A team of researchers from South Korea found 30 vulnerabilities in the file upload mechanisms of 23 web applications. Among them are popular open source solutions, forums, CMS and so on.
Essentially, such vulnerabilities allow hackers to use file upload forms to host a wide variety of malicious files on victims’ websites.To conduct this study, experts developed their own tool for automatic pentest, called FUSE.
It is intended to detect vulnerabilities such as UFU (unrestricted executable file upload) and UEFU (unrestricted executable file upload,” unlimited downloads of executable files) in PHP applications”, – say the researchers.
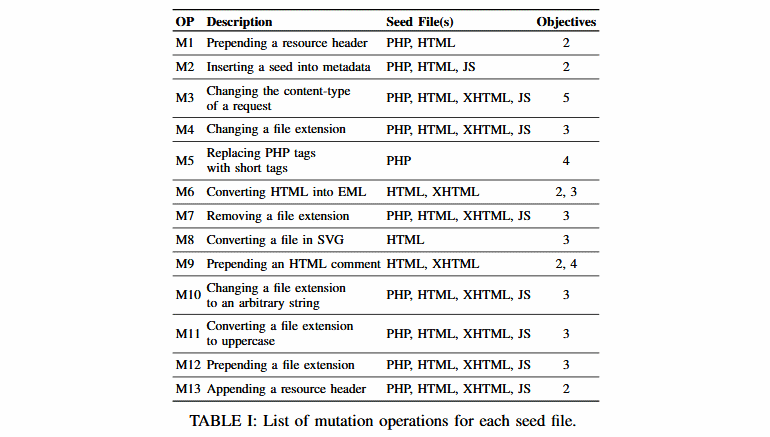
Before creating FUSE, researchers examined previously discovered file upload errors and identified eight of the most common patterns and methods for operating them. As a result, the tool contains the eight mentioned patterns, as well as five new variations developed by the research team itself.
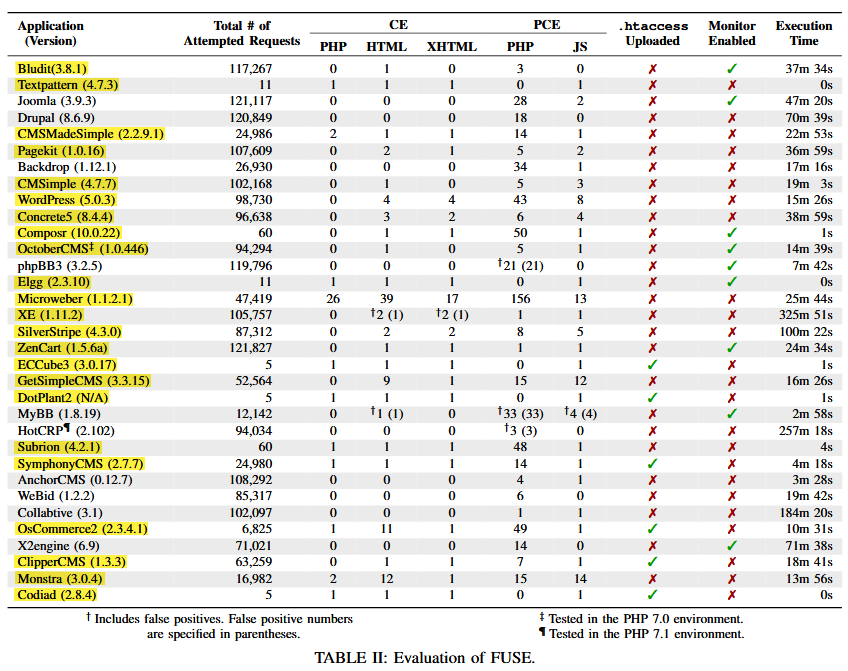
FUSE was tested on 33 popular web applications, including forums, CMS, corporate products and software for creating online stores. Using a series of automated queries, the researchers used file upload mechanisms in these web applications, trying to implement various malware (PHP, JS, HTML, XHTML, htaccess). As you can see in the table below, as a result, 30 different errors were detected, which affected 23 of the 33 tested applications.
Since the analysis was carried out a year ago, in February 2019, many web applications marked as vulnerable in the table have already received updates. However, the researchers write that over the course of a year, not all projects fixed the problems, and some may still be vulnerable.
Product names (with or without corrections) have not yet been disclosed to prevent attacks on web applications that have not yet released patches.
We reported about all 30 UEFU vulnerabilities to the respective vendors and received 15 CVEs for 9 applications. 8 vulnerabilities in products of 5 providers have already been fixed. Another 5 vulnerabilities in the products of 4 suppliers, including WordPress, have been confirmed by developers and will be fixed. Confirmations from the respective vendors expect 15 errors. Two suppliers refused to fix the vulnerabilities found”, – the researchers write.
Information security experts suggest that some previously disclosed vulnerabilities in WordPress plugins were discovered exclusively in this study, but were not publicized.
Many errors have not yet been fixed and are not in the priority for developers for the simple reason that 14 out of 30 vulnerabilities found require administrative access for exploitation, and a hacker with administrator rights can in any case establish full control over a vulnerable server.