What is Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq infection?
In this short article you will certainly discover concerning the meaning of Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq and also its negative effect on your computer system. Such ransomware are a form of malware that is specified by on-line scams to demand paying the ransom money by a sufferer.
In the majority of the cases, Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq infection will instruct its sufferers to start funds transfer for the function of neutralizing the changes that the Trojan infection has introduced to the victim’s device.
Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq Summary
These alterations can be as follows:
- Executable code extraction. Cybercriminals often use binary packers to hinder the malicious code from reverse-engineered by malware analysts. A packer is a tool that compresses, encrypts, and modifies a malicious file’s format. Sometimes packers can be used for legitimate ends, for example, to protect a program against cracking or copying.
- Injection (inter-process);
- Injection (Process Hollowing);
- Attempts to connect to a dead IP:Port (1 unique times);
- Presents an Authenticode digital signature;
- Creates RWX memory. There is a security trick with memory regions that allows an attacker to fill a buffer with a shellcode and then execute it. Filling a buffer with shellcode isn’t a big deal, it’s just data. The problem arises when the attacker is able to control the instruction pointer (EIP), usually by corrupting a function’s stack frame using a stack-based buffer overflow, and then changing the flow of execution by assigning this pointer to the address of the shellcode.
- Mimics the system’s user agent string for its own requests;
- Possible date expiration check, exits too soon after checking local time;
- A process attempted to delay the analysis task.;
- A named pipe was used for inter-process communication;
- Expresses interest in specific running processes;
- Repeatedly searches for a not-found process, may want to run with startbrowser=1 option;
- A process created a hidden window;
- Performs some HTTP requests;
- Uses Windows utilities for basic functionality;
- Executed a process and injected code into it, probably while unpacking;
- A system process is generating network traffic likely as a result of process injection;
- Installs itself for autorun at Windows startup.
There is simple tactic using the Windows startup folder located at:
C:\Users\[user-name]\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\StartMenu\Programs\Startup Shortcut links (.lnk extension) placed in this folder will cause Windows to launch the application each time [user-name] logs into Windows.The registry run keys perform the same action, and can be located in different locations:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
- Checks the CPU name from registry, possibly for anti-virtualization;
- Attempts to modify proxy settings. This trick used for inject malware into connection between browser and server;
