The Darknet, also known as the dark web, is a portion of the internet that is intentionally hidden and not accessible through traditional search engines. The dark web was created as a means for individuals to communicate and share information anonymously and securely. But how does Darknet work? And how to use it? Let me explain.
How does the Darknet work?
The architecture of the Darknet is based on a peer-to-peer (P2P) network. Rather than relying on centralized servers like the traditional internet, the Darknet is made up of a decentralized network of computers that communicate with each other directly. This means that there is no central authority or controlling entity, making it difficult to shut down or monitor. However, a shutdown of a major number relay holders may cause certain issues, primarily low connection speed and high response times.
Aforementioned architecture provides high anonymity rates, as traffic goes through random nodes, making it impossible to track. For each connection, a random path is chosen. It somewhat resembles a proxy connection, but there are at least three additional servers you’re having a sequential connection to. If needed, the connection may be routed through an even bigger number of relays. Considering the encryption applied to each step of the connection, it becomes almost impossible to read the packages sent. The only downside of that scheme is a way slower connection speed – in some cases over 10 times less compared to “normal” connections.
Darknet History
There is a common misconception that the Darknet, particularly its early variant, was created by the U.S. military as an addition to the ARPANET. However, this is not entirely accurate. The ARPANET was a precursor to the modern Internet and was indeed created by the U.S. military in the 1960s. It was designed as a communication system for military and government organizations.
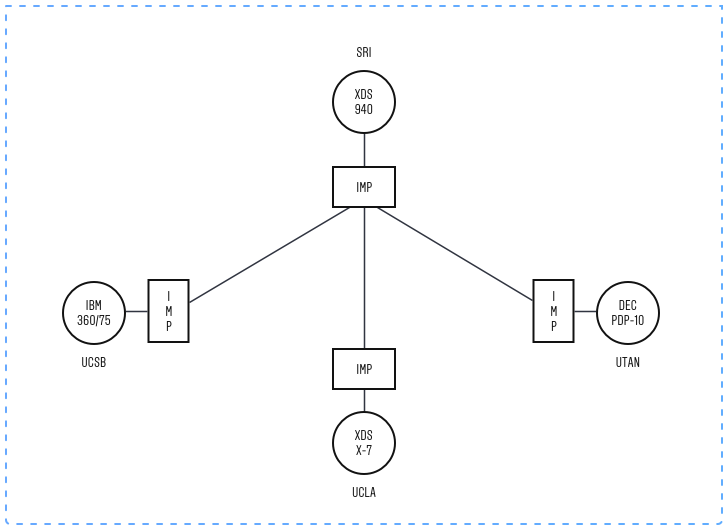
The architecture of the ARPANET on its early stages
On the other hand, the Darknet rather evolved from the early days of the Internet – i.e. from the ARPANET. Researchers and privacy advocates began to develop ways to communicate and share information anonymously and securely. One of the earliest attempts to create an anonymous network was the Cypherpunk mailing list, founded in 1992. The group was composed of individuals who were interested in cryptography and privacy. They discussed various ways to protect online communication from surveillance and censorship.
In the years that followed, a number of technologies were developed that allowed users to communicate and share information anonymously. These included anonymous remailers, and peer-to-peer networks, used for file sharing. However, the biggest growth for both popularity and infrastructure diversity happened after the appearance of the Tor network.
HiddenWiki – probably, the first page of Darknet all eager users visit
The Tor network, which is now one of the most popular ways to access the Darknet, was developed in the early 2000s by the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory. Initially, it was made for military and government use, but was later released as public open-source software. So yes, Darknet should say “thank you” to the U.S. military services for its current popularity, but not for the invention.
Is Darknet anonymous?
What makes the Darknet anonymous is the use of encrypted connections and routing protocols that mask the identity of its users. The Tor (The Onion Router) network is one such protocol used on the Darknet. When a user connects to the Tor network, their connection is routed through a series of nodes or relays, each of which adds a layer of encryption to the user’s data. This makes it difficult for anyone to trace the user’s online activities back to their physical location.
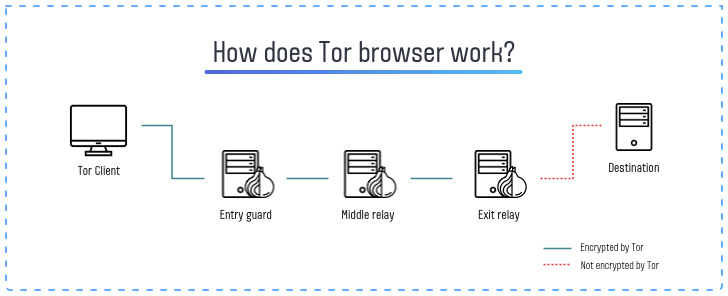
Apparently, it is still possible to trace the user even though it uses the Tor network. The key here is to control a significant portion of relays, so each stage of the connection may be controlled. Still, the packages will be nearly impossible to read. Even having all the nodes under control, the keys used to encrypt the package at the first connection – both from and to the target user, remain in secret. Nonetheless, to avoid IP address leaks, VPN service is recommended to use.
Most common ways to access the Darknet – Tor browser and its derivatives – also offer to adjust the level of privacy protection. This includes the aforementioned ability to use more nodes to establish the connection, as well as disable scripts on the websites. The latter can, intentionally or not, expose the true IP of a user, its system configuration, or other sensitive details. For persons who seek for advanced anonymity, such an exposure may be threatening to their freedom or even lives.
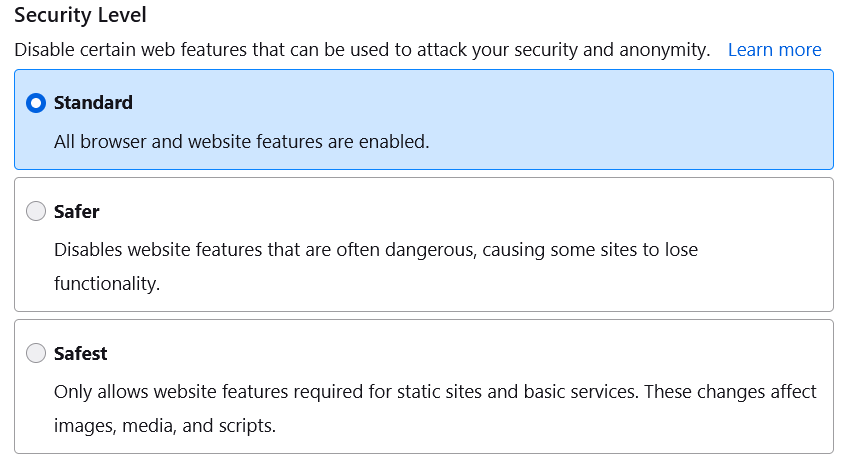
3 modes of privacy settings – from the one similar to a regular browser to a paranoid mode
Darknet and illegal activities
The Darknet is infamous for its association with illegal activities, including drug trafficking, weapons sales, and cyber crimes. Aforementioned anonymity and advanced security measures implemented in browsers used to access the Darknet make it convenient for various criminals. Actually, these features gave a punch towards creating a whole infrastructure network that serves for crimes. It received especially noteworthy popularity among cybercriminals. Anonymous email services, marketplaces, forums, even messengers – everything that villainous hackers may ever need.
The lobby of the RAMP forum, known as a haven for cybercriminals
Still, it’s worth noting that not all things that happen in the Darknet are illegal. It still serves for its initial purpose – anonymous communications and (almost) untraceable Internet access. Such services are highly demanded by state-persecuted journalists and activists. Regular mailing services, chats and things like that can be read, and the location may be uncovered using the IP address. With the services from the Darknet, it is not possible.
How to access the Darknet?
To access Darknet websites, users typically need to use a specialized browser such as Tor. The Tor browser is free and open-source software that can be downloaded and installed on most devices. Once the browser is installed, users can access Darknet websites by entering the site’s URL into the browser’s address bar. This, however, may be tricky, as sites often change their addresses, and address books available online are not updating frequently enough. It’s also important to note that accessing the Darknet can be risky. Users should take precautions such as using a VPN and avoiding downloading malware or sharing sensitive information.
Alternatively to the Tor browser, there is a lineup of browser plugins for regular web browsers that allow accessing the hidden network. However, it is not sufficient to retain the anonymity level of the primary access method. All these plugins do is give the browsers proper instructions about how to connect to the Onion sites. Multi-layer traffic redirection with consequent encryption, as well as the ability to disable potentially deanonymizing elements, are not available.
Is it illegal to access the Darknet?
Accessing the Darknet itself is not illegal in most countries. The Darknet is simply a network of hidden websites that can be accessed using specific software or configurations. Unless you are involved in illegal actions, like malware spreading, human trafficking, drug or weapon dealership – you’re totally fine. However, using the Darknet for the aforementioned purposes will most likely render you wanted by the authorities.
It is also important to remember that some countries may have specific laws regarding the use of anonymity tools. Using Tor, or accessing the Darknet in any other way may be illegal, so it’s important to research and understand the laws in your jurisdiction.

