The information stealer targeting Windows users is called ThirdEye Infostealer. Although this malware is not highly advanced, its primary objective is to extract sensitive information from compromised systems. Subsequent cyber-attacks can be built upon the stolen data.
Discovery of ThirdEye Infostealer
Researchers (FortiGuard Labs) discovered the earliest sample of ThirdEye Infostealer on April 3, 2023, at 12:36:37 GMT. This sample collected client_hash, OS_type, host_name, and user_name and sent them to the C2 server glovatickets[.]ru with a custom web request header:
Cookie: 3rd_eye=[client_hash value]
It was submitted to a file scanning service on April 4, 2023.
A variant was found a few weeks later with a compile timestamp of April 26, 09:56:55 GMT. This variant collected additional data, including the BIOS vendor and release date, RAM size, CPU core number, the user’s desktop files list, list of registered users on the device, and network interface data. However, this version crashes in some virtual machines.
One day later, a new variant was found with just one change: it used a PDF icon. This variant used “ohmycars[.]ru/ch3ckState” as C2 communications.
Later, another variant was found that gathered additional data such as total and free disk space on the C drive, domain name, network ports list, list of programs and version numbers, system uptime, CD-ROM, drive letters volume information, currently running processes list, and programs installed in the Program Files directory.
Further details about ThirdEye Infostealer
The ThirdEye information stealer has a fairly straightforward functionality. It collects system information from compromised machines, including BIOS and hardware details. Additionally, it scans for files, folders, running processes, and network information. ThirdEye transmits the gathered data to its designated Command-and-Control (C2) server.
The system information obtained from compromised machines, including BIOS and hardware details, can be used by cybercriminals for various malicious purposes. By analyzing this information, they can identify vulnerabilities or weaknesses in the system that can be exploited for unauthorized access or further compromise.
For example, knowledge of the hardware and BIOS version may help them target specific exploits or devise sophisticated attacks. In summary, cybercriminals can leverage the obtained information to plan targeted attacks, gain unauthorized access, perform identity theft, or facilitate other malicious activities.
Understanding the capabilities and risks associated with ThirdEye emphasizes the need for individuals and organizations to remain vigilant, stay informed about emerging threats, and implement effective cybersecurity measures to safeguard their systems and sensitive data.
Functionalities of ThirdEye Infostealer
| Name | ThirdEye Infostealer |
| Detection | Trojan:Win32/Wacatac.B!ml on VirusTotal1 |
| Similar behavior | Umbral, RedEnergy, and RDStealer. |
| Damage | Damage refers to the potential harm or negative consequences that can result from the activities of ThirdEye Infostealer or similar malware. This includes unauthorized access to sensitive information, such as personal data, financial details, or login credentials, which can lead to identity theft, financial loss, or privacy breaches. Additionally, ThirdEye Infostealer can provide cybercriminals with valuable insights into system vulnerabilities, allowing them to launch targeted attacks or compromise the security of affected systems. |
| C2 | hxxp://shlalala[.]ru/general/ch3ckState hxxp://ohmycars[.]ru/general/ch3ckState hxxp://anime-clab[.]ru/ch3ckState hxxp://glovatickets[.]ru/ch3ckState |
| Fix Tool | See If Your System Has Been Affected by ThirdEye Virus |
In their blog post, researchers from FortiGuard Labs revealed that ThirdEye Infostealer can steal system data from infected devices, including BIOS and hardware information. It can also enumerate folder files, running processes, and network data.
Upon execution, the infostealer quickly gathers the data and transmits it to a C2 server hosted at “shlalala[.]ru/general/ch3ckState” Apart from this, ThirdEye Infostealer does not perform any other function.
While researching, an interesting feature was noted – a string named “3rd eye,” from which they derived the name of this malware family. The malware decrypts this string and uses it with another hash value to identify the C2 server. ThirdEye Infostealer isn’t too sophisticated. However, it is evolving rapidly. Some recently collected samples stole more system data than the previously discovered versions.
Moreover, researchers noted that the infostealer targets Windows-based systems with a medium severity level. Currently, there is no evidence that ThirdEye Infostealer has been used in attacks.
However, since it is designed to collect data from compromised devices and systems, it can be useful for cybercriminals in launching attacks. Researchers believe that all previous and latest variants of ThirdEye Infostealer are named in Russian, indicating that the attacker is probably targeting Russian-speaking organizations to deploy the malware.
How did ThirdEye Stealer infiltrate my computer?