- Collects information to fingerprint the system. There are behavioral human characteristics that can be used to digitally identify a person to grant access to systems, devices, or data. Unlike passwords and verification codes, fingerprints are fundamental parts of user’s identities. Among the threats blocked on biometric data processing and storage systems is spyware, the malware used in phishing attacks (mostly spyware downloaders and droppers), ransomware, and Banking Trojans as posing the greatest danger.
- Ciphering the files found on the victim’s hard disk — so the target can no longer utilize the information;
- Preventing regular accessibility to the target’s workstation;
Similar behavior
Related domains
| z.whorecord.xyz | W32/GenKryptik.ELIQ!tr.ransom |
| a.tomx.xyz | W32/GenKryptik.ELIQ!tr.ransom |
| www.ip-adress.com | W32/GenKryptik.ELIQ!tr.ransom |
Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq
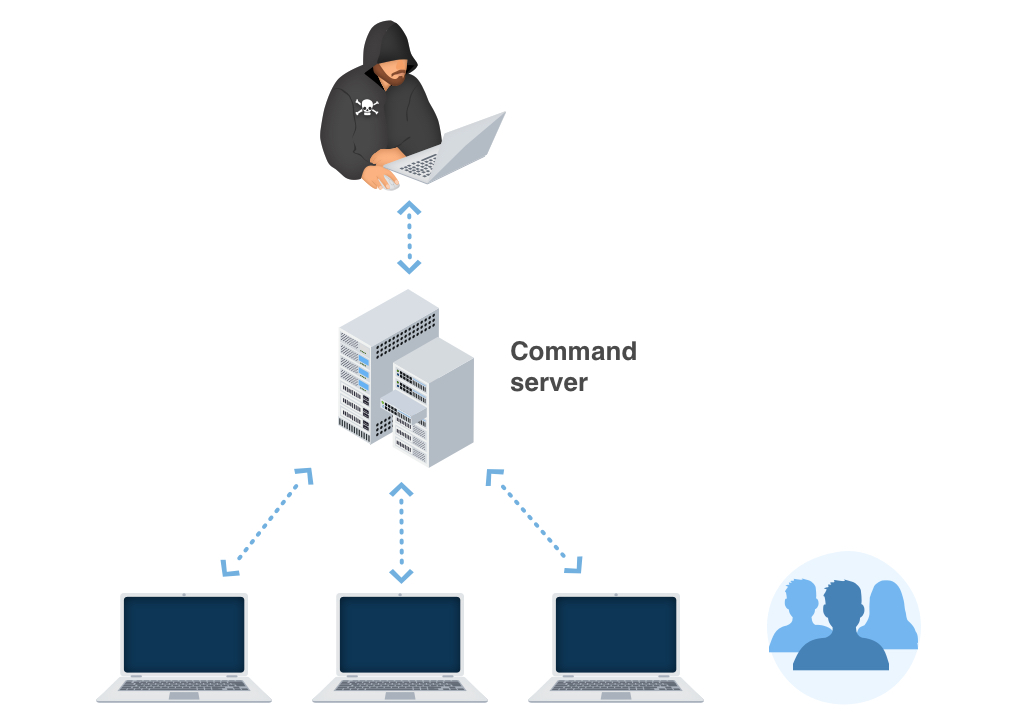
One of the most common networks through which Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq Ransomware are infused are:
- By means of phishing emails;
- As a repercussion of customer winding up on a source that organizes a harmful software;
As soon as the Trojan is successfully infused, it will either cipher the information on the sufferer’s computer or avoid the gadget from working in an appropriate fashion – while also positioning a ransom money note that discusses the need for the victims to effect the settlement for the function of decrypting the records or bring back the data system back to the initial problem. In many instances, the ransom money note will show up when the client restarts the COMPUTER after the system has already been harmed.
Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq distribution networks.
In different corners of the globe, Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq grows by jumps as well as bounds. Nevertheless, the ransom notes as well as tricks of obtaining the ransom quantity might differ depending on certain regional (local) setups. The ransom notes as well as tricks of extorting the ransom amount may differ depending on specific regional (local) setups.
For example:
Faulty signals regarding unlicensed software.
In specific areas, the Trojans usually wrongfully report having detected some unlicensed applications made it possible for on the victim’s tool. The alert then demands the individual to pay the ransom money.
Faulty statements regarding unlawful web content.
In nations where software application piracy is much less preferred, this technique is not as reliable for the cyber fraudulences. Additionally, the Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq popup alert may incorrectly claim to be originating from a police organization as well as will certainly report having located kid pornography or various other prohibited data on the gadget.
Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq popup alert may falsely assert to be obtaining from a legislation enforcement institution as well as will report having situated child porn or other prohibited data on the gadget. The alert will similarly include a requirement for the customer to pay the ransom.
Technical details
File Info:
