Zaraza, a type of malware known as a stealer, operates by extracting (stealing) information from infected systems and installed applications, posing serious threats to user privacy. The term “Zaraza” is a slang word in Russian that can be likened to the word “infection”.
Once Zaraza infiltrates a device, it begins collecting relevant data such as the operating system version, hardware details, device name, user account name, IP addresses (geolocations), and more.
Zaraza Stealer Overview
As mentioned earlier, Zaraza and similar stealers can obtain data from both the system and the software installed on it. This malware is capable of downloading system and user files. It can extract data from various applications, including browsers, email clients, messengers, password managers, cryptocurrency wallets, FTPs, gaming-related software, VPNs, and more.
| Name | Zaraza Stealer |
| Detection | Trojan:MSIL/ZarazaStelaer.CTP!MTB read more here |
| Damage | Can extract data from the system as well as from various applications such as browsers, email clients, messengers, password managers, cryptocurrency wallets, and more. The information of interest includes browsing activity, login credentials, personally identifiable details, finance-related data, and credit card numbers. |
| Fix Tool | See If Your System Has Been Affected by Zaraza Virus |
The information targeted by Zaraza includes browsing activity, Internet cookies, log-in credentials (IDs, usernames, email addresses, passwords, passphrases, etc.), personally identifiable information, finance-related data, credit card numbers, and more. The collected information can be sold to third parties or exploited for profit. It’s important to note that stealer-type malware may have additional functionalities, and future iterations can come with new features.
In summary, having software like Zaraza on devices can lead to severe privacy issues, significant financial losses, and even identity theft. If you suspect your device is infected with the Zaraza stealer or any other malware, it’s crucial to use an antivirus immediately to eliminate it.
Stealer-type malware examples
When it comes to examples of stealer-type malware, we have analyzed thousands of malicious programs, including , Mystic, and Raccoon. Regardless of how malware operates, its presence on a system endangers device integrity and user safety. Therefore, all threats must be removed promptly upon detection.
How did Zaraza infiltrate your computer?
Now, let’s discuss how Zaraza infiltrates computers. Malware primarily spreads using phishing and social engineering techniques. Malicious software is often disguised as or bundled with ordinary programs or media.
Infectious files can be in the form of documents (e.g., Microsoft OneNote, Microsoft Office, PDF, etc.), archives (e.g., ZIP, RAR, etc.), executables (e.g., .exe, .run, etc.), JavaScript, and more. When such a file is executed, run, or opened, the infection process is triggered.
The most common methods of proliferation include stealthy/deceptive downloads (drive-by downloads), online scams, malicious attachments and links in spam emails/messages, malvertising, untrustworthy download channels (e.g., freeware and third-party sites, P2P sharing networks, etc.), illegal software activation tools (“cracks”), and fake updates.
Furthermore, some malicious programs can self-spread through local networks and removable storage devices such as external hard drives and USB flash drives.
To avoid installing malware, it’s strongly recommended to exercise caution while browsing since fraudulent and malicious online content often appears legitimate and harmless. Opening attachments or links found in suspicious or irrelevant emails and messages is not advised, as they can be infectious.
Downloading only from official and verified sources is another recommendation. Activating and updating software using functions and tools provided by genuine developers is advised, as illegal activation tools and third-party updaters can contain malware.
Emphasizing the importance of having a reputable antivirus installed and regularly updated is crucial. Security programs should be used to run regular system scans and eliminate detected threats and issues. If you suspect your computer is already infected, running a scan with Gridinsoft Anti-Malware is recommended to automatically eliminate infiltrated malware.
Updates of Zaraza Stealer
Update May 5, 2023
The malware utilizes various tactics such as obfuscation, masquerading, and screen capture to avoid detection and bypass security measures.
Update April 24, 2023
A new variant of Zaraza has been discovered. This iteration has been observed being promoted through Russian hacker channels on Telegram. The stealer targets over thirty browsers, including Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Opera, Brave, Yandex, Torch, Kometa, and more. Zaraza has sophisticated log-in credential extraction and decryption abilities. The stolen information is sent to the attackers via Telegram. Additionally, this malware can take screenshots of active windows.
