What is Win32/Kryptik.FDHE infection?
In this post you will certainly discover concerning the definition of Win32/Kryptik.FDHE as well as its unfavorable effect on your computer. Such ransomware are a kind of malware that is clarified by online frauds to require paying the ransom money by a victim.
In the majority of the situations, Win32/Kryptik.FDHE ransomware will certainly advise its targets to launch funds move for the function of neutralizing the changes that the Trojan infection has introduced to the victim’s tool.
Win32/Kryptik.FDHE Summary
These modifications can be as follows:
- Executable code extraction. Cybercriminals often use binary packers to hinder the malicious code from reverse-engineered by malware analysts. A packer is a tool that compresses, encrypts, and modifies a malicious file’s format. Sometimes packers can be used for legitimate ends, for example, to protect a program against cracking or copying.
- Attempts to connect to a dead IP:Port (1 unique times);
- Creates RWX memory. There is a security trick with memory regions that allows an attacker to fill a buffer with a shellcode and then execute it. Filling a buffer with shellcode isn’t a big deal, it’s just data. The problem arises when the attacker is able to control the instruction pointer (EIP), usually by corrupting a function’s stack frame using a stack-based buffer overflow, and then changing the flow of execution by assigning this pointer to the address of the shellcode.
- Reads data out of its own binary image. The trick that allows the malware to read data out of your computer’s memory.
Everything you run, type, or click on your computer goes through the memory. This includes passwords, bank account numbers, emails, and other confidential information. With this vulnerability, there is the potential for a malicious program to read that data.
- Drops a binary and executes it. Trojan-Downloader installs itself to the system and waits until an Internet connection becomes available to connect to a remote server or website in order to download additional malware onto the infected computer.
- HTTP traffic contains suspicious features which may be indicative of malware related traffic;
- Creates an excessive number of UDP connection attempts to external IP addresses;
- Performs some HTTP requests;
- Unconventionial binary language: Russian;
- Unconventionial language used in binary resources: Russian;
- The binary likely contains encrypted or compressed data. In this case, encryption is a way of hiding virus’ code from antiviruses and virus’ analysts.
- Uses Windows utilities for basic functionality;
- Exhibits behavior characteristic of Cerber ransomware;
- Creates or sets a registry key to a long series of bytes, possibly to store a binary or malware config;
- Mimics the file times of a Windows system file;
- Installs itself for autorun at Windows startup.
There is simple tactic using the Windows startup folder located at:
C:\Users\[user-name]\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\StartMenu\Programs\Startup Shortcut links (.lnk extension) placed in this folder will cause Windows to launch the application each time [user-name] logs into Windows.The registry run keys perform the same action, and can be located in different locations:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
- HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce
- Creates a hidden or system file. The malware adds the hidden attribute to every file and folder on your system, so it appears as if everything has been deleted from your hard drive.
- Attempts to identify installed AV products by installation directory;
- Creates a copy of itself;
- Uses suspicious command line tools or Windows utilities;
- Ciphering the records situated on the sufferer’s hard disk drive — so the victim can no longer utilize the information;
- Preventing routine access to the target’s workstation. This is the typical behavior of a virus called locker. It blocks access to the computer until the victim pays the ransom.
Similar behavior
Related domains
| ip-api.com | Trojan.Ransom.Cerber.1 |
| redirector.gvt1.com | Trojan.Ransom.Cerber.1 |
| r4—sn-4g5e6nzs.gvt1.com | Trojan.Ransom.Cerber.1 |
Win32/Kryptik.FDHE
One of the most regular channels where Win32/Kryptik.FDHE Ransomware are infused are:
- By ways of phishing emails;
- As an effect of individual ending up on a resource that hosts a harmful software application;
As soon as the Trojan is effectively infused, it will either cipher the information on the target’s computer or avoid the tool from functioning in a proper manner – while also putting a ransom note that mentions the requirement for the sufferers to effect the payment for the purpose of decrypting the files or recovering the file system back to the initial problem. In most circumstances, the ransom money note will come up when the customer restarts the COMPUTER after the system has actually currently been damaged.
Win32/Kryptik.FDHE circulation channels.
In numerous corners of the world, Win32/Kryptik.FDHE expands by leaps as well as bounds. However, the ransom notes and also techniques of obtaining the ransom amount might differ relying on particular local (local) settings. The ransom money notes as well as tricks of extorting the ransom money quantity might differ depending on certain regional (local) settings.