crc32: 7AEC8B91md5: fea5bcfb57a43511117d0ca16bf6c042name: 111111.pngsha1: dcdffa4706fd64001b9e3a1fa5218a646c30860bsha256: 429b7da5539fff1f060cd73ba2bf3d73e3ef6da691a55014a70b9f02e0db8326sha512: d8767dcca631b80b95299fb59b095cc03b472b7c66b5bc6b36988b67a467ef192a63a1c8114ea573f6faeac03b02a3c81f5388ef911df72262de1887b5dd7fd0ssdeep: 6144:qMhkpTK06/aA6udzpNi1yna2PiQ0erLeROSEGo89QNn/o8S2M1KpWwR+SHvRu4T:qMEK06CmNi1L54Z89QNNpJgC5jtype: PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for MS WindowsVersion Info:
0: [No Data]
Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq also known as:
| GridinSoft | Trojan.Ransom.Gen |
| Elastic | malicious (high confidence) |
| MicroWorld-eScan | Trojan.GenericKDZ.69475 |
| ALYac | Trojan.GenericKDZ.69475 |
| VIPRE | Trojan.Win32.Generic!BT |
| Sangfor | Malware |
| K7AntiVirus | Trojan ( 0056c9731 ) |
| BitDefender | Trojan.GenericKDZ.69475 |
| K7GW | Trojan ( 0056c9731 ) |
| Cybereason | malicious.706fd6 |
| TrendMicro | TROJ_GEN.R002C0DHH20 |
| Symantec | ML.Attribute.HighConfidence |
| ESET-NOD32 | a variant of Win32/GenKryptik.EQKI |
| APEX | Malicious |
| Kaspersky | Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq |
| Alibaba | Trojan:Win32/Generic.58a4cb1e |
| Rising | [email protected] (RDML:xWrSq7SkOK1/GRo/0pqkGQ) |
| Ad-Aware | Trojan.GenericKDZ.69475 |
| Comodo | .UnclassifiedMalware@0 |
| F-Secure | Trojan.TR/AD.Qbot.FM |
| DrWeb | BackDoor.Qbot.538 |
| Invincea | heuristic |
| Fortinet | W32/GenKryptik.ELIQ!tr.ransom |
| FireEye | Generic.mg.fea5bcfb57a43511 |
| Sophos | Mal/Generic-S |
| Ikarus | Trojan.Cryptic |
| Avira | TR/AD.Qbot.FM |
| MAX | malware (ai score=81) |
| Arcabit | Trojan.Generic.D10F63 |
| ZoneAlarm | Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq |
| Microsoft | Trojan:Win32/Qakbot.AR!MTB |
| Cynet | Malicious (score: 100) |
| McAfee | GenericRXLR-QD!FEA5BCFB57A4 |
| Malwarebytes | Backdoor.Qbot |
| Panda | Trj/CI.A |
| TrendMicro-HouseCall | TROJ_GEN.R002C0DHH20 |
| SentinelOne | DFI – Malicious PE |
| GData | Trojan.GenericKDZ.69475 |
| AVG | Win32:DangerousSig [Trj] |
| Avast | Win32:DangerousSig [Trj] |
| CrowdStrike | win/malicious_confidence_60% (D) |
| Qihoo-360 | Generic/HEUR/QVM19.1.408F.Malware.Gen |
How to remove Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq virus?
Unwanted application has ofter come with other viruses and spyware. This threats can steal account credentials, or crypt your documents for ransom.
Reasons why I would recommend GridinSoft1
The is an excellent way to deal with recognizing and removing threats – using Gridinsoft Anti-Malware. This program will scan your PC, find and neutralize all suspicious processes.2.
Download GridinSoft Anti-Malware.
You can download GridinSoft Anti-Malware by clicking the button below:
Run the setup file.
When setup file has finished downloading, double-click on the setup-antimalware-fix.exe file to install GridinSoft Anti-Malware on your system.
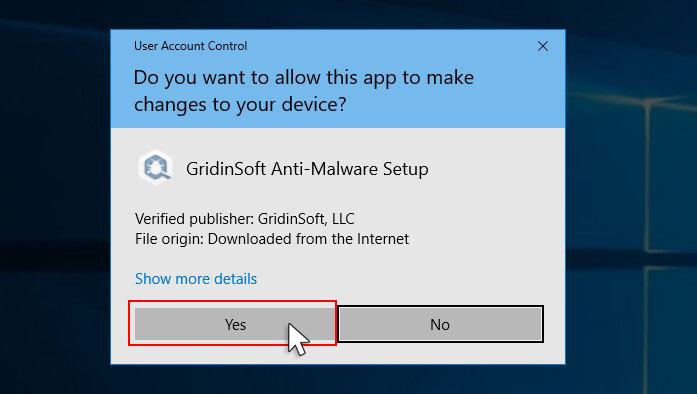
An User Account Control asking you about to allow GridinSoft Anti-Malware to make changes to your device. So, you should click “Yes” to continue with the installation.
Press “Install” button.
Once installed, Anti-Malware will automatically run.