The full list of targeted browsers includes 7Star, Amigo, AVAST Software, AVG Browser, Blisk, Brave Browser, CentBrowser, Chedot, Chrome, Chromium | SRWare Iron Browser, Citrio, CocCoc, Coowon, CoolNovo, Edge Chromium, Elements Browser, Epic Privacy Browser, Iridium Browser, Kinza, Kometa, Liebao Browser, Opera, Opera GX, Opera Neon, Orbitum, QIP Surf, SalamWeb, Slimjet, Sputnik, Sleipnir 6, Torch Browser, URBrowser, uCozMedia, and Vivaldi.
How to remove the Zaraza from my PC?
Zaraza malware is extremely hard to erase by hand. It places its files in several places throughout the disk, and can get back itself from one of the elements. Furthermore, a number of modifications in the registry, networking settings and also Group Policies are pretty hard to identify and return to the initial. It is far better to make use of a special tool – exactly, an anti-malware tool. GridinSoft Anti-Malware will fit the best for malware removal objectives.
Why GridinSoft Anti-Malware? It is very light-weight and has its databases updated almost every hour. Moreover, it does not have such bugs and vulnerabilities as Microsoft Defender does. The combination of these facts makes GridinSoft Anti-Malware ideal for getting rid of malware of any kind.
Remove the Zaraza with GridinSoft Anti-Malware
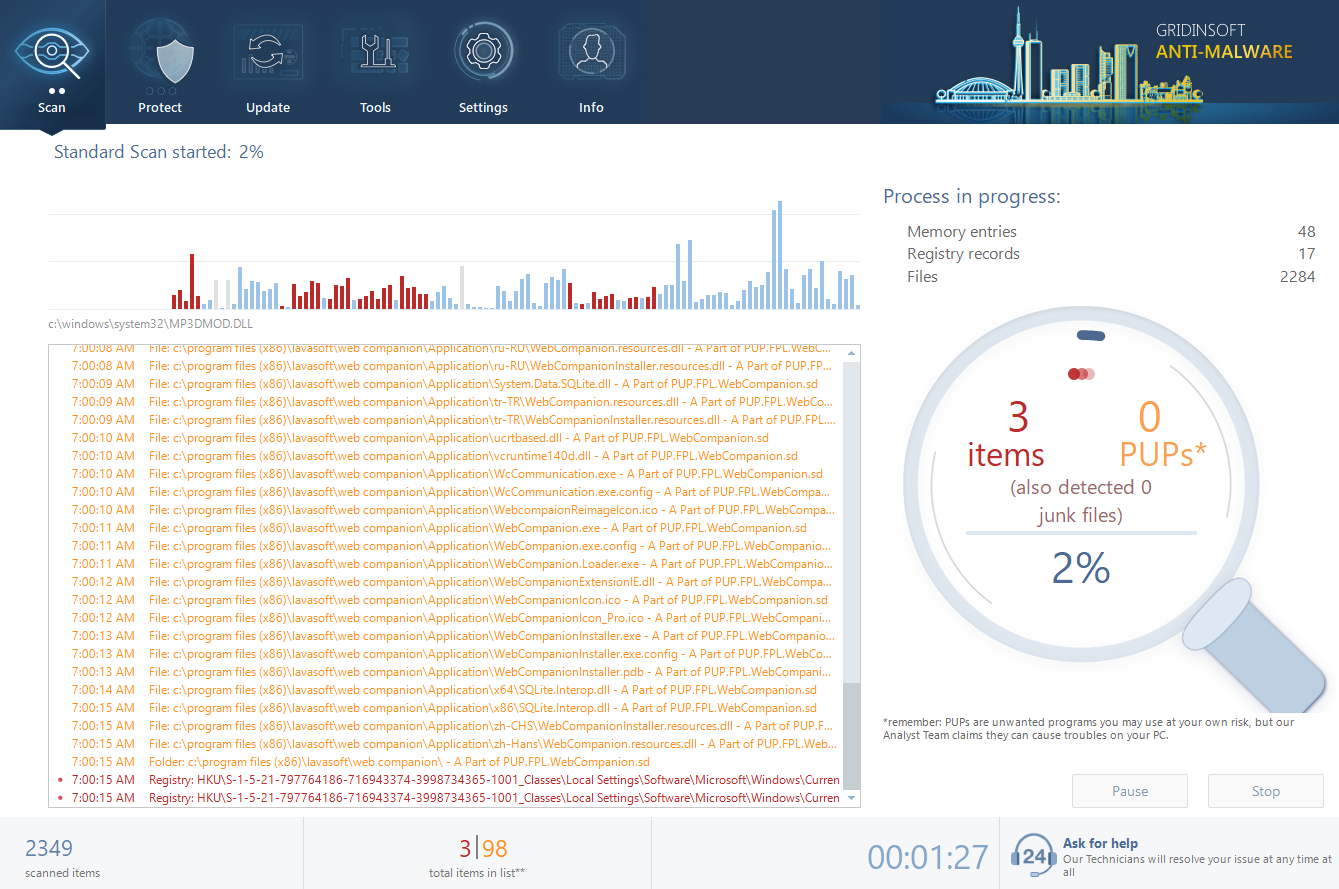
- Download and install GridinSoft Anti-Malware. After the installation, you will be offered to perform the Standard Scan. Approve this action.