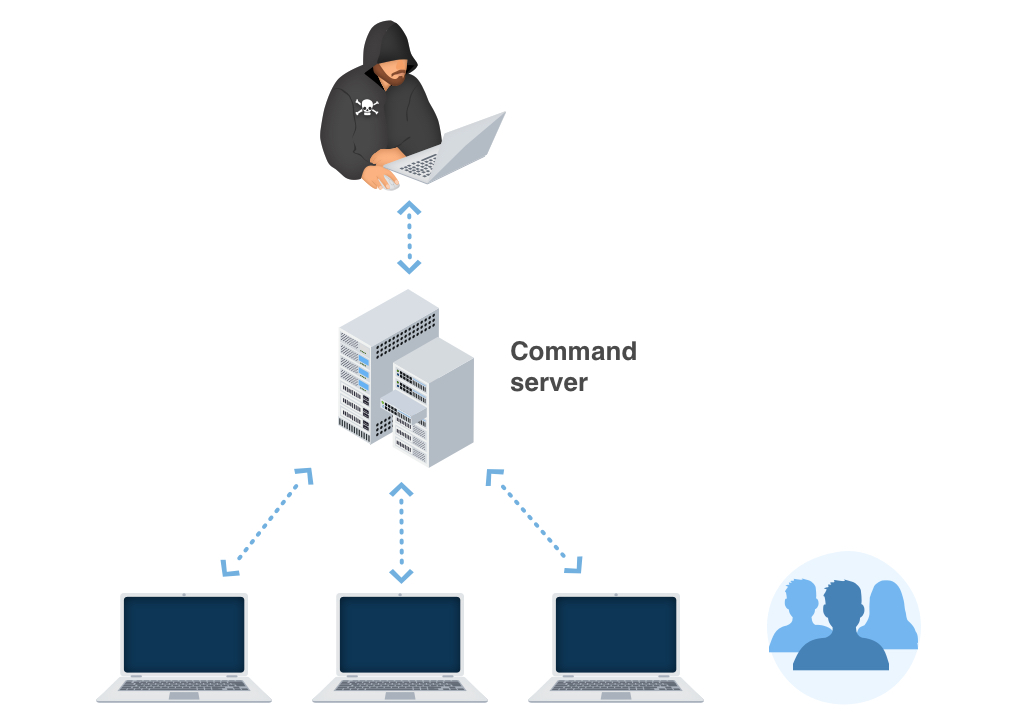
For example:
Faulty alerts regarding unlicensed software program.
In certain locations, the Trojans typically wrongfully report having actually spotted some unlicensed applications made it possible for on the victim’s device. The sharp after that demands the customer to pay the ransom money.
Faulty statements about illegal material.
In nations where software piracy is less popular, this approach is not as efficient for the cyber fraudulences. Conversely, the Win32/Kryptik.FDHE popup alert might wrongly claim to be deriving from a police organization and also will report having located child pornography or various other prohibited information on the gadget.
Win32/Kryptik.FDHE popup alert might wrongly declare to be obtaining from a law enforcement establishment and will report having located child porn or other illegal data on the device. The alert will in a similar way include a requirement for the customer to pay the ransom money.
Technical details
File Info:
crc32: 069BB3F2md5: afc1938955e21df97c24920cfe55acd7name: AFC1938955E21DF97C24920CFE55ACD7.mlwsha1: 81f95143a249dffec618ee9b463dc9e3fd0b9307sha256: 75dd3608de0296ec53cebaf935b7142265799894b4eeea2a7794a059ffc5e3e6sha512: 854d74ed6bb29576deeb4992b30c72766f0faaa2f57b35fd2945c8bdcc93e1b16657749585518e66ea4df26e4a4247546b812e26af4479af3d4338e0aa5c46eassdeep: 3072:3ThF64nITgkEzhNQrg7qgIJsvArxl0BrlnURZYvoVgNXhlvQ/+Us2HKIacaUc225:Aqsso+rlURZqoVgXhs/DdDYuWZtype: PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for MS WindowsVersion Info:
FileVersion: 3.2.3.51OriginalFilename: puntounloader.exeProductName: Punt o Switcher Translation: 0x0419 0x04b0
Win32/Kryptik.FDHE also known as:
| GridinSoft | Trojan.Ransom.Gen |
| Bkav | W32.AIDetectVM.malware1 |
| Elastic | malicious (high confidence) |
| DrWeb | Trojan.Encoder.5189 |
| MicroWorld-eScan | Trojan.Ransom.Cerber.1 |
| FireEye | Generic.mg.afc1938955e21df9 |
| CAT-QuickHeal | Ransom.Cerber.G4 |
| McAfee | Ransom-Cerber!AFC1938955E2 |
| Cylance | Unsafe |
| VIPRE | Trojan.Win32.Generic!BT |
| Sangfor | Malware |
| K7AntiVirus | Trojan ( 005224381 ) |
| BitDefender | Trojan.Ransom.Cerber.1 |
| K7GW | Trojan ( 005224381 ) |
| Cybereason | malicious.955e21 |
| TrendMicro | Ransom_HPCERBER.SM3 |
| BitDefenderTheta | AI:Packer.1B346B8F1F |
| Cyren | W32/Cerber.VJAM-1855 |
| Symantec | Trojan.Gen.MBT |
| APEX | Malicious |
| Avast | Win32:MalOb-IF [Cryp] |
| ClamAV | Win.Ransomware.Cerber-9777248-0 |
