, you will not be able to edit the root directory of the system, where it is stored, without granting yourself permission for this action. And its deletion will surely lead to a system crash without a possibility of loading the system back, because the crucial component is absent.
That process consumes literally nothing, so you will likely see no occasions when there is a need to make it less greedy with resources. However, if you see that it takes more than 20-30% of your CPU and the same amount of RAM, it is likely a virus. Perform the guide I wrote above.
As it was mentioned in the previous question, the CPU/RAM consumption of the original process is very low. So, the Host Process for Windows Tasks that uses a lot of hardware capacity is definitely a virus. Another way to understand that this process belongs to a malicious program is its location inside of the Task Manager. System processes are listed in the corresponding thread, so that process’ application among the user’s background processes is a sign of malware presence.
User Review
( votes)References
- Official Microsoft answer about the Host Process for Windows Tasks purpose.
- Explanation why do I recommend you to use GridinSoft Anti-Malware.