- Standard scan checks the logical disk where the system files are stored, together with the files of programs you have already installed. The scan lasts up to 6 minutes.
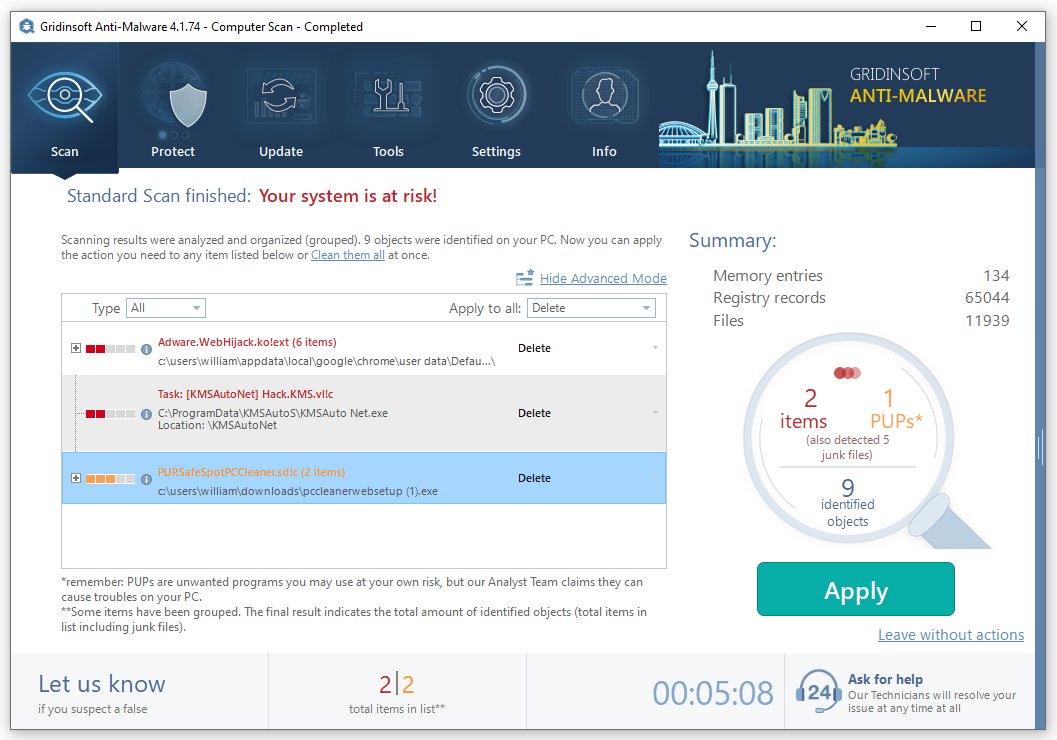
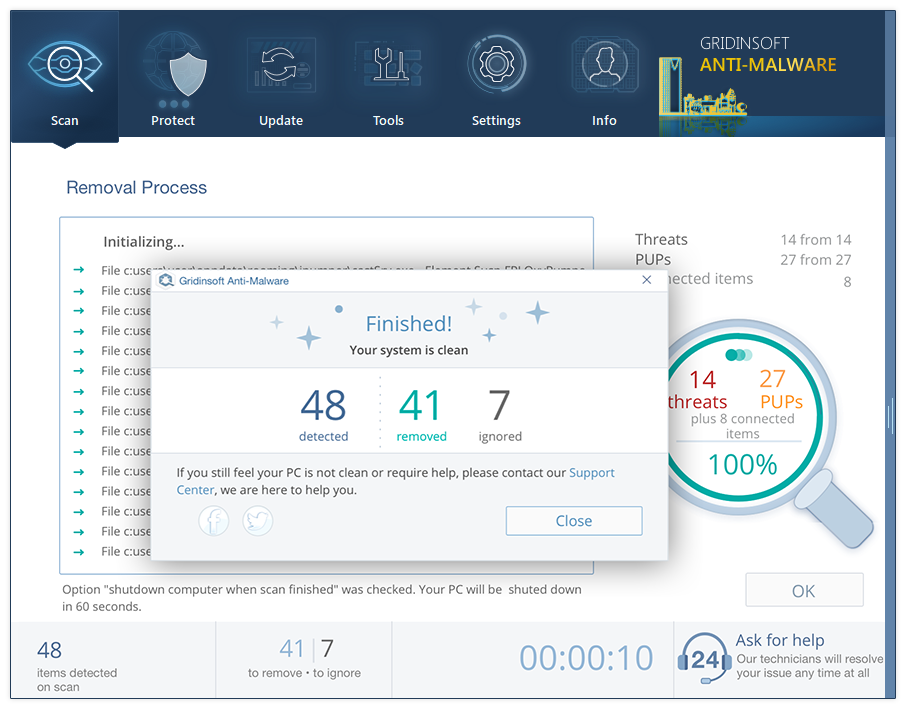
- When the scan is over, you may choose the action for each detected virus. For all files of Zaraza the default option is “Delete”. Press “Apply” to finish the malware removal.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Zaraza malware is a type of stealer that operates by extracting information from infected systems and installed applications. It poses significant threats to user privacy and can target various types of data.
“Zaraza” is a slang word in Russian that is analogous to the word “infection,” which reflects the nature of this malware.
It can extract data from the system as well as from various applications such as browsers, email clients, messengers, password managers, cryptocurrency wallets, and more. The information of interest includes browsing activity, login credentials, personally identifiable details, finance-related data, and credit card numbers.
The presence of Zaraza or similar malware on devices can lead to severe privacy issues, significant financial losses, and even identity theft.
It primarily spreads through phishing and social engineering techniques. It often disguises itself as or is bundled with ordinary programs or media. Infectious files can be documents, archives, executables, JavaScript, and more. When these files are executed or opened, the infection process begins.
To avoid malware infections, it is recommended to exercise caution while browsing, avoid opening suspicious email attachments and links, download software only from official and verified sources, and activate and update software using tools provided by genuine developers. It is also crucial to have reputable antivirus software installed and regularly updated.