ThirdEye spreads through a ZIP file containing two executable (.exe) files disguised as regular documents (PDF docs) by using additional file extensions. The ZIP file containing the ThirdEye malware can be distributed through various methods, including email attachments, malicious websites, file-sharing networks, or disguised as legitimate software downloads.
Cybercriminals may use social engineering techniques, such as phishing emails or deceptive websites, to trick users into downloading and opening the contents of the ZIP file, unknowingly infecting their system with the malware.
How to avoid malware?
Exercise caution when opening email attachments or clicking on links, especially if they are from unknown or suspicious sources. Only download programs or files from reputable sources such as official websites or trusted app stores. Avoid downloading from shady websites or Peer-to-Peer networks, as they may contain malicious software.
Keep your operating system and all software up to date by installing the latest security patches and updates. Use reliable antivirus software and keep it regularly updated. Avoid clicking on suspicious ads or pop-ups, and be cautious when visiting unfamiliar websites. Stick to well-known and trusted websites to minimize the risk of encountering malicious content.
If your computer is already infected, we recommend running a scan with Gridinsoft Anti-Malware to automatically eliminate infiltrated malware.
How to remove the ThirdEye from my PC?
ThirdEye malware is extremely hard to remove manually. It puts its data in a variety of locations throughout the disk, and can restore itself from one of the parts. Additionally, a lot of changes in the registry, networking setups and Group Policies are fairly hard to locate and revert to the original. It is far better to use a special program – exactly, an anti-malware program. GridinSoft Anti-Malware will definitely fit the most ideal for virus removal purposes.