| Kaspersky | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Zerber.jcb |
| Tencent | Malware.Win32.Gencirc.11b0739c |
| Ad-Aware | Trojan.Ransom.Cerber.1 |
| Sophos | Mal/Cerber-B |
| Comodo | Application.Win32.Adware.LoadMoney.AX@6nn8c4 |
| F-Secure | Heuristic.HEUR/AGEN.1105900 |
| Baidu | Win32.Trojan.Kryptik.avk |
| Invincea | ML/PE-A + Mal/Cerber-B |
| McAfee-GW-Edition | BehavesLike.Win32.Ransomware.dh |
| Emsisoft | Trojan.Ransom.Cerber.1 (B) |
| Ikarus | Trojan-Ransom.FileCrypter |
| Jiangmin | Trojan.Zerber.elg |
| MaxSecure | Trojan.Malware.9771936.susgen |
| Avira | HEUR/AGEN.1105900 |
| Microsoft | Ransom:Win32/Cerber.A |
| Gridinsoft | Ransom.Win32.Ransom.oa!s2 |
| Arcabit | Trojan.Ransom.Cerber.1 |
| ZoneAlarm | Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Zerber.jcb |
| GData | Win32.Trojan-Ransom.Cerber.KZY4AN |
| Cynet | Malicious (score: 100) |
| AhnLab-V3 | Win-Trojan/Cerber.Gen |
| Acronis | suspicious |
| VBA32 | BScope.Trojan.Vucha |
| ALYac | Trojan.Ransom.Cerber.1 |
| MAX | malware (ai score=89) |
| Zoner | Trojan.Win32.44666 |
| ESET-NOD32 | a variant of Win32/Kryptik.FDHE |
| TrendMicro-HouseCall | Ransom_HPCERBER.SM3 |
| Rising | Trojan.Kryptik!1.AF0E (CLASSIC) |
| Yandex | Trojan.GenAsa!ZlIOe44JNcM |
| SentinelOne | Static AI – Malicious PE |
| eGambit | Unsafe.AI_Score_99% |
| Fortinet | W32/Kryptik.HCAW!tr |
| Webroot | W32.Trojan.Gen |
| AVG | Win32:MalOb-IF [Cryp] |
| CrowdStrike | win/malicious_confidence_100% (D) |
| Qihoo-360 | HEUR/QVM20.1.3F29.Malware.Gen |
How to remove Win32/Kryptik.FDHE virus?
Unwanted application has ofter come with other viruses and spyware. This threats can steal account credentials, or crypt your documents for ransom.
Reasons why I would recommend GridinSoft1
The is an excellent way to deal with recognizing and removing threats – using Gridinsoft Anti-Malware. This program will scan your PC, find and neutralize all suspicious processes.2.
Download GridinSoft Anti-Malware.
You can download GridinSoft Anti-Malware by clicking the button below:
Run the setup file.
When setup file has finished downloading, double-click on the setup-antimalware-fix.exe file to install GridinSoft Anti-Malware on your system.
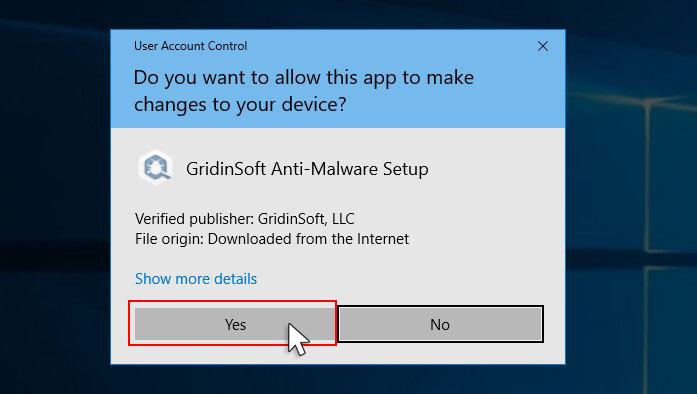
An User Account Control asking you about to allow GridinSoft Anti-Malware to make changes to your device. So, you should click “Yes” to continue with the installation.
Press “Install” button.
Once installed, Anti-Malware will automatically run.