If you suspect your device is infected it is important to take immediate action. Use antivirus software to scan and eliminate the detected threats. For Zaraza, running a scan with Combo Cleaner Antivirus for Windows is recommended.
Yes, there are various examples of stealer-type malware, including RootFinder, Cinoshi, SYS01, and ImBetter. All of these malware types pose threats to device integrity and user safety.
Malware developers often improve upon their creations, so future iterations of Zaraza may have additional or different features. These updates can include tactics like obfuscation, masquerading, and screen capture to evade detection and bypass security measures.
The latest variant of Zaraza targets over thirty browsers, including Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Opera, Brave, Yandex, Torch, Kometa, and more. This variant possesses advanced log-in credential extraction and decryption abilities and sends stolen information to the attackers via Telegram.
It is important to stay vigilant while browsing, avoid suspicious email attachments and links, download from official sources, use reputable antivirus software, and regularly update and scan your system for potential threats. These practices help ensure ongoing security against malware.
How to Remove Zaraza Stealer?
Name: Zaraza
Description: Zaraza, a type of malware known for stealing information from infected systems and applications, poses significant threats to user privacy. This malware, whose name is a Russian slang term meaning "infection," operates by extracting data from various sources. Upon infiltration, Zaraza starts collecting relevant device data such as the operating system version, hardware details, device name, user account name, and IP addresses. Additionally, it has the capability to download system and user files.
Offer price: 0.0
Operating System: Windows
Application Category: Malware