Why GridinSoft Anti-Malware? It is very lightweight and has its databases updated practically every hour. Moreover, it does not have such bugs and exploits as Microsoft Defender does. The combination of these facts makes GridinSoft Anti-Malware perfect for taking out malware of any kind.
Remove the ThirdEye with GridinSoft Anti-Malware
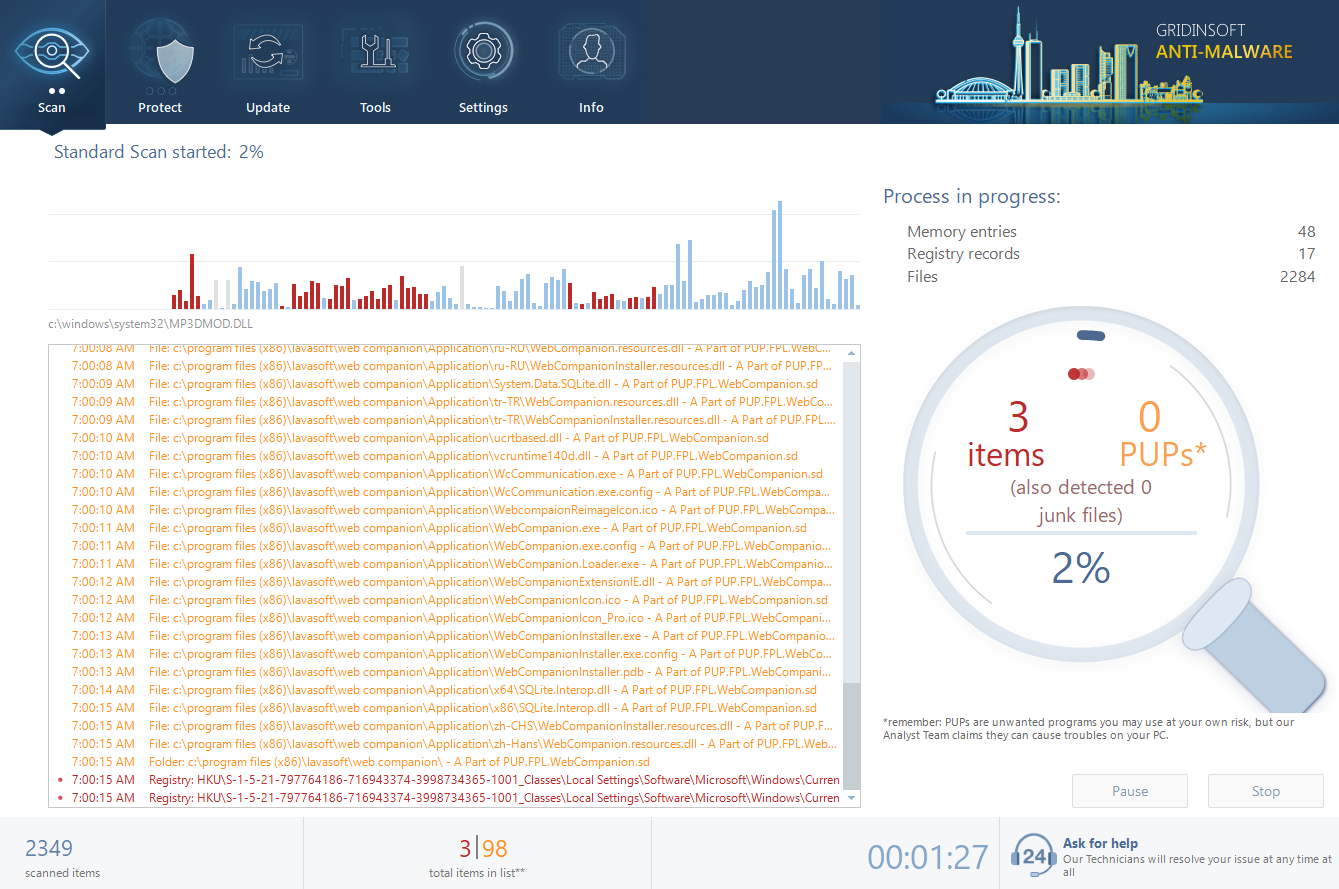
- Download and install GridinSoft Anti-Malware. After the installation, you will be offered to perform the Standard Scan. Approve this action.
- Standard scan checks the logical disk where the system files are stored, together with the files of programs you have already installed. The scan lasts up to 6 minutes.
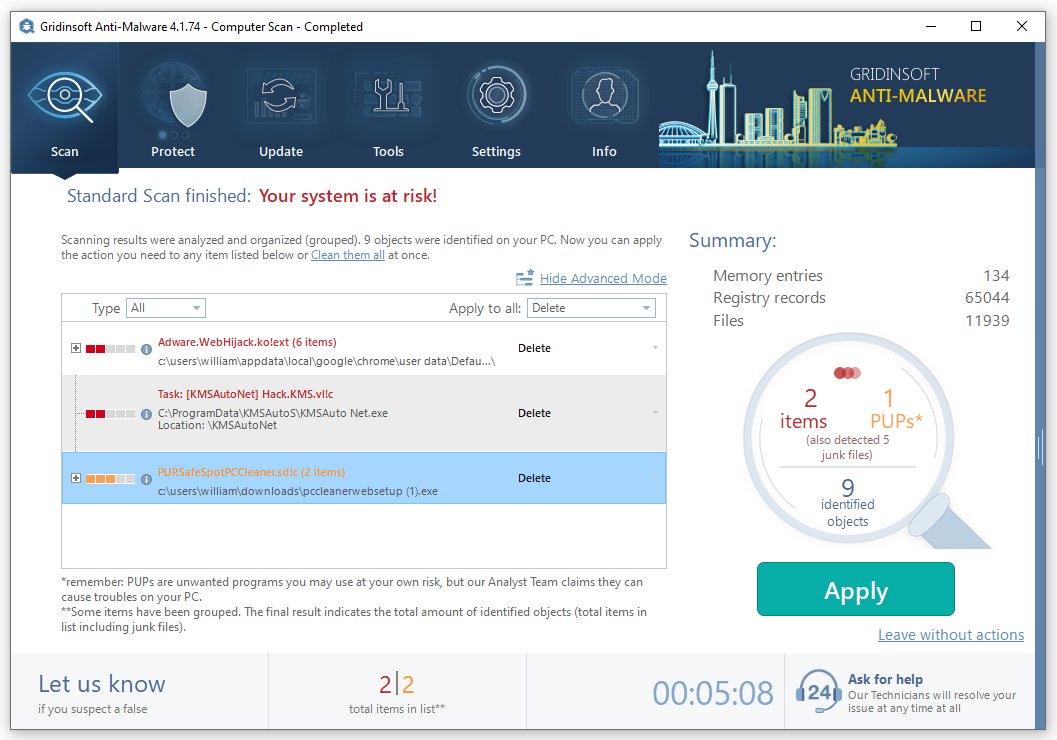
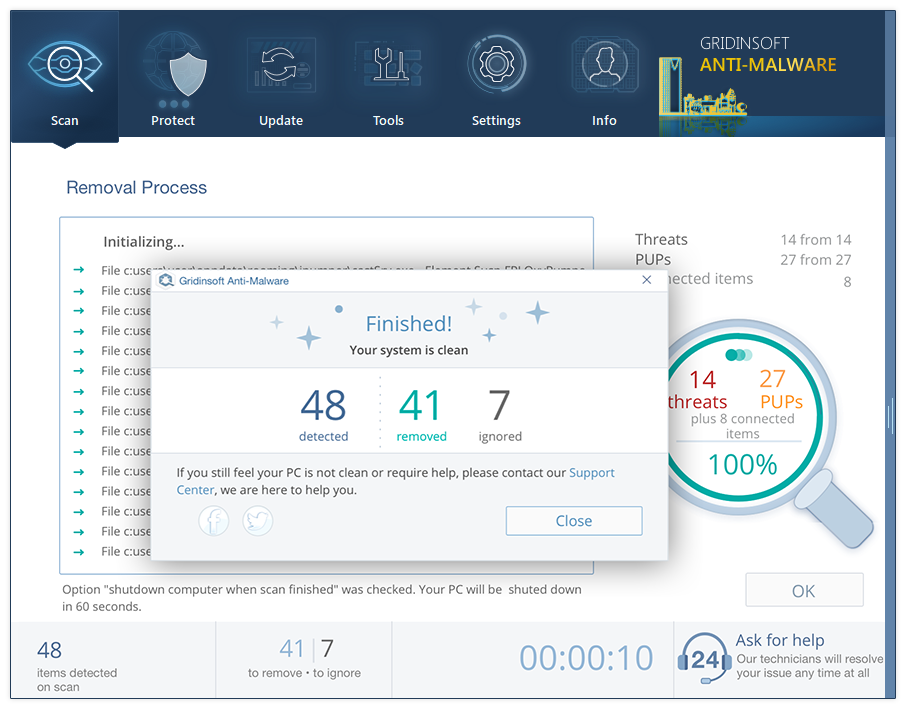
- When the scan is over, you may choose the action for each detected virus. For all files of ThirdEye the default option is “Delete”. Press “Apply” to finish the malware removal.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
ThirdEye Infostealer is a type of malware that targets Windows users with the aim of extracting sensitive information from compromised systems.
The earliest sample of ThirdEye Infostealer was discovered on April 3, 2023, at 12:36:37 GMT. It was found to collect various system data and transmit it to a Command-and-Control (C2) server.
ThirdEye Infostealer collects system information such as BIOS and hardware details, files and folders, running processes, and network data.
Once the data is gathered, ThirdEye Infostealer sends it to a designated C2 server for further processing and potential exploitation by cybercriminals.
The stolen information can be utilized by cybercriminals for various malicious purposes. They can analyze vulnerabilities, plan targeted attacks, gain unauthorized access, perform identity theft, or engage in other malicious activities.
