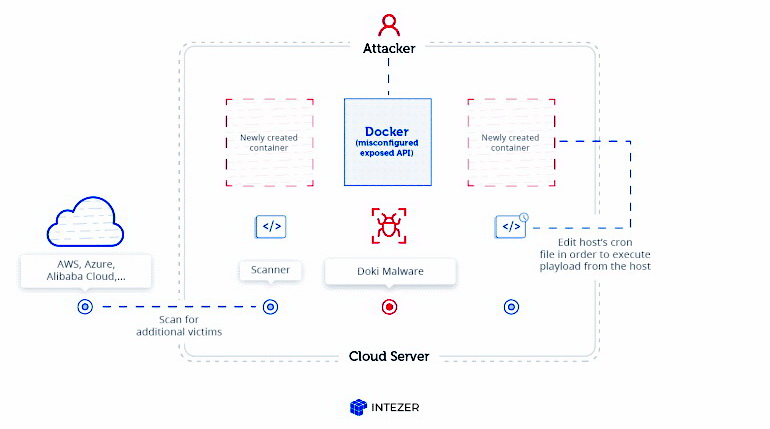
Intezer Labs discovered Doki, new Linux malware, targeting poorly secured Docker installations. According to their report, the Doki malware exploits the Dogecoin API to communicate with C&C servers.
Researchers say that the Ngrok group, which has been active at least since 2018, is behind the creation of this backdoor Trojan. The group got this name due to the fact that it often used the eponymous Ngrok service to host its control servers.Intezer Labs researchers say that the latest Ngrok campaign targets poorly secured Docker installations where the API is publicly available. For example, attackers abuse the Docker API to deploy new servers in the victim company’s cloud infrastructure, and then these servers running Alpine Linux become infected with mining malware and Doki.
Based on the samples uploaded to VirusTotal, Doki has been present since January 2020, but the malware still goes unnoticed by most of the scanners featured on VirusTotal.
Doki’s primary mission is simple, so that hackers can seamlessly control their Alpine Linux servers and monitor mining operations.
However, from a technical point of view, Doki is very different from other similar backdoors. The point is that the malware detects the URL of its C&C server in a very interesting way”, – note Intezer Labs note experts.
Typically, other malware refers to specific IP addresses or hard-coded URLs for this, but Doki uses the domain generation algorithm (DGA) and the Dogecoin cryptocurrency API to determine the address of its C&C server.
Scheme of the attack:
- The malware requests the dogechain.info API for the amount that was sent (spent) from a hard-coded wallet, which is under the control of attackers. Request format: https://dogechain.info/api/v1/address/sent/enjaddress}.
- SHA256 is used for the returned value.
- The first 12 characters of the obtained hexadecimal value will be the subdomain name.
- As a result, the address of the command and control server is formed by adding ddns.net to the resulting subdomain. For example, you get an address of the format 6d77335c4f23[.]Ddns[.]N
Essentially, hackers can change the address of their C&C server from which Doki receives commands by simply executing a transaction from their Dogecoin wallet. If DynDNS (ddns.net) receives a complaint about abuse of the current URL, Ngrok members simply initiate a new transaction, determine the subdomain value, create a new DynDNS account, and use the correct subdomain.
Experts note that this mechanism is very effective in preventing the seizure of the Doki backend infrastructure, because for this, law enforcement officers would need to take control of the Dogecoin wallet owned by hackers, and this is hardly possible without the appropriate cryptographic key.
Note that malware for attacks on Linux systems consists a fairly small percentage of the total number of cybercriminal developments, but still, as we can see, it exists an is actively developing.