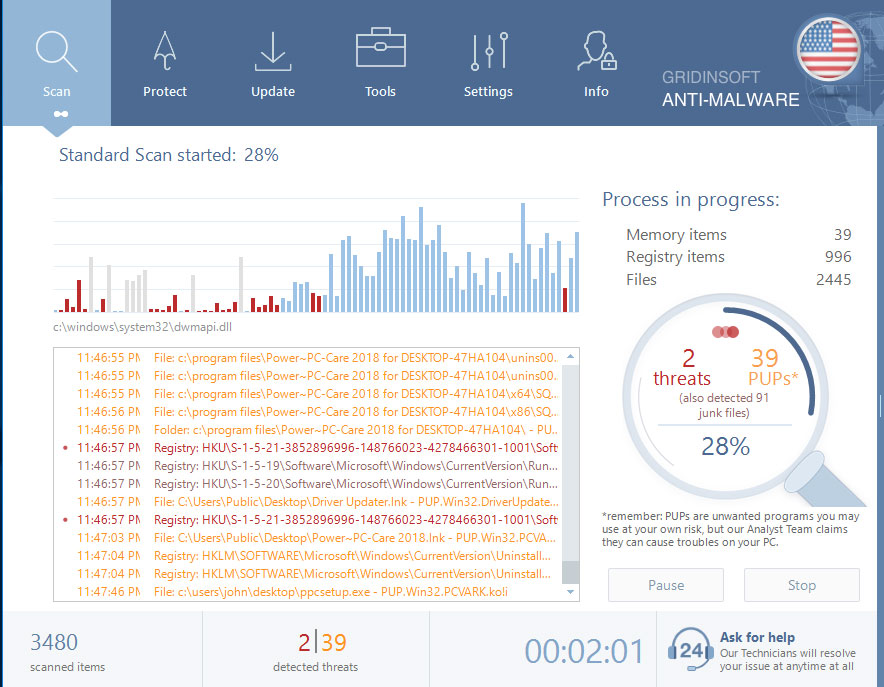
Wait for the Anti-Malware scan to complete.
GridinSoft Anti-Malware will automatically start scanning your system for Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq files and other malicious programs. This process can take a 20-30 minutes, so I suggest you periodically check on the status of the scan process.
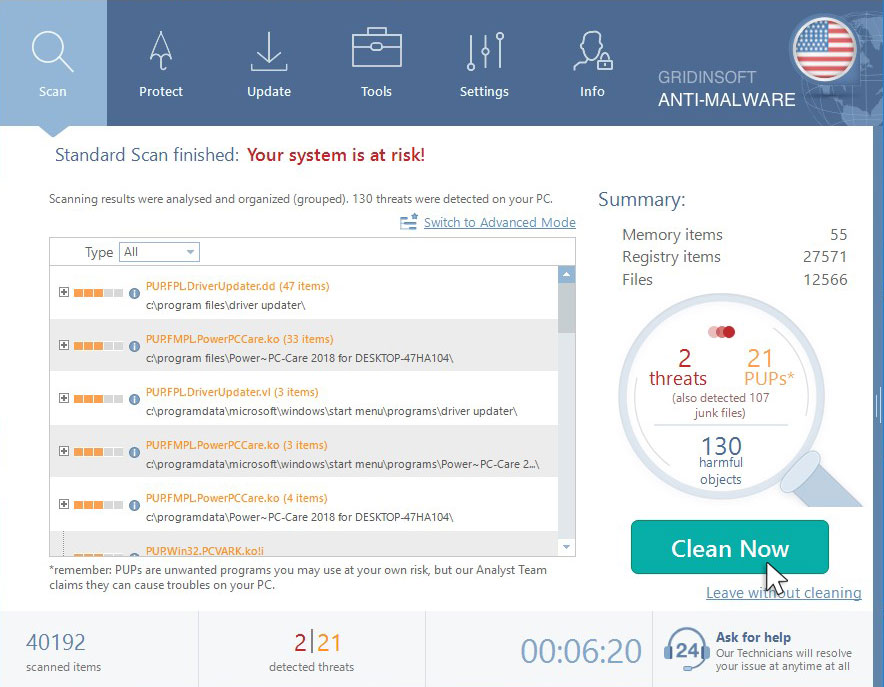
Click on “Clean Now”.
When the scan has finished, you will see the list of infections that GridinSoft Anti-Malware has detected. To remove them click on the “Clean Now” button in right corner.
Are Your Protected?
GridinSoft Anti-Malware will scan and clean your PC for free in the trial period. The free version offer real-time protection for first 2 days. If you want to be fully protected at all times – I can recommended you to purchase a full version:
If the guide doesn’t help you to remove Trojan.Win32.Qbot.aq you can always ask me in the comments for getting help.
User Review
( votes)References
- GridinSoft Anti-Malware Review from HowToFix site: https://howtofix.guide/gridinsoft-anti-malware/
- More information about GridinSoft products: https://gridinsoft.com/comparison