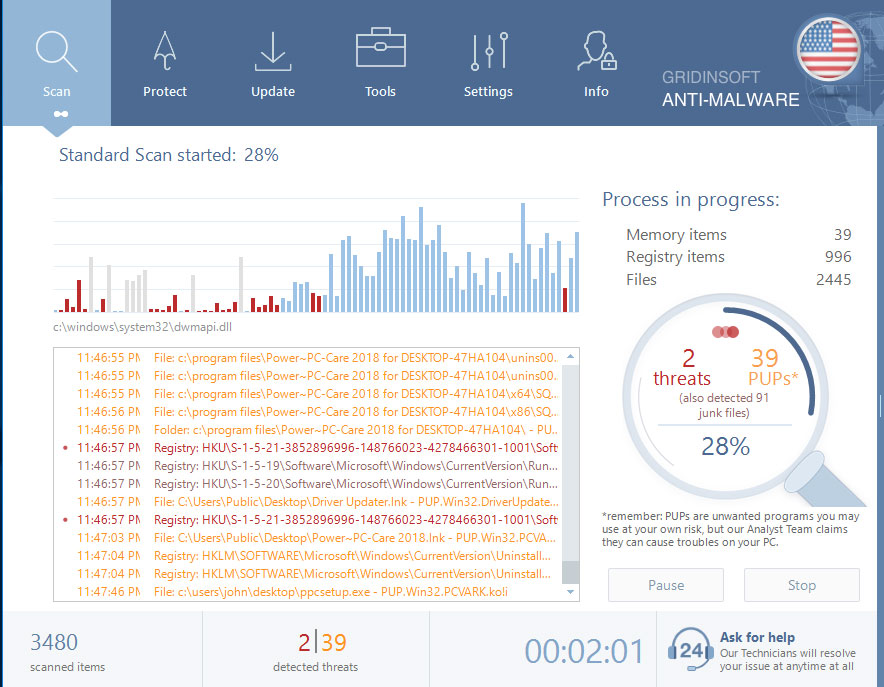
Wait for the Anti-Malware scan to complete.
GridinSoft Anti-Malware will automatically start scanning your system for Win32/Kryptik.FDHE files and other malicious programs. This process can take a 20-30 minutes, so I suggest you periodically check on the status of the scan process.
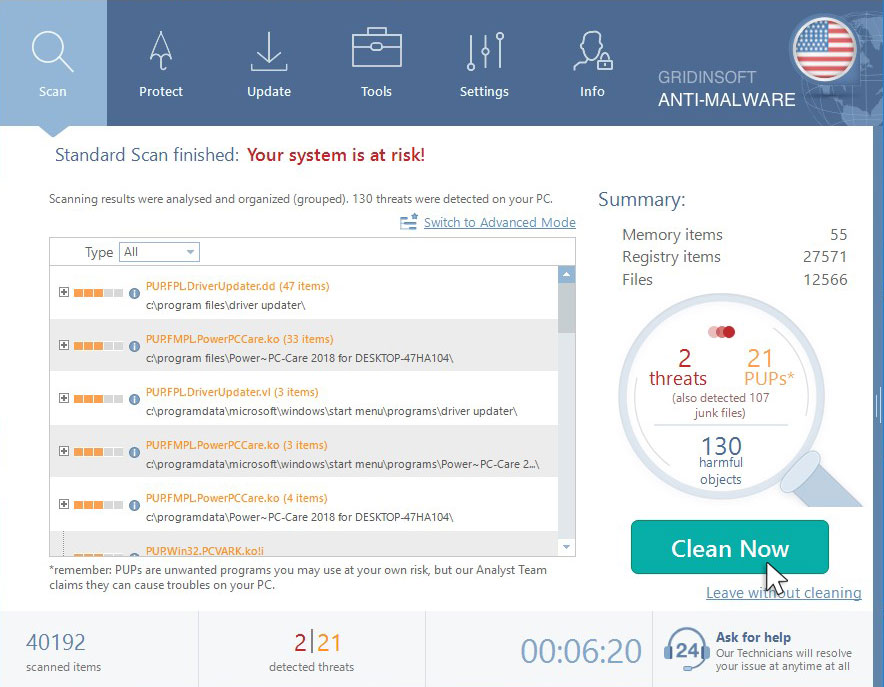
Click on “Clean Now”.
When the scan has finished, you will see the list of infections that GridinSoft Anti-Malware has detected. To remove them click on the “Clean Now” button in right corner.
Are Your Protected?
GridinSoft Anti-Malware will scan and clean your PC for free in the trial period. The free version offer real-time protection for first 2 days. If you want to be fully protected at all times – I can recommended you to purchase a full version:
If the guide doesn’t help you to remove Win32/Kryptik.FDHE you can always ask me in the comments for getting help.
User Review
( votes)References
- GridinSoft Anti-Malware Review from HowToFix site: https://howtofix.guide/gridinsoft-anti-malware/
- More information about GridinSoft products: https://gridinsoft.com/comparison