Analysts from the RWTH Aachen published a study according to which tens of thousands of container images in Docker Hub contain various secrets, which exposes software, online platforms and users to the risk of massive attacks.
German experts say they analyzed 337,171 images from Docker Hub and thousands of private registries and found that approximately 8.5% contain sensitive data, including private keys and API secrets. Even worse, further investigation revealed that many of these keys are in active use, for example, undermining the security of hundreds of certificates.
Let me also remind you that we talked about the fact that Researchers Find over 1,600 Malicious Images on Docker Hub. And also that Many Repositories on GitHub Are Cloned and Distribute Malware, and also information security specialists warned about attacks on Kubernetes clusters.
To conduct the study, an impressive dataset was collected, consisting of 1,647,300 layers from 337,171 Docker images, and then analysts tried to extract the latest versions of the images from each repository.
As a result, analysis using regular expressions to find specific secrets revealed that 28,621 images contained 52,107 valid private keys and 3,158 API secrets.
Most of the “leaked” secrets (95% of private keys and 90% of API tokens) were found in single-user images, that is, they were most likely discovered by accident.
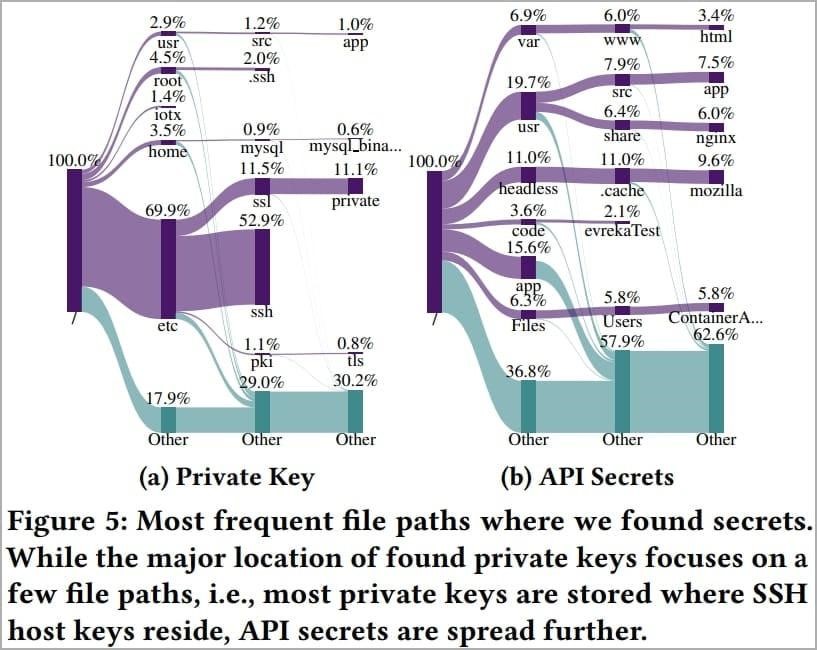
With a 9.0% secret-break rate on Docker Hub and private registries breaking secrets 6.3% of the time, the researchers believe that Docker Hub users understand container security less than people who set up private repositories.

After that, the researchers decided to determine how many “leaked” secrets are actually used. In particular, 22,082 compromised certificates based on disclosed private keys were found (including 7,546 private certificates signed by a certification authority and 1,060 public certificates signed by a certification authority). At the time of the study, 141 certificates signed by a certification authority were still valid.
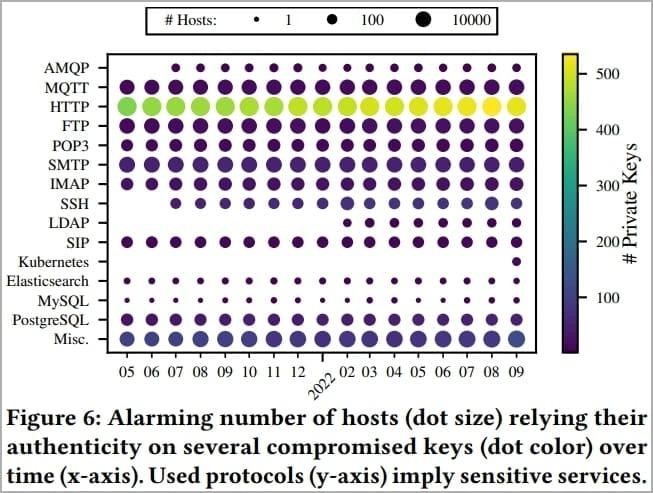
Also, based on the Censys database, the researchers identified 275,269 hosts that rely on compromised keys:
- 8674 MQTT hosts and 19 AMQP hosts that can potentially transmit sensitive data related to the Internet of things;
- 6672 FTP, 426 PostgreSQL , 3 Elasticsearch and 3 MySQL instances that serve potentially sensitive data;
- 216 SIP hosts used for telephony;
- 8,165 SMTP, 1,516 POP3 and 1,798 IMAP servers used for email;
- 240 SSH servers and 24 Kubernetes installations that use “leaked” keys, which can lead to unauthorized remote access, botnet entry or data access.
In terms of API tokens, the analysis showed that the majority of containers (2920) belong to cloud providers such as Amazon AWS, although some also belong to financial services such as Stripe. However, the researchers did not engage in an in-depth study of this issue for ethical reasons.
