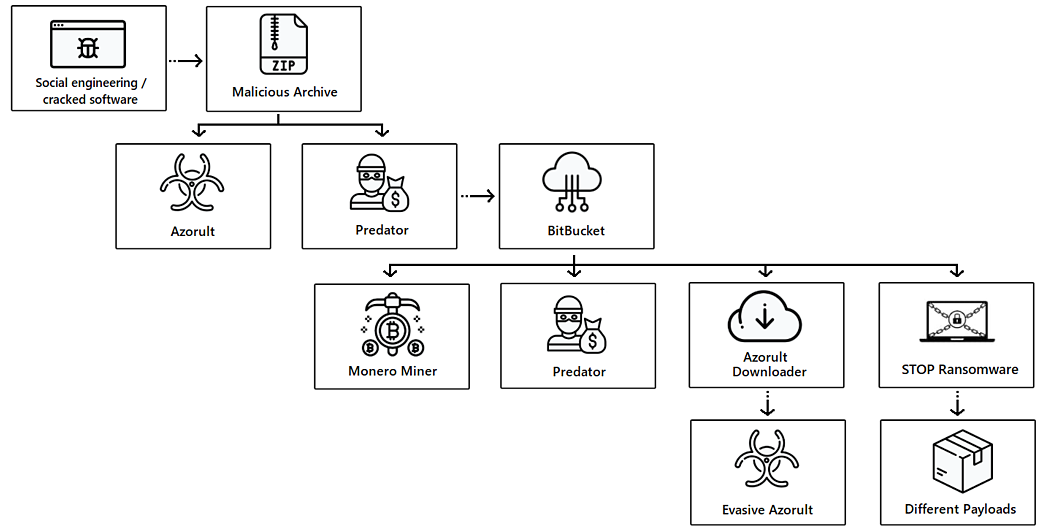
Cybereason company specialists discovered that hackers used the Bitbucket service to host and distribute several types of malware.
Researchers have found seven species of malware involved in the campaign, which is still active. According to experts, more than 500,000 machines have already become victims of this campaign, which eventually infected up with a variety of threats, including miners, cryptographers and trojans.Criminals have long used for their purposes many legitimate platforms, including GitHub, Dropbox and Google Drive, because the activity associated with these services left almost unsuspicious. Now the same fate befell Bitbucket”, – say Cybereason researchers.
As was recently reported, hackers could even use the Twitter API to discredit users.
To store malware, attackers use several Bitbucket accounts, and malware was regularly updated. These ongoing updates, as well as the use of Themida and CypherIT Autoit packers, help to avoid detection and protected threats against analysis. Among the payloads discovered by experts were:
- Predator: infostiller, steals credentials from browsers, steals information about cryptocurrency wallets, takes screenshots, uses the camera to take photos;
- Azorult: another infostiller, steals passwords, credentials from e-mail, cookies, browser history, ID, cryptocurrency and has backdoor capabilities;
- Evasive Monero Miner: a dropper for XMRig Miner, which uses advanced masking methods for silent mining of Monero cryptocurrency;
- STOP Ransomware: ransomware built on an open source platform that also has bootloader capabilities and is used to infect the system with additional malware;
- Vidar: infostiller, steals cookies, browser history, electronic wallet data, two-factor authentication data, and also capable to take screenshots;
- Amadey bot: a simple trojan, mainly used to collect initial information about an infected machine;
- IntelRapid: designed to steal cryptocurrencies, steals information about various types of wallets.
In the framework of this campaign, either attacks start with phishing emails enhanced by social engineering, or with downloading pirated versions of “hacked” software hackers mask the malware using Adobe Photoshop, Microsoft Office, etc.
At the same time, attackers try to infect the target machine with several types of malvari at once in order to maximize the effect.
In some ways, this attack takes persistent revenue to the next level. These attackers infect the target machine with different kinds of malware to get as much sensitive data as possible, alongside miner capabilities and ransomware capabilities. This attack is the epitome of “have your cake and eat it too”, with attackers layering malware for maximum impact”, — explain Cybereason researchers.
So, stolen information can be sold on the darknet, cryptocurrency can be withdrawn from the victim’s wallets, next may be applied miner to extract new tokens, and then, when there is nothing more to squeeze out of the infected system, use extortion malware.
Representatives of Bitbucket report that they deleted all the malicious files found by the researchers within a few hours after receiving a warning.