ThirdEye Infostealer is typically distributed through a ZIP file disguised as regular documents, such as PDF files. Users may unknowingly download and open these files through methods like email attachments, malicious websites, or deceptive software downloads.
To protect your computer, exercise caution when opening email attachments or clicking on links. Download programs and files only from reputable sources. Keep your operating system and software up to date with the latest security patches. Use reliable antivirus software and avoid suspicious ads or pop-ups.
Currently, there is no evidence of ThirdEye Infostealer being used in attacks. However, its capabilities pose a potential risk, especially for compromised devices and systems.
If you suspect your computer is infected, it is recommended to run a scan with reputable anti-malware software, such as Gridinsoft Anti-Malware, to detect and remove the infiltrated malware.
Yes, there are other information stealers in existence, such as Umbral, RedEnergy, and RDStealer, which also target sensitive data on compromised systems.
How to Remove ThirdEye Malware
Name: ThirdEye
Description: ThirdEye Infostealer is a type of malware specifically designed to target Windows users. Its primary objective is to extract sensitive information from compromised systems. While it may not be classified as highly advanced, ThirdEye Infostealer can still pose a significant threat to users' privacy and security. The stolen data serves as a foundation for subsequent cyber-attacks, allowing malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities, gain unauthorized access, perform identity theft, or engage in other malicious activities. It is crucial for individuals and organizations to remain vigilant, implement robust cybersecurity measures, and stay informed about emerging threats to protect their systems and sensitive data from ThirdEye Infostealer and similar malware.
Operating System: Windows
Application Category: Malware
User Review
( votes)References
- Sample of ThirdEye Infostealer at VirusTotal